树中 K 长度路径的数量
给定一棵有N个节点和一个整数K的树,任务是找到长度为 K 的路径的总数。
例子:
Input: N = 5, K = 2
tree = 1
/ \
2 5
/ \
3 4
Output: 4
Explanation: The paths having length 2 are
1 – 2 – 3, 1 – 2 – 4, 2 – 1 – 5, 3 – 2 – 4
Input: N = 2, K = 2
tree = 1
/
2
Output: 0
Explanation: There is no path in the tree having length 2.
直觉:主要思想是从每个节点中找到 K 长度的路径并将它们相加。
- 查找从给定节点“节点”“起源”的 K 长度路径的数量。这里的“起源”意味着“节点”将在路径中的所有节点中具有最小的深度。例如,下图显示了源自 1 的 2 长度路径。
- 将所有节点的值相加,这将是所需的答案。
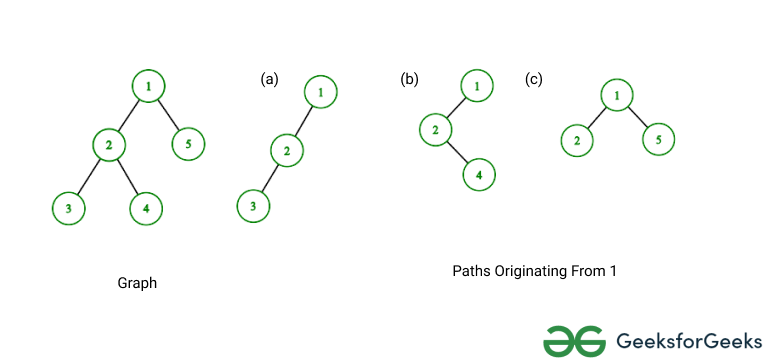
朴素方法:为了计算源自“节点”的 K 长度路径,使用了两个 DFS。说这整个过程是: paths_originating_from(node)
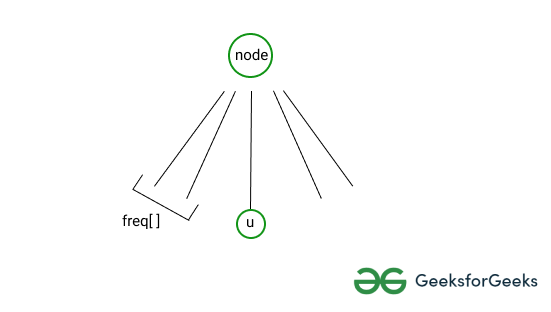
- 假设“节点”有多个子节点,当前正在处理子节点“u”。
- 对于所有先前的孩子,已经计算了特定深度的节点频率。更正式地说,当 'u' 之前的 'node' 的唯一子级已被处理时,freq[d] 给出深度 'd' 处的节点数。
- 如果在深度 'd' 处有一个节点 'x',则源自 'node' 并通过 'x' 的 K 长度路径的数量将是 freq[K - d]。
- 第一个 DFSF 将有助于最终答案,第二个 DFS 将更新 freq[] 数组以供将来使用。
- 总结树的所有节点的“paths_originating_from(node)”,这将是必需的答案。
请参阅下图以更好地理解第二点。
下面是上述方法的实现。
C++
// C++ code to implement above approach
#include
using namespace std;
int mx_depth = 0, ans = 0;
int N, K;
vector freq;
vector > g;
// This dfs is responsible for calculating ans
// and updating freq vector
void dfs(int node, int par, int depth,
bool contri)
{
if (depth > K)
return;
mx_depth = max(mx_depth, depth);
if (contri) {
ans += freq[K - depth];
}
else {
freq[depth]++;
}
for (auto nebr : g[node]) {
if (nebr != par) {
dfs(nebr, node, depth + 1,
contri);
}
}
}
// Function to calculate K length paths
// originating from node
void paths_originating_from(int node,
int par)
{
mx_depth = 0;
freq[0] = 1;
// For every not-removed nebr,
// calculate its contribution,
// then update freq vector for it
for (auto nebr : g[node]) {
if (nebr != par) {
dfs(nebr, node, 1, true);
dfs(nebr, node, 1, false);
}
}
// Re-initialize freq vector
for (int i = 0; i <= mx_depth; ++i) {
freq[i] = 0;
}
// Repeat the same for children
for (auto nebr : g[node]) {
if (nebr != par) {
paths_originating_from(nebr,
node);
}
}
}
// Utility method to add edges to tree
void edge(int a, int b)
{
a--;
b--;
g[a].push_back(b);
g[b].push_back(a);
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
N = 5, K = 2;
freq = vector(N);
g = vector >(N);
edge(1, 2);
edge(1, 5);
edge(2, 3);
edge(2, 4);
paths_originating_from(0, -1);
cout << ans << endl;
} C++
// C++ code to implement above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Struct for centroid decomposition
struct CD {
// 1. mx_depth will be used to store
// the height of a node
// 2. g[] is adjacency list for tree
// 3. freq[] stores frequency of nodes
// at particular height, it is maintained
