给定一个有向和两个顶点 ‘u’ 和 ‘v’,找到从 ‘u’ 到 ‘v’ 的最短路径,路径上正好有 k 条边。
该图以邻接矩阵表示形式给出,其中 graph[i][j] 的值表示从顶点 i 到顶点 j 的边的权重,值 INF(infinite) 表示从 i 到 j 没有边。
例如,考虑下图。设源’u’为顶点0,目的地’v’为3,k为2。有两条长度为2的游走,游走是{0, 2, 3}和{0, 1, 3}。两者中最短的是{0, 2, 3},路径权重为3+6 = 9。
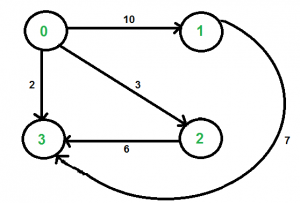
这个想法是使用上一篇文章中讨论的方法浏览从 u 到 v 长度为 k 的所有路径,并返回最短路径的权重。一个简单的解决方案是从 u 开始,到所有相邻的顶点,对相邻顶点递归,k 为 k-1,源为相邻顶点,目标为 v。以下是这个简单解决方案的 C++ 和Java实现。
C++
// C++ program to find shortest path with exactly k edges
#include
using namespace std;
// Define number of vertices in the graph and infinite value
#define V 4
#define INF INT_MAX
// A naive recursive function to count walks from u to v with k edges
int shortestPath(int graph[][V], int u, int v, int k)
{
// Base cases
if (k == 0 && u == v) return 0;
if (k == 1 && graph[u][v] != INF) return graph[u][v];
if (k <= 0) return INF;
// Initialize result
int res = INF;
// Go to all adjacents of u and recur
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
if (graph[u][i] != INF && u != i && v != i)
{
int rec_res = shortestPath(graph, i, v, k-1);
if (rec_res != INF)
res = min(res, graph[u][i] + rec_res);
}
}
return res;
}
// driver program to test above function
int main()
{
/* Let us create the graph shown in above diagram*/
int graph[V][V] = { {0, 10, 3, 2},
{INF, 0, INF, 7},
{INF, INF, 0, 6},
{INF, INF, INF, 0}
};
int u = 0, v = 3, k = 2;
cout << "Weight of the shortest path is " <<
shortestPath(graph, u, v, k);
return 0;
} Java
// Dynamic Programming based Java program to find shortest path
// with exactly k edges
import java.util.*;
import java.lang.*;
import java.io.*;
class ShortestPath
{
// Define number of vertices in the graph and infinite value
static final int V = 4;
static final int INF = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
// A naive recursive function to count walks from u to v
// with k edges
int shortestPath(int graph[][], int u, int v, int k)
{
// Base cases
if (k == 0 && u == v) return 0;
if (k == 1 && graph[u][v] != INF) return graph[u][v];
if (k <= 0) return INF;
// Initialize result
int res = INF;
// Go to all adjacents of u and recur
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
if (graph[u][i] != INF && u != i && v != i)
{
int rec_res = shortestPath(graph, i, v, k-1);
if (rec_res != INF)
res = Math.min(res, graph[u][i] + rec_res);
}
}
return res;
}
public static void main (String[] args)
{
/* Let us create the graph shown in above diagram*/
int graph[][] = new int[][]{ {0, 10, 3, 2},
{INF, 0, INF, 7},
{INF, INF, 0, 6},
{INF, INF, INF, 0}
};
ShortestPath t = new ShortestPath();
int u = 0, v = 3, k = 2;
System.out.println("Weight of the shortest path is "+
t.shortestPath(graph, u, v, k));
}
}Python3
# Python3 program to find shortest path
# with exactly k edges
# Define number of vertices in the graph
# and infinite value
# A naive recursive function to count
# walks from u to v with k edges
def shortestPath(graph, u, v, k):
V = 4
INF = 999999999999
# Base cases
if k == 0 and u == v:
return 0
if k == 1 and graph[u][v] != INF:
return graph[u][v]
if k <= 0:
return INF
# Initialize result
res = INF
# Go to all adjacents of u and recur
for i in range(V):
if graph[u][i] != INF and u != i and v != i:
rec_res = shortestPath(graph, i, v, k - 1)
if rec_res != INF:
res = min(res, graph[u][i] + rec_res)
return res
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
INF = 999999999999
