给定一个字符串形式的大数N ,任务是确定可以通过对数字N进行改组而形成的不同数字的计数。
笔记:
- N可以包含前导零。
- 数字本身也被考虑在内。
- 由于答案可能非常大,因此以10 9 +7为模数打印结果。
例子:
Input: N = “23”
Output: 2
Explanation:
23 can be shuffled as {23, 32}
Input: N = “0223”
Output: 12
Explanation:
0223 can be shuffled as {2230, 2203, 2023, 3220, 3202, 3022, 2320, 2302, 2032, 0232, 0322, 0223 }
幼稚的方法:幼稚的想法是找到给定数字的所有排列并打印生成的唯一数字的计数。但是由于给定数N非常大,因此无法使用。
时间复杂度: O(N * N!)
辅助空间: O(1)
高效方法:为了优化上述方法,其思想是使用置换和组合的概念以及费马小定理。步骤如下:
- 使用费马小定理在模M下找到模乘法乘法逆,其中M为10 9 +7 。
- 而不是找到所有排列,结果将是给定数字N的长度的阶乘除以一个数字计数的阶乘的乘积,即:
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com count = \frac{K!}{C[i]!}](https://mangdo-1254073825.cos.ap-chengdu.myqcloud.com//front_eng_imgs/geeksforgeeks2021/Count%20of%20distinct%20numbers%20formed%20by%20shuffling%20the%20digits%20of%20a%20large%20number%20N_0.jpg)
where,
K is the number of digits in N,
C[i] is the count of digits(from 0 to 9) in N. - 创建一个数组,在该数组的每个索引中存储该索引的阶乘。
- 为了存储每个数字的计数,请创建一个大小为10的数组,并将其初始化为0。
- 使用N的长度的阶乘值初始化变量答案。对于数字的每个计数,发现它是模m和倍数下的模乘法逆,其结果为:
Since the count is
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com count = \frac{K!}{\sum_{i = 0}^{9}{C[i]!}}](https://mangdo-1254073825.cos.ap-chengdu.myqcloud.com//front_eng_imgs/geeksforgeeks2021/Count%20of%20distinct%20numbers%20formed%20by%20shuffling%20the%20digits%20of%20a%20large%20number%20N_1.jpg)
According to fermat little theorm:
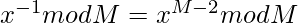
Therefore the count is given by:
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com count = ((K!)* ( \sum_{i = 0}^{9}(factorial[i]^{m - 2})mod M) mod M)](https://mangdo-1254073825.cos.ap-chengdu.myqcloud.com//front_eng_imgs/geeksforgeeks2021/Count%20of%20distinct%20numbers%20formed%20by%20shuffling%20the%20digits%20of%20a%20large%20number%20N_3.jpg)
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
#define ll long long int
// Recursive function to return the value
// of (x ^ n) % m
ll modexp(ll x, ll n, ll m)
{
// Base Case
if (n == 0) {
return 1;
}
// If N is even
else if (n % 2 == 0) {
return modexp((x * x) % m,
n / 2, m);
}
// Else N is odd
else {
return (x * modexp((x * x) % m,
(n - 1) / 2, m)
% m);
}
}
// Function to find modular inverse
// of a number x under modulo m
ll modInverse(ll x, ll m)
{
// Using Fermat's little theorem
return modexp(x, m - 2, m);
}
// Function to count of numbers formed by
// shuffling the digits of a large number N
void countNumbers(string N)
{
// Modulo value
ll m = 1000000007;
// Array to store the factorials
// upto the maximum value of N
ll factorial[100001];
// Store factorial of i at index i
factorial[0] = 1;
for (ll i = 1; i < 100001; i++) {
factorial[i] = (factorial[i - 1] * i) % m;
}
// To store count of occurrence
// of a digit
ll count[10];
for (ll i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
count[i] = 0;
}
ll length = N.length();
for (ll i = 0; i < length; i++)
// Increment the count of
// digit occured
count[N[i] - '0']++;
// Assign the factorial of
// length of input
ll result = factorial[length];
// Multiplying result with the
// modulo multiplicative inverse of
// factorial of count of i
for (ll i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
result = (result
* modInverse(factorial[count[i]], m))
% m;
}
// Print the result
cout << result;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Given Number as string
string N = "0223";
// Function call
countNumbers(N);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Recursive function to return the value
// of (x ^ n) % m
static long modexp(long x, long n, long m)
{
// Base Case
if (n == 0)
{
return 1;
}
// If N is even
else if (n % 2 == 0)
{
return modexp((x * x) % m,
n / 2, m);
}
// Else N is odd
else
{
return (x * modexp((x * x) % m,
(n - 1) / 2, m) % m);
}
}
// Function to find modular inverse
// of a number x under modulo m
static long modInverse(long x, long m)
{
// Using Fermat's little theorem
return modexp(x, m - 2, m);
}
// Function to count of numbers formed by
// shuffling the digits of a large number N
static void countNumbers(String N)
{
// Modulo value
long m = 1000000007;
// Array to store the factorials
// upto the maximum value of N
long factorial[] = new long [100001];
// Store factorial of i at index i
factorial[0] = 1;
for(int i = 1; i < 100001; i++)
{
factorial[i] = (factorial[i - 1] * i) % m;
}
// To store count of occurrence
// of a digit
long count[] = new long [10];
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
count[i] = 0;
}
long length = N.length();
for(int i = 0; i < length; i++)
// Increment the count of
// digit occured
count[N.charAt(i) - '0']++;
// Assign the factorial of
// length of input
long result = factorial[(int)length];
// Multiplying result with the
// modulo multiplicative inverse of
// factorial of count of i
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
result = (result *
modInverse(
factorial[(int)count[i]], m)) % m;
}
// Print the result
System.out.println(result);
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Given number as string
String N = "0223";
// Function call
countNumbers(N);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Stream_CipherPython3
# Python3 program for the above approach
# Recursive function to return the value
# of (x ^ n) % m
def modexp(x, n, m):
# Base Case
if (n == 0):
return 1
# If N is even
else:
if (n % 2 == 0):
return modexp((x * x) % m,
n / 2, m);
# Else N is odd
else:
return (x * modexp((x * x) % m,
(n - 1) / 2, m) % m)
# Function to find modular inverse
# of a number x under modulo m
def modInverse(x, m):
# Using Fermat's little theorem
return modexp(x, m - 2, m)
# Function to count of numbers formed by
# shuffling the digits of a large number N
def countNumbers(N):
# Modulo value
m = 1000000007
# Array to store the factorials
# upto the maximum value of N
factorial = [0 for x in range(100001)]
# Store factorial of i at index i
factorial[0] = 1;
for i in range(1, 100001):
factorial[i] = (factorial[i - 1] * i) % m
# To store count of occurrence
# of a digit
count = [0 for x in range(10)]
for i in range(0, 10):
count[i] = 0
