给定两个整数N和K ,任务是从由K的幂生成的子集序列中找到第N个子集,即{1,K 1 ,K 2 ,K 3 ,…..},以便排列子集按照其和的增加顺序,任务是从序列中找到第N个子集。
例子:
Input: N = 5, K = 3
Output: 1 9
Explanation:
Sequence of subsets along with their sum are:
- Subset = {1}, Sum = 1
- Subset = {3}, Sum = 3
- Subset = {1, 3}, Sum = 4
- Subset = {9}, Sum = 9
- Subset = {1, 9}, Sum = 10
Therefore, the subset at position 5 is {1, 9}.
Input: N = 4, K = 4
Output: 16
方法:
让我们参考下面给出的K = 3所需的序列:
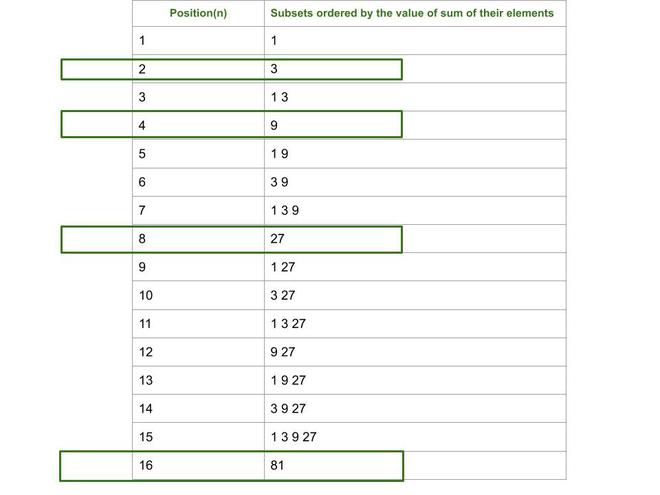
从以上序列可以看出,子集{3}具有位置2,子集{9}具有位置4,子集{27}具有位置8,依此类推。子集{1,3},{1,9},{1,27}分别占据位置3、5和9。因此,可以通过找到小于或等于N的最接近2的幂来获得所需的第N个子集的所有元素。
Illustration:
N = 6, K = 3
1st iteration:
- p = log2(6) = 2
- 32 = 9, Subset = {9}
- N = 6 % 4 = 2
2nd iteration:
- p = log2(2) = 1
- 31 = 3, Subset = {3, 9}
- N = 2 % 2 = 0
Therefore the required subset is {3, 9}
请按照以下步骤解决问题:
- 计算小于或等于N的2的最近幂,即p 。因此,P =日志2 N。
- 现在,子集的元素将是K p 。将其插入子集的前面。
- 更新N到N%2页。
- 重复上述步骤,直到N变为0,然后打印获得的子集。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
#include
using namespace std;
#define lli long long int
// Function to print the
// required N-th subset
void printSubset(lli n, int k)
{
vector answer;
while(n > 0)
{
// Nearest power of 2<=N
lli p = log2(n);
// Now insert k^p in the answer
answer.push_back(pow(k, p));
// update n
n %= (int)pow(2, p);
}
// Print the ans in sorted order
reverse(answer.begin(), answer.end());
for(auto x: answer)
{
cout << x << " ";
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
lli n = 5;
int k = 4;
printSubset(n, k);
}
// This code is contributed by winter_soldier Java
// Java program for above approach
import java.util.*;
import java.lang.*;
import java.io.*;
class GFG
{
// Function to print the
// required N-th subset
static void printSubset(long n, int k)
{
ArrayList answer = new ArrayList<>();
while(n > 0)
{
// Nearest power of 2<=N
long p = (long)(Math.log(n) / Math.log(2));;
// Now insert k^p in the answer
answer.add((long)(Math.pow(k, p)));
// update n
n %= (int)Math.pow(2, p);
}
// Print the ans in sorted order
Collections.sort(answer);
for(Long x: answer)
{
System.out.print(x + " ");
}
}
// Driver function
public static void main (String[] args)
{
long n = 5;
int k = 4;
printSubset(n, k);
}
}
// This code is contributed by offbeat Python3
# Python3 program for
# the above approach
import math
# Function to print the
# required N-th subset
def printSubset(N, K):
# Stores the subset
answer = ""
while(N > 0):
# Nearest power of 2 <= N
p = int(math.log(N, 2))
# Insert K ^ p in the subset
answer = str(K**p)+" "+answer
# Update N
N = N % (2**p)
# Print the subset
print(answer)
# Driver Code
N = 5
K = 4
printSubset(N, K)C#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG {
// Function to print the
// required N-th subset
static void printSubset(int n, int k)
{
List answer = new List();
while(n > 0)
{
// Nearest power of 2<=N
int p = (int)Math.Log(n,2);
// Now insert k^p in the answer
answer.Add((int)Math.Pow(k, p));
// update n
n %= (int)Math.Pow(2, p);
}
// Print the ans in sorted order
answer.Reverse();
foreach(int x in answer)
{
Console.Write(x + " ");
}
}
// Driver code
static void Main() {
int n = 5;
int k = 4;
printSubset(n, k);
}
}
// This code is contributed by divyeshrabadiya07. C++
// C++ program to print subset
// at the nth position ordered
// by the sum of the elements
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to print the elements of
// the subset at pos n
void printsubset(int n,int k)
{
// Initialize count=0 and x=0
int count = 0, x = 0;
// create a vector for