// for children of a node
int n, k, mx_depth, ans;
vector removed;
vector size, freq;
vector > g;
// Constructor for struct
CD(int n1, int k1)
{
n = n1;
k = k1;
ans = mx_depth = 0;
g.resize(n);
size.resize(n);
freq.resize(n);
removed.assign(n, false);
}
// Utility method to add edges to tree
void edge(int u, int v)
{
u--;
v--;
g[u].push_back(v);
g[v].push_back(u);
}
// Finds size of a subtree,
// ignoring removed nodes in the way
int get_size(int node, int par)
{
if (removed[node])
return 0;
size[node] = 1;
for (auto nebr : g[node]) {
if (nebr != par) {
size[node] += get_size(nebr,
node);
}
}
return size[node];
}
// Calculates centroid of a subtree
// of 'node' of size 'sz'
int get_centroid(int node, int par,
int sz)
{
for (auto nebr : g[node]) {
if (nebr != par && !removed[nebr]
&& size[nebr] > sz / 2) {
return get_centroid(nebr,
node, sz);
}
}
return node;
}
// Decompose the tree
// into various centroids
void decompose(int node, int par)
{
get_size(node, -1);
// c is centroid of subtree 'node'
int c = get_centroid(node, par,
size[node]);
// Find paths_originating_from 'c'
paths_originating_from(c);
// Mark this centroid as removed
removed = true;
// Find other centroids
for (auto nebr : g) {
if (!removed[nebr]) {
decompose(nebr, c);
}
}
}
// This dfs is responsible for
// calculating ans and
// updating freq vector
void dfs(int node, int par, int depth,
bool contri)
{
if (depth > k)
return;
mx_depth = max(mx_depth, depth);
if (contri) {
ans += freq[k - depth];
}
else {
freq[depth]++;
}
for (auto nebr : g[node]) {
if (nebr != par &&
!removed[nebr]) {
dfs(nebr, node,
depth + 1, contri);
}
}
}
// Function to find K-length paths
// originating from node
void paths_originating_from(int node)
{
mx_depth = 0;
freq[0] = 1;
// For every not-removed nebr,
// calculate its contribution,
// then update freq vector for it
for (auto nebr : g[node]) {
if (!removed[nebr]) {
dfs(nebr, node, 1, true);
dfs(nebr, node, 1, false);
}
}
// Re-initialize freq vector
for (int i = 0; i <= mx_depth; ++i) {
freq[i] = 0;
}
}
};
// Driver code
int main()
{
int N = 5, K = 2;
CD cd_s(N, K);
cd_s.edge(1, 2);
cd_s.edge(1, 5);
cd_s.edge(2, 3);
cd_s.edge(2, 4);
cd_s.decompose(0, -1);
cout << cd_s.ans;
return 0;
} 4
时间复杂度: O(N * H) 其中 H 是树的高度,最大可以是 N
辅助空间: O(N)
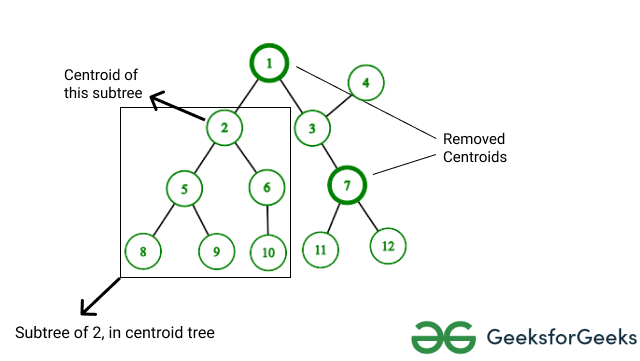
高效方法:这种方法基于质心分解的概念。步骤如下:
- 找到当前树T的质心。
- 从T可到达的所有“未删除”节点都属于其子树。调用paths_originating_from(T) ,然后将T标记为“已移除”。
- 对T的所有“未删除”邻居重复上述过程。
下图显示了具有当前质心的树及其子树。请注意,具有粗边框的节点之前已经被选为质心,并且不属于当前质心的子树。
下面是上述方法的实现。
C++
