最小产品生成树
给定一个连通无向图,该图的生成树是一个子图,它是一棵树,将所有顶点连接在一起。一个图可以有许多不同的生成树。加权、连通和无向图的最小乘积生成树是一棵生成树,其权重乘积小于或等于所有其他生成树的权重乘积。生成树的权重乘积是生成树的每条边对应的权重的乘积。为简单起见,给定图的所有权重都是正数。
例子:
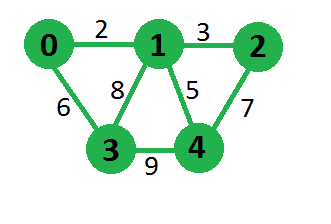
Minimum Product that we can obtain is
180 for above graph by choosing edges
0-1, 1-2, 0-3 and 1-4这个问题可以使用标准的最小生成树算法(如 krushkal 和 prim 算法)来解决,但我们需要修改我们的图以使用这些算法。最小生成树算法试图最小化权重的总和,这里我们需要最小化权重的总乘积。我们可以利用对数的性质来克服这个问题。
据我们所知,
log(w1* w2 * w3 * …. * wN) =
log(w1) + log(w2) + log(w3) ….. + log(wN)我们可以用它的 log 值替换每个图的权重,然后我们应用任何最小生成树算法,该算法将尝试最小化 log(wi) 的总和,从而最小化权重乘积。
例如图表,步骤如下图所示,
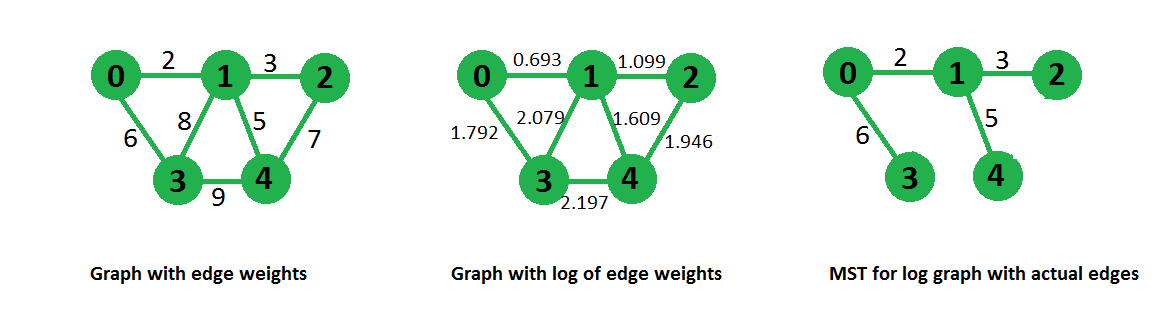
在下面的代码中,我们首先从给定的输入图构建了对数图,然后将该图作为输入给 prim 的 MST 算法,这将最小化树的权重总和。由于修改图的权重是实际输入图的对数,因此我们实际上最小化了生成树权重的乘积。
C++
// A C++ program for getting minimum product
// spanning tree The program is for adjacency matrix
// representation of the graph
#include
// Number of vertices in the graph
#define V 5
// A utility function to find the vertex with minimum
// key value, from the set of vertices not yet included
// in MST
int minKey(int key[], bool mstSet[])
{
// Initialize min value
int min = INT_MAX, min_index;
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++)
if (mstSet[v] == false && key[v] < min)
min = key[v], min_index = v;
return min_index;
}
// A utility function to print the constructed MST
// stored in parent[] and print Minimum Obtainable
// product
int printMST(int parent[], int n, int graph[V][V])
{
printf("Edge Weight\n");
int minProduct = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < V; i++) {
printf("%d - %d %d \n",
parent[i], i, graph[i][parent[i]]);
minProduct *= graph[i][parent[i]];
}
printf("Minimum Obtainable product is %d\n",
minProduct);
}
// Function to construct and print MST for a graph
// represented using adjacency matrix representation
// inputGraph is sent for printing actual edges and
// logGraph is sent for actual MST operations
void primMST(int inputGraph[V][V], double logGraph[V][V])
{
int parent[V]; // Array to store constructed MST
int key[V]; // Key values used to pick minimum
// weight edge in cut
bool mstSet[V]; // To represent set of vertices not
// yet included in MST
// Initialize all keys as INFINITE
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
key[i] = INT_MAX, mstSet[i] = false;
// Always include first 1st vertex in MST.