// storing the elements
// of subsets
vector vec;
// doing until all the
// set bits of n are used
while (n) {
x = n & 1;
// this part is executed only
// when the last bit is
// set
if (x) {
vec.push_back(pow(k, count));
}
// right shift the bit by one position
n = n >> 1;
// incresing the count each time by one
count++;
}
// printing the values os elements
for (int i = 0; i < vec.size(); i++)
cout << vec[i] << " ";
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int n = 7,k=4;
printsubset(n,k);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by shivkant Java
// Java program to print subset
// at the nth position ordered
// by the sum of the elements
import java.util.*;
import java.lang.*;
class GFG{
// Function to print the
// elements of the subset
// at pos n
static void printsubset(int n,
int k)
{
// Initialize count=0 and x=0
int count = 0, x = 0;
// Create a vector for
// storing the elements
// of subsets
ArrayList vec =
new ArrayList<>();
// Doing until all the
// set bits of n are used
while (n != 0)
{
x = n & 1;
// This part is executed only
// when the last bit is
// set
if (x != 0)
{
vec.add((int)Math.pow(k,
count));
}
// Right shift the bit
// by one position
n = n >> 1;
// Incresing the count
// each time by one
count++;
}
// Printing the values os elements
for (int i = 0; i < vec.size(); i++)
System.out.print(vec.get(i) + " ");
}
// Driver function
public static void main (String[] args)
{
int n = 7, k = 4;
printsubset(n, k);
}
}
// This code is contributed by offbeat Python3
# Python3 program to print subset
# at the nth position ordered
# by the sum of the elements
import math
# Function to print the elements of
# the subset at pos n
def printsubset(n, k):
# Initialize count=0 and x=0
count = 0
x = 0
# Create a vector for
# storing the elements
# of subsets
vec = []
# Doing until all the
# set bits of n are used
while (n > 0):
x = n & 1
# This part is executed only
# when the last bit is
# set
if (x):
vec.append(pow(k, count))
# Right shift the bit by one position
n = n >> 1
# Increasing the count each time by one
count += 1
# Printing the values os elements
for item in vec:
print(item, end = " ")
# Driver Code
n = 7
k = 4
printsubset(n, k)
# This code is contributed by Stream_CipherC#
// C# program to print subset
// at the nth position ordered
// by the sum of the elements
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System;
class GFG{
// Function to print the
// elements of the subset
// at pos n
static void printsubset(int n, int k)
{
// Initialize count=0 and x=0
int count = 0, x = 0;
// Create a vector for
// storing the elements
// of subsets
List vec = new List();
// Doing until all the
// set bits of n are used
while (n != 0)
{
x = n & 1;
// This part is executed only
// when the last bit is
// set
if (x != 0)
{
vec.Add((int)Math.Pow(k, count));
}
// Right shift the bit
// by one position
n = n >> 1;
// Incresing the count
// each time by one
count++;
}
// Printing the values os elements
for(int i = 0; i < vec.Count; i++)
Console.Write(vec[i] + " ");
}
// Driver code
public static void Main ()
{
int n = 7, k = 4;
printsubset(n, k);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Stream_Cipher 输出
1 16 时间复杂度: O(logN)
辅助空间: O(1)
方法:
- 初始化count,将x初始化为0。此外,还有一个用于存储子集元素的向量。
- 当n大于0时执行以下操作。
- 设置x = n&1,以查找是否设置了数字的最后一位。
- 现在,如果n不为0,则将元素3计数到子集中。
- 通过右移1个单位将n减少2。
- 将计数值增加1。
- 最后,数组中的元素是第N个子集的元素。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program to print subset