// C++ code to implement above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Struct for centroid decomposition
struct CD {
// 1. mx_depth will be used to store
// the height of a node
// 2. g[] is adjacency list for tree
// 3. freq[] stores frequency of nodes
// at particular height, it is maintained
// for children of a node
int n, k, mx_depth, ans;
vector removed;
vector size, freq;
vector > g;
// Constructor for struct
CD(int n1, int k1)
{
n = n1;
k = k1;
ans = mx_depth = 0;
g.resize(n);
size.resize(n);
freq.resize(n);
removed.assign(n, false);
}
// Utility method to add edges to tree
void edge(int u, int v)
{
u--;
v--;
g[u].push_back(v);
g[v].push_back(u);
}
// Finds size of a subtree,
// ignoring removed nodes in the way
int get_size(int node, int par)
{
if (removed[node])
return 0;
size[node] = 1;
for (auto nebr : g[node]) {
if (nebr != par) {
size[node] += get_size(nebr,
node);
}
}
return size[node];
}
// Calculates centroid of a subtree
// of 'node' of size 'sz'
int get_centroid(int node, int par,
int sz)
{
for (auto nebr : g[node]) {
if (nebr != par && !removed[nebr]
&& size[nebr] > sz / 2) {
return get_centroid(nebr,
node, sz);
}
}
return node;
}
// Decompose the tree
// into various centroids
void decompose(int node, int par)
{
get_size(node, -1);
// c is centroid of subtree 'node'
int c = get_centroid(node, par,
size[node]);
// Find paths_originating_from 'c'
paths_originating_from(c);
// Mark this centroid as removed
removed = true;
// Find other centroids
for (auto nebr : g) {
if (!removed[nebr]) {
decompose(nebr, c);
}
}
}
// This dfs is responsible for
// calculating ans and
// updating freq vector
void dfs(int node, int par, int depth,
bool contri)
{
if (depth > k)
return;
mx_depth = max(mx_depth, depth);
if (contri) {
ans += freq[k - depth];
}
else {
freq[depth]++;
}
for (auto nebr : g[node]) {
if (nebr != par &&
!removed[nebr]) {
dfs(nebr, node,
depth + 1, contri);
}
}
}
// Function to find K-length paths
// originating from node
void paths_originating_from(int node)
{
mx_depth = 0;
freq[0] = 1;
// For every not-removed nebr,
// calculate its contribution,
// then update freq vector for it
for (auto nebr : g[node]) {
if (!removed[nebr]) {
dfs(nebr, node, 1, true);
dfs(nebr, node, 1, false);
}
}
// Re-initialize freq vector
for (int i = 0; i <= mx_depth; ++i) {
freq[i] = 0;
}
}
};
// Driver code
int main()
{
int N = 5, K = 2;
CD cd_s(N, K);
cd_s.edge(1, 2);
cd_s.edge(1, 5);
cd_s.edge(2, 3);
cd_s.edge(2, 4);
cd_s.decompose(0, -1);
cout << cd_s.ans;
return 0;
}
4时间复杂度: O(N * log(N)) 其中 log N 是树的高度
辅助空间: O(N)