用于合并排序的链表的Python程序
合并排序通常是对链表进行排序的首选。链表的缓慢随机访问性能使得其他一些算法(如快速排序)表现不佳,而其他算法(如堆排序)则完全不可能。
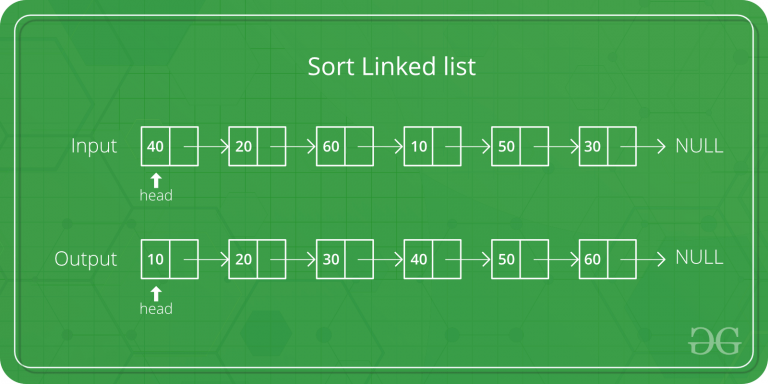
设 head 为要排序的链表的第一个节点, headRef 为指向 head 的指针。请注意,我们需要在 MergeSort() 中引用 head,因为下面的实现会更改下一个链接以对链表(不是节点处的数据)进行排序,因此如果原始头部的数据不是链表中的最小值。
MergeSort(headRef)
1) If the head is NULL or there is only one element in the Linked List
then return.
2) Else divide the linked list into two halves.
FrontBackSplit(head, &a, &b); /* a and b are two halves */
3) Sort the two halves a and b.
MergeSort(a);
MergeSort(b);
4) Merge the sorted a and b (using SortedMerge() discussed here)
and update the head pointer using headRef.
*headRef = SortedMerge(a, b);Python3
# Python3 program to merge sort of linked list
# create Node using class Node.
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
# push new value to linked list
# using append method
def append(self, new_value):
# Allocate new node
new_node = Node(new_value)
# if head is None, initialize it to new node
if self.head is None:
self.head = new_node
return
curr_node = self.head
while curr_node.next is not None:
curr_node = curr_node.next
# Append the new node at the end
# of the linked list
curr_node.next = new_node
def sortedMerge(self, a, b):
result = None
# Base cases
if a == None:
return b
if b == None:
return a
# pick either a or b and recur..
if a.data <= b.data:
result = a
result.next = self.sortedMerge(a.next, b)
else:
result = b
result.next = self.sortedMerge(a, b.next)
return result
def mergeSort(self, h):
# Base case if head is None
if h == None or h.next == None:
return h
# get the middle of the list
middle = self.getMiddle(h)
nexttomiddle = middle.next
# set the next of middle node to None
middle.next = None
# Apply mergeSort on left list
left = self.mergeSort(h)
# Apply mergeSort on right list
right = self.mergeSort(nexttomiddle)
# Merge the left and right lists
sortedlist = self.sortedMerge(left, right)
return sortedlist
# Utility function to get the middle
# of the linked list
def getMiddle(self, head):
if (head == None):
return head
slow = head
fast = head
while (fast.next != None and
fast.next.next != None):
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
return slow
# Utility function to print the linked list
def printList(head):
if head is None:
print(' ')
return
curr_node = head
while curr_node:
print(curr_node.data, end = " ")
curr_node = curr_node.next
print(' ')
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
li = LinkedList()