key[0] = 0; // Make key 0 so that this vertex is
// picked as first vertex
parent[0] = -1; // First node is always root of MST
// The MST will have V vertices
for (int count = 0; count < V - 1; count++) {
// Pick the minimum key vertex from the set of
// vertices not yet included in MST
int u = minKey(key, mstSet);
// Add the picked vertex to the MST Set
mstSet[u] = true;
// Update key value and parent index of the
// adjacent vertices of the picked vertex.
// Consider only those vertices which are not yet
// included in MST
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++)
// logGraph[u][v] is non zero only for
// adjacent vertices of m mstSet[v] is false
// for vertices not yet included in MST
// Update the key only if logGraph[u][v] is
// smaller than key[v]
if (logGraph[u][v] > 0 && mstSet[v] == false && logGraph[u][v] < key[v])
parent[v] = u, key[v] = logGraph[u][v];
}
// print the constructed MST
printMST(parent, V, inputGraph);
}
// Method to get minimum product spanning tree
void minimumProductMST(int graph[V][V])
{
double logGraph[V][V];
// Constructing logGraph from original graph
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < V; j++) {
if (graph[i][j] > 0)
logGraph[i][j] = log(graph[i][j]);
else
logGraph[i][j] = 0;
}
}
// Applying standard Prim's MST algorithm on
// Log graph.
primMST(graph, logGraph);
}
// driver program to test above function
int main()
{
/* Let us create the following graph
2 3
(0)--(1)--(2)
| / \ |
6| 8/ \5 |7
| / \ |
(3)-------(4)
9 */
int graph[V][V] = {
{ 0, 2, 0, 6, 0 },
{ 2, 0, 3, 8, 5 },
{ 0, 3, 0, 0, 7 },
{ 6, 8, 0, 0, 9 },
{ 0, 5, 7, 9, 0 },
};
// Print the solution
minimumProductMST(graph);
return 0;
} Java
// A Java program for getting minimum product
// spanning tree The program is for adjacency matrix
// representation of the graph
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
// Number of vertices in the graph
static int V = 5;
// A utility function to find the vertex with minimum
// key value, from the set of vertices not yet included
// in MST
static int minKey(int key[], boolean[] mstSet)
{
// Initialize min value
int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE, min_index = 0;
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) {
if (mstSet[v] == false && key[v] < min) {
min = key[v];
min_index = v;
}
}
return min_index;
}
// A utility function to print the constructed MST
// stored in parent[] and print Minimum Obtainable
// product
static void printMST(int parent[], int n, int graph[][])
{
System.out.printf("Edge Weight\n");
int minProduct = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < V; i++) {
System.out.printf("%d - %d %d \n",
parent[i], i, graph[i][parent[i]]);
minProduct *= graph[i][parent[i]];
}
System.out.printf("Minimum Obtainable product is %d\n",
minProduct);
}
// Function to construct and print MST for a graph
// represented using adjacency matrix representation
// inputGraph is sent for printing actual edges and
// logGraph is sent for actual MST operations
static void primMST(int inputGraph[][], double logGraph[][])
{
int[] parent = new int[V]; // Array to store constructed MST
int[] key = new int[V]; // Key values used to pick minimum
// weight edge in cut
boolean[] mstSet = new boolean[V]; // To represent set of vertices not
// yet included in MST
// Initialize all keys as INFINITE
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
key[i] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
mstSet[i] = false;
}
// Always include first 1st vertex in MST.
key[0] = 0; // Make key 0 so that this vertex is
// picked as first vertex
parent[0] = -1; // First node is always root of MST
// The MST will have V vertices
for (int count = 0; count < V - 1; count++) {
// Pick the minimum key vertex from the set of
// vertices not yet included in MST
int u = minKey(key, mstSet);
// Add the picked vertex to the MST Set
mstSet[u] = true;
// Update key value and parent index of the
// adjacent vertices of the picked vertex.