// at the nth position ordered
// by the sum of the elements
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to print the elements of
// the subset at pos n
void printsubset(int n,int k)
{
// Initialize count=0 and x=0
int count = 0, x = 0;
// create a vector for
// storing the elements
// of subsets
vector vec;
// doing until all the
// set bits of n are used
while (n) {
x = n & 1;
// this part is executed only
// when the last bit is
// set
if (x) {
vec.push_back(pow(k, count));
}
// right shift the bit by one position
n = n >> 1;
// incresing the count each time by one
count++;
}
// printing the values os elements
for (int i = 0; i < vec.size(); i++)
cout << vec[i] << " ";
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int n = 7,k=4;
printsubset(n,k);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by shivkant
Java
// Java program to print subset
// at the nth position ordered
// by the sum of the elements
import java.util.*;
import java.lang.*;
class GFG{
// Function to print the
// elements of the subset
// at pos n
static void printsubset(int n,
int k)
{
// Initialize count=0 and x=0
int count = 0, x = 0;
// Create a vector for
// storing the elements
// of subsets
ArrayList vec =
new ArrayList<>();
// Doing until all the
// set bits of n are used
while (n != 0)
{
x = n & 1;
// This part is executed only
// when the last bit is
// set
if (x != 0)
{
vec.add((int)Math.pow(k,
count));
}
// Right shift the bit
// by one position
n = n >> 1;
// Incresing the count
// each time by one
count++;
}
// Printing the values os elements
for (int i = 0; i < vec.size(); i++)
System.out.print(vec.get(i) + " ");
}
// Driver function
public static void main (String[] args)
{
int n = 7, k = 4;
printsubset(n, k);
}
}
// This code is contributed by offbeat
Python3
# Python3 program to print subset
# at the nth position ordered
# by the sum of the elements
import math
# Function to print the elements of
# the subset at pos n
def printsubset(n, k):
# Initialize count=0 and x=0
count = 0
x = 0
# Create a vector for
# storing the elements
# of subsets
vec = []
# Doing until all the
# set bits of n are used
while (n > 0):
x = n & 1
# This part is executed only
# when the last bit is
# set
if (x):
vec.append(pow(k, count))
# Right shift the bit by one position
n = n >> 1
# Increasing the count each time by one
count += 1
# Printing the values os elements
for item in vec:
print(item, end = " ")
# Driver Code
n = 7
k = 4
printsubset(n, k)
# This code is contributed by Stream_Cipher
C#
// C# program to print subset
// at the nth position ordered
// by the sum of the elements
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System;
class GFG{
// Function to print the
// elements of the subset
// at pos n
static void printsubset(int n, int k)
{
// Initialize count=0 and x=0
int count = 0, x = 0;
// Create a vector for
// storing the elements
// of subsets
List vec = new List();
// Doing until all the
// set bits of n are used
while (n != 0)
{
x = n & 1;
// This part is executed only
// when the last bit is
// set
if (x != 0)
{
vec.Add((int)Math.Pow(k, count));
}
// Right shift the bit
// by one position
n = n >> 1;
// Incresing the count
// each time by one
count++;
}
// Printing the values os elements
for(int i = 0; i < vec.Count; i++)
Console.Write(vec[i] + " ");
}
// Driver code
public static void Main ()
{
int n = 7, k = 4;
printsubset(n, k);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Stream_Cipher
输出
1 4 16