# Let us create a unsorted linked list
# to test the functions created.
# The list shall be a: 2->3->20->5->10->15
li.append(15)
li.append(10)
li.append(5)
li.append(20)
li.append(3)
li.append(2)
# Apply merge Sort
li.head = li.mergeSort(li.head)
print ("Sorted Linked List is:")
printList(li.head)
# This code is contributed by Vikas ChitturiPython3
# Python program for the above approach
# Node Class
class Node:
def __init__(self,key):
self.data=key
self.next=None
# Function to merge sort
def mergeSort(head):
if (head.next == None):
return head
mid = findMid(head)
head2 = mid.next
mid.next = None
newHead1 = mergeSort(head)
newHead2 = mergeSort(head2)
finalHead = merge(newHead1, newHead2)
return finalHead
# Function to merge two linked lists
def merge(head1,head2):
merged = Node(-1)
temp = merged
# While head1 is not null and head2
# is not null
while (head1 != None and head2 != None):
if (head1.data < head2.data):
temp.next = head1
head1 = head1.next
else:
temp.next = head2
head2 = head2.next
temp = temp.next
# While head1 is not null
while (head1 != None):
temp.next = head1
head1 = head1.next
temp = temp.next
# While head2 is not null
while (head2 != None):
temp.next = head2
head2 = head2.next
temp = temp.next
return merged.next
# Find mid using The Tortoise and The Hare approach
def findMid(head):
slow = head
fast = head.next
while (fast != None and fast.next != None):
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
return slow
# Function to print list
def printList(head):
while (head != None):
print(head.data,end=" ")
head=head.next
# Driver Code
head = Node(7)
temp = head
temp.next = Node(10);
temp = temp.next;
temp.next = Node(5);
temp = temp.next;
temp.next = Node(20);
temp = temp.next;
temp.next = Node(3);
temp = temp.next;
temp.next = Node(2);
temp = temp.next;
# Apply merge Sort
head = mergeSort(head);
print("
Sorted Linked List is:
");
printList(head);
# This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155输出:
Sorted Linked List is:
2 3 5 10 15 20时间复杂度: O(n*log n)
空间复杂度: O(n*log n)
方法 2:这种方法更简单,使用 log n 空间。
合并排序():
- 如果链表的大小为 1 则返回头部
- 使用龟兔赛跑方法找到中间点
- 将 mid 的下一个存储在 head2 中,即右子链表。
- 现在使下一个中点为空。
- 递归调用左右子链表的mergeSort(),存储左右链表的新头。
- 给定左右子链表的新头参数,调用merge(),并存储合并后返回的最终头。
- 返回合并链表的最终头。
合并(头1,头2):
- 取一个指针,说合并以将合并列表存储在其中并在其中存储一个虚拟节点。
- 取一个指针 temp 并为其分配合并。
- 如果 head1 的数据小于 head2 的数据,则将 head1 存储在 temp 的 next 中并将 head1 移动到 head1 的 next 中。
- 否则将 head2 存储在 temp 的下一个并将 head2 移动到 head2 的下一个。
- 将 temp 移到 temp 的下一个。
- 重复步骤 3、4 和 5,直到 head1 不等于 null 并且 head2 不等于 null。
- 现在将第一个或第二个链表的任何剩余节点添加到合并的链表中。
- 返回合并后的下一个(将忽略虚拟并返回最终合并链表的头部)
Python3
# Python program for the above approach
# Node Class
class Node:
def __init__(self,key):
self.data=key
self.next=None
# Function to merge sort
def mergeSort(head):
if (head.next == None):
return head
mid = findMid(head)
head2 = mid.next
mid.next = None
newHead1 = mergeSort(head)
newHead2 = mergeSort(head2)
finalHead = merge(newHead1, newHead2)
return finalHead
# Function to merge two linked lists
def merge(head1,head2):
merged = Node(-1)
temp = merged
# While head1 is not null and head2
# is not null
while (head1 != None and head2 != None):
if (head1.data < head2.data):
temp.next = head1
head1 = head1.next
else:
temp.next = head2
head2 = head2.next
temp = temp.next
# While head1 is not null
while (head1 != None):
temp.next = head1
head1 = head1.next
temp = temp.next
# While head2 is not null
while (head2 != None):
temp.next = head2
head2 = head2.next
temp = temp.next
return merged.next
# Find mid using The Tortoise and The Hare approach
def findMid(head):
slow = head
fast = head.next
while (fast != None and fast.next != None):
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
return slow
# Function to print list
def printList(head):
while (head != None):
print(head.data,end=" ")
head=head.next
# Driver Code
head = Node(7)
temp = head
temp.next = Node(10);
temp = temp.next;
temp.next = Node(5);
temp = temp.next;
temp.next = Node(20);
temp = temp.next;
temp.next = Node(3);
temp = temp.next;
temp.next = Node(2);
temp = temp.next;
# Apply merge Sort
head = mergeSort(head);
print("
Sorted Linked List is:
");
printList(head);
# This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155
输出:
Sorted Linked List is:
2 3 5 7 10 20 时间复杂度:O(n*log n)
空间复杂度: O(log n)
有关详细信息,请参阅有关链接列表的合并排序的完整文章!