# Let us create the graph shown
# in above diagram
graph = [[0, 10, 3, 2],
[INF, 0, INF, 7],
[INF, INF, 0, 6],
[INF, INF, INF, 0]]
u = 0
v = 3
k = 2
print("Weight of the shortest path is",
shortestPath(graph, u, v, k))
# This code is contributed by PranchalKC#
// Dynamic Programming based C# program to
// find shortest pathwith exactly k edges
using System;
class GFG
{
// Define number of vertices in the
// graph and infinite value
const int V = 4;
const int INF = Int32.MaxValue;
// A naive recursive function to count
// walks from u to v with k edges
int shortestPath(int[,] graph, int u,
int v, int k)
{
// Base cases
if (k == 0 && u == v) return 0;
if (k == 1 && graph[u, v] != INF) return graph[u, v];
if (k <= 0) return INF;
// Initialize result
int res = INF;
// Go to all adjacents of u and recur
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
if (graph[u, i] != INF && u != i && v != i)
{
int rec_res = shortestPath(graph, i, v, k - 1);
if (rec_res != INF)
res = Math.Min(res, graph[u, i] + rec_res);
}
}
return res;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main ()
{
/* Let us create the graph
shown in above diagram*/
int[,] graph = new int[,]{{0, 10, 3, 2},
{INF, 0, INF, 7},
{INF, INF, 0, 6},
{INF, INF, INF, 0}};
GFG t = new GFG();
int u = 0, v = 3, k = 2;
Console.WriteLine("Weight of the shortest path is "+
t.shortestPath(graph, u, v, k));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Akanksha RaiJavascript
C++
// Dynamic Programming based C++ program to find shortest path with
// exactly k edges
#include
#include
using namespace std;
// Define number of vertices in the graph and infinite value
#define V 4
#define INF INT_MAX
// A Dynamic programming based function to find the shortest path from
// u to v with exactly k edges.
int shortestPath(int graph[][V], int u, int v, int k)
{
// Table to be filled up using DP. The value sp[i][j][e] will store
// weight of the shortest path from i to j with exactly k edges
int sp[V][V][k+1];
// Loop for number of edges from 0 to k
for (int e = 0; e <= k; e++)
{
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) // for source
{
for (int j = 0; j < V; j++) // for destination
{
// initialize value
sp[i][j][e] = INF;
// from base cases
if (e == 0 && i == j)
sp[i][j][e] = 0;
if (e == 1 && graph[i][j] != INF)
sp[i][j][e] = graph[i][j];
//go to adjacent only when number of edges is more than 1
if (e > 1)
{
for (int a = 0; a < V; a++)
{
// There should be an edge from i to a and a
// should not be same as either i or j
if (graph[i][a] != INF && i != a &&
j!= a && sp[a][j][e-1] != INF)
sp[i][j][e] = min(sp[i][j][e], graph[i][a] +
sp[a][j][e-1]);
}
}
}
}
}
return sp[u][v][k];
}
// driver program to test above function
int main()
{
/* Let us create the graph shown in above diagram*/
int graph[V][V] = { {0, 10, 3, 2},
{INF, 0, INF, 7},
{INF, INF, 0, 6},
{INF, INF, INF, 0}
};
int u = 0, v = 3, k = 2;
cout << shortestPath(graph, u, v, k);
return 0;
} Java
// Dynamic Programming based Java program to find shortest path with
// exactly k edges
import java.util.*;
import java.lang.*;
import java.io.*;
class ShortestPath
{
// Define number of vertices in the graph and infinite value
static final int V = 4;
static final int INF = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
// A Dynamic programming based function to find the shortest path
// from u to v with exactly k edges.