// Consider only those vertices which are not yet
// included in MST
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) // logGraph[u][v] is non zero only for
// adjacent vertices of m mstSet[v] is false
// for vertices not yet included in MST
// Update the key only if logGraph[u][v] is
// smaller than key[v]
{
if (logGraph[u][v] > 0
&& mstSet[v] == false
&& logGraph[u][v] < key[v]) {
parent[v] = u;
key[v] = (int)logGraph[u][v];
}
}
}
// print the constructed MST
printMST(parent, V, inputGraph);
}
// Method to get minimum product spanning tree
static void minimumProductMST(int graph[][])
{
double[][] logGraph = new double[V][V];
// Constructing logGraph from original graph
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < V; j++) {
if (graph[i][j] > 0) {
logGraph[i][j] = Math.log(graph[i][j]);
}
else {
logGraph[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
// Applying standard Prim's MST algorithm on
// Log graph.
primMST(graph, logGraph);
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
/* Let us create the following graph
2 3
(0)--(1)--(2)
| / \ |
6| 8/ \5 |7
| / \ |
(3)-------(4)
9 */
int graph[][] = {
{ 0, 2, 0, 6, 0 },
{ 2, 0, 3, 8, 5 },
{ 0, 3, 0, 0, 7 },
{ 6, 8, 0, 0, 9 },
{ 0, 5, 7, 9, 0 },
};
// Print the solution
minimumProductMST(graph);
}
}
// This code has been contributed by 29AjayKumarPython3
# A Python3 program for getting minimum
# product spanning tree The program is
# for adjacency matrix representation
# of the graph
import math
# Number of vertices in the graph
V = 5
# A utility function to find the vertex
# with minimum key value, from the set
# of vertices not yet included in MST
def minKey(key, mstSet):
# Initialize min value
min = 10000000
min_index = 0
for v in range(V):
if (mstSet[v] == False and
key[v] < min):
min = key[v]
min_index = v
return min_index
# A utility function to print the constructed
# MST stored in parent[] and print Minimum
# Obtainable product
def printMST(parent, n, graph):
print("Edge Weight")
minProduct = 1
for i in range(1, V):
print("{} - {} {} ".format(parent[i], i,
graph[i][parent[i]]))
minProduct *= graph[i][parent[i]]
print("Minimum Obtainable product is {}".format(
minProduct))
# Function to construct and print MST for
# a graph represented using adjacency
# matrix representation inputGraph is
# sent for printing actual edges and
# logGraph is sent for actual MST
# operations
def primMST(inputGraph, logGraph):
# Array to store constructed MST
parent = [0 for i in range(V)]
# Key values used to pick minimum
key = [10000000 for i in range(V)]
# weight edge in cut
# To represent set of vertices not
mstSet = [False for i in range(V)]
# Yet included in MST
# Always include first 1st vertex in MST
# Make key 0 so that this vertex is
key[0] = 0
# Picked as first vertex
# First node is always root of MST
parent[0] = -1
# The MST will have V vertices
for count in range(0, V - 1):
# Pick the minimum key vertex from
# the set of vertices not yet
# included in MST
u = minKey(key, mstSet)
# Add the picked vertex to the MST Set
mstSet[u] = True
# Update key value and parent index
# of the adjacent vertices of the
# picked vertex. Consider only those
# vertices which are not yet
# included in MST
for v in range(V):
# logGraph[u][v] is non zero only
# for adjacent vertices of m
# mstSet[v] is false for vertices
# not yet included in MST. Update
# the key only if logGraph[u][v] is
# smaller than key[v]
if (logGraph[u][v] > 0 and
mstSet[v] == False and
logGraph[u][v] < key[v]):
parent[v] = u
key[v] = logGraph[u][v]
# Print the constructed MST
printMST(parent, V, inputGraph)
# Method to get minimum product spanning tree
def minimumProductMST(graph):
logGraph = [[0 for j in range(V)]
for i in range(V)]
# Constructing logGraph from
# original graph
for i in range(V):
for j in range(V):
if (graph[i][j] > 0):
logGraph[i][j] = math.log(graph[i][j])
else:
logGraph[i][j] = 0
# Applying standard Prim's MST algorithm
# on Log graph.
primMST(graph, logGraph)
# Driver code
if __name__=='__main__':
''' Let us create the following graph
2 3
(0)--(1)--(2)
| / \ |
6| 8/ \5 |7
| / \ |
(3)-------(4)
9 '''
graph = [ [ 0, 2, 0, 6, 0 ],
[ 2, 0, 3, 8, 5 ],
[ 0, 3, 0, 0, 7 ],
[ 6, 8, 0, 0, 9 ],
[ 0, 5, 7, 9, 0 ], ]
# Print the solution
minimumProductMST(graph)
# This code is contributed by rutvik_56C#
// C# program for getting minimum product
// spanning tree The program is for adjacency matrix
// representation of the graph
using System;
class GFG {
// Number of vertices in the graph
static int V = 5;
// A utility function to find the vertex with minimum
// key value, from the set of vertices not yet included
// in MST
static int minKey(int[] key, Boolean[] mstSet)
{
// Initialize min value
int min = int.MaxValue, min_index = 0;
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) {
if (mstSet[v] == false && key[v] < min) {
min = key[v];
min_index = v;
}
}
return min_index;
}
// A utility function to print the constructed MST
// stored in parent[] and print Minimum Obtainable
// product
static void printMST(int[] parent, int n, int[, ] graph)
{
Console.Write("Edge Weight\n");
int minProduct = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < V; i++) {
Console.Write("{0} - {1} {2} \n",
parent[i], i, graph[i, parent[i]]);
minProduct *= graph[i, parent[i]];
}
Console.Write("Minimum Obtainable product is {0}\n",
minProduct);
}
// Function to construct and print MST for a graph
// represented using adjacency matrix representation
// inputGraph is sent for printing actual edges and
// logGraph is sent for actual MST operations
static void primMST(int[, ] inputGraph, double[, ] logGraph)
{
int[] parent = new int[V]; // Array to store constructed MST
int[] key = new int[V]; // Key values used to pick minimum
// weight edge in cut
Boolean[] mstSet = new Boolean[V]; // To represent set of vertices not
// yet included in MST
// Initialize all keys as INFINITE
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
key[i] = int.MaxValue;
mstSet[i] = false;
}
// Always include first 1st vertex in MST.
key[0] = 0; // Make key 0 so that this vertex is
// picked as first vertex
parent[0] = -1; // First node is always root of MST
// The MST will have V vertices
for (int count = 0; count < V - 1; count++) {
// Pick the minimum key vertex from the set of
// vertices not yet included in MST
int u = minKey(key, mstSet);
// Add the picked vertex to the MST Set
mstSet[u] = true;
// Update key value and parent index of the
// adjacent vertices of the picked vertex.
// Consider only those vertices which are not yet
// included in MST
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) // logGraph[u, v] is non zero only for
// adjacent vertices of m mstSet[v] is false
// for vertices not yet included in MST
// Update the key only if logGraph[u, v] is
// smaller than key[v]
{
if (logGraph[u, v] > 0
&& mstSet[v] == false
&& logGraph[u, v] < key[v]) {
parent[v] = u;
key[v] = (int)logGraph[u, v];
}
}
}
// print the constructed MST
printMST(parent, V, inputGraph);
}
// Method to get minimum product spanning tree
static void minimumProductMST(int[, ] graph)
{
double[, ] logGraph = new double[V, V];
// Constructing logGraph from original graph
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < V; j++) {
if (graph[i, j] > 0) {
logGraph[i, j] = Math.Log(graph[i, j]);
}
else {
logGraph[i, j] = 0;
}
}
}
// Applying standard Prim's MST algorithm on
// Log graph.
primMST(graph, logGraph);
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
/* Let us create the following graph
2 3
(0)--(1)--(2)
| / \ |
6| 8/ \5 |7
| / \ |
(3)-------(4)
9 */
int[, ] graph = {
{ 0, 2, 0, 6, 0 },
{ 2, 0, 3, 8, 5 },
{ 0, 3, 0, 0, 7 },
{ 6, 8, 0, 0, 9 },
{ 0, 5, 7, 9, 0 },
};
// Print the solution
minimumProductMST(graph);
}
}
/* This code contributed by PrinciRaj1992 */Javascript
输出:
Edge Weight
0 - 1 2
1 - 2 3
0 - 3 6
1 - 4 5
Minimum Obtainable product is 180