int shortestPath(int graph[][], int u, int v, int k)
{
// Table to be filled up using DP. The value sp[i][j][e] will
// store weight of the shortest path from i to j with exactly
// k edges
int sp[][][] = new int[V][V][k+1];
// Loop for number of edges from 0 to k
for (int e = 0; e <= k; e++)
{
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) // for source
{
for (int j = 0; j < V; j++) // for destination
{
// initialize value
sp[i][j][e] = INF;
// from base cases
if (e == 0 && i == j)
sp[i][j][e] = 0;
if (e == 1 && graph[i][j] != INF)
sp[i][j][e] = graph[i][j];
// go to adjacent only when number of edges is
// more than 1
if (e > 1)
{
for (int a = 0; a < V; a++)
{
// There should be an edge from i to a and
// a should not be same as either i or j
if (graph[i][a] != INF && i != a &&
j!= a && sp[a][j][e-1] != INF)
sp[i][j][e] = Math.min(sp[i][j][e],
graph[i][a] + sp[a][j][e-1]);
}
}
}
}
}
return sp[u][v][k];
}
public static void main (String[] args)
{
/* Let us create the graph shown in above diagram*/
int graph[][] = new int[][]{ {0, 10, 3, 2},
{INF, 0, INF, 7},
{INF, INF, 0, 6},
{INF, INF, INF, 0}
};
ShortestPath t = new ShortestPath();
int u = 0, v = 3, k = 2;
System.out.println("Weight of the shortest path is "+
t.shortestPath(graph, u, v, k));
}
}
//This code is contributed by Aakash HasijaPython3
# Dynamic Programming based Python3
# program to find shortest path with
# A Dynamic programming based function
# to find the shortest path from u to v
# with exactly k edges.
def shortestPath(graph, u, v, k):
global V, INF
# Table to be filled up using DP. The
# value sp[i][j][e] will store weight
# of the shortest path from i to j
# with exactly k edges
sp = [[None] * V for i in range(V)]
for i in range(V):
for j in range(V):
sp[i][j] = [None] * (k + 1)
# Loop for number of edges from 0 to k
for e in range(k + 1):
for i in range(V): # for source
for j in range(V): # for destination
# initialize value
sp[i][j][e] = INF
# from base cases
if (e == 0 and i == j):
sp[i][j][e] = 0
if (e == 1 and graph[i][j] != INF):
sp[i][j][e] = graph[i][j]
# go to adjacent only when number
# of edges is more than 1
if (e > 1):
for a in range(V):
# There should be an edge from
# i to a and a should not be
# same as either i or j
if (graph[i][a] != INF and i != a and
j!= a and sp[a][j][e - 1] != INF):
sp[i][j][e] = min(sp[i][j][e], graph[i][a] +
sp[a][j][e - 1])
return sp[u][v][k]
# Driver Code
# Define number of vertices in
# the graph and infinite value
V = 4
INF = 999999999999
# Let us create the graph shown
# in above diagram
graph = [[0, 10, 3, 2],
[INF, 0, INF, 7],
[INF, INF, 0, 6],
[INF, INF, INF, 0]]
u = 0
v = 3
k = 2
print("Weight of the shortest path is",
shortestPath(graph, u, v, k))
# This code is contributed by PranchalKC#
// Dynamic Programming based C# program to find
// shortest path with exactly k edges
using System;
class GFG
{
// Define number of vertices in the graph
// and infinite value
static readonly int V = 4;
static readonly int INF = int.MaxValue;
// A Dynamic programming based function to
// find the shortest path from u to v
// with exactly k edges.
int shortestPath(int [,]graph, int u, int v, int k)
{
// Table to be filled up using DP. The value
// sp[i][j][e] will store weight of the shortest
// path from i to j with exactly k edges
int [,,]sp = new int[V, V, k + 1];
// Loop for number of edges from 0 to k
for (int e = 0; e <= k; e++)
{
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) // for source
{
for (int j = 0; j < V; j++) // for destination
{
// initialize value
sp[i, j, e] = INF;
// from base cases
if (e == 0 && i == j)
sp[i, j, e] = 0;
if (e == 1 && graph[i, j] != INF)
sp[i, j, e] = graph[i, j];
// go to adjacent only when number of
// edges is more than 1
if (e > 1)
{
for (int a = 0; a < V; a++)
{
// There should be an edge from i to a and
// a should not be same as either i or j
if (graph[i, a] != INF && i != a &&
j!= a && sp[a, j, e - 1] != INF)
sp[i, j, e] = Math.Min(sp[i, j, e],
graph[i, a] + sp[a, j, e - 1]);
}
}
}
}
}
return sp[u, v, k];
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
/* Let us create the graph shown in above diagram*/
int [,]graph = new int[,]{ {0, 10, 3, 2},
{INF, 0, INF, 7},
{INF, INF, 0, 6},
{INF, INF, INF, 0} };
GFG t = new GFG();
int u = 0, v = 3, k = 2;
Console.WriteLine("Weight of the shortest path is "+
t.shortestPath(graph, u, v, k));
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumarJavascript
输出:
Weight of the shortest path is 9上述函数的最坏情况时间复杂度为 O(V k ),其中 V 是给定图中的顶点数。我们可以通过绘制递归树来简单地分析时间复杂度。最坏的情况发生在完整的图上。在最坏的情况下,递归树的每个内部节点都会有正好 V 个孩子。
我们可以使用动态规划优化上述解决方案。这个想法是建立一个 3D 表,其中第一维是源,第二维是目的地,第三维是从源到目的地的边数,值是行走次数。与其他动态规划问题一样,我们以自下而上的方式填充 3D 表。
C++
// Dynamic Programming based C++ program to find shortest path with
// exactly k edges
#include
#include
using namespace std;
// Define number of vertices in the graph and infinite value
#define V 4
#define INF INT_MAX
// A Dynamic programming based function to find the shortest path from
// u to v with exactly k edges.
int shortestPath(int graph[][V], int u, int v, int k)
{
// Table to be filled up using DP. The value sp[i][j][e] will store
// weight of the shortest path from i to j with exactly k edges
int sp[V][V][k+1];
// Loop for number of edges from 0 to k
for (int e = 0; e <= k; e++)
{
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) // for source
{
for (int j = 0; j < V; j++) // for destination
{
// initialize value
sp[i][j][e] = INF;
// from base cases
if (e == 0 && i == j)
sp[i][j][e] = 0;
if (e == 1 && graph[i][j] != INF)
sp[i][j][e] = graph[i][j];
//go to adjacent only when number of edges is more than 1
if (e > 1)
{
for (int a = 0; a < V; a++)
{
// There should be an edge from i to a and a
// should not be same as either i or j
if (graph[i][a] != INF && i != a &&
j!= a && sp[a][j][e-1] != INF)
sp[i][j][e] = min(sp[i][j][e], graph[i][a] +
sp[a][j][e-1]);
}
}
}
}
}
return sp[u][v][k];
}
// driver program to test above function
int main()
{
/* Let us create the graph shown in above diagram*/
int graph[V][V] = { {0, 10, 3, 2},
{INF, 0, INF, 7},
{INF, INF, 0, 6},
{INF, INF, INF, 0}
};
int u = 0, v = 3, k = 2;
cout << shortestPath(graph, u, v, k);
return 0;
}
Java
// Dynamic Programming based Java program to find shortest path with
// exactly k edges
import java.util.*;
import java.lang.*;
import java.io.*;
class ShortestPath
{
// Define number of vertices in the graph and infinite value
static final int V = 4;
static final int INF = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
// A Dynamic programming based function to find the shortest path
// from u to v with exactly k edges.
int shortestPath(int graph[][], int u, int v, int k)
{
// Table to be filled up using DP. The value sp[i][j][e] will
// store weight of the shortest path from i to j with exactly
// k edges
int sp[][][] = new int[V][V][k+1];
// Loop for number of edges from 0 to k
for (int e = 0; e <= k; e++)
{
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) // for source
{
for (int j = 0; j < V; j++) // for destination
{
// initialize value
sp[i][j][e] = INF;
// from base cases
if (e == 0 && i == j)
sp[i][j][e] = 0;
if (e == 1 && graph[i][j] != INF)
sp[i][j][e] = graph[i][j];
// go to adjacent only when number of edges is
// more than 1
if (e > 1)
{
for (int a = 0; a < V; a++)
{
// There should be an edge from i to a and
// a should not be same as either i or j
if (graph[i][a] != INF && i != a &&
j!= a && sp[a][j][e-1] != INF)
sp[i][j][e] = Math.min(sp[i][j][e],
graph[i][a] + sp[a][j][e-1]);
}
}
}
}
}
return sp[u][v][k];
}
public static void main (String[] args)
{
/* Let us create the graph shown in above diagram*/
int graph[][] = new int[][]{ {0, 10, 3, 2},
{INF, 0, INF, 7},
{INF, INF, 0, 6},
{INF, INF, INF, 0}
};
ShortestPath t = new ShortestPath();
int u = 0, v = 3, k = 2;
System.out.println("Weight of the shortest path is "+
t.shortestPath(graph, u, v, k));
}
}
//This code is contributed by Aakash Hasija
蟒蛇3
# Dynamic Programming based Python3
# program to find shortest path with
# A Dynamic programming based function
# to find the shortest path from u to v
# with exactly k edges.
def shortestPath(graph, u, v, k):
global V, INF
# Table to be filled up using DP. The
# value sp[i][j][e] will store weight
# of the shortest path from i to j
# with exactly k edges
sp = [[None] * V for i in range(V)]
for i in range(V):
for j in range(V):
sp[i][j] = [None] * (k + 1)
# Loop for number of edges from 0 to k
for e in range(k + 1):
for i in range(V): # for source
for j in range(V): # for destination
# initialize value
sp[i][j][e] = INF
# from base cases
if (e == 0 and i == j):
sp[i][j][e] = 0
if (e == 1 and graph[i][j] != INF):
sp[i][j][e] = graph[i][j]
# go to adjacent only when number
# of edges is more than 1
if (e > 1):
for a in range(V):
# There should be an edge from
# i to a and a should not be
# same as either i or j
if (graph[i][a] != INF and i != a and
j!= a and sp[a][j][e - 1] != INF):
sp[i][j][e] = min(sp[i][j][e], graph[i][a] +
sp[a][j][e - 1])
return sp[u][v][k]
# Driver Code
# Define number of vertices in
# the graph and infinite value
V = 4
INF = 999999999999
# Let us create the graph shown
# in above diagram
graph = [[0, 10, 3, 2],
[INF, 0, INF, 7],
[INF, INF, 0, 6],
[INF, INF, INF, 0]]
u = 0
v = 3
k = 2
print("Weight of the shortest path is",
shortestPath(graph, u, v, k))
# This code is contributed by PranchalK
C#
// Dynamic Programming based C# program to find
// shortest path with exactly k edges
using System;
class GFG
{
// Define number of vertices in the graph
// and infinite value
static readonly int V = 4;
static readonly int INF = int.MaxValue;
// A Dynamic programming based function to
// find the shortest path from u to v
// with exactly k edges.
int shortestPath(int [,]graph, int u, int v, int k)
{
// Table to be filled up using DP. The value
// sp[i][j][e] will store weight of the shortest
// path from i to j with exactly k edges
int [,,]sp = new int[V, V, k + 1];
// Loop for number of edges from 0 to k
for (int e = 0; e <= k; e++)
{
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) // for source
{
for (int j = 0; j < V; j++) // for destination
{
// initialize value
sp[i, j, e] = INF;
// from base cases
if (e == 0 && i == j)
sp[i, j, e] = 0;
if (e == 1 && graph[i, j] != INF)
sp[i, j, e] = graph[i, j];
// go to adjacent only when number of
// edges is more than 1
if (e > 1)
{
for (int a = 0; a < V; a++)
{
// There should be an edge from i to a and
// a should not be same as either i or j
if (graph[i, a] != INF && i != a &&
j!= a && sp[a, j, e - 1] != INF)
sp[i, j, e] = Math.Min(sp[i, j, e],
graph[i, a] + sp[a, j, e - 1]);
}
}
}
}
}
return sp[u, v, k];
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
/* Let us create the graph shown in above diagram*/
int [,]graph = new int[,]{ {0, 10, 3, 2},
{INF, 0, INF, 7},
{INF, INF, 0, 6},
{INF, INF, INF, 0} };
GFG t = new GFG();
int u = 0, v = 3, k = 2;
Console.WriteLine("Weight of the shortest path is "+
t.shortestPath(graph, u, v, k));
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar
Javascript
输出:
Weight of the shortest path is 9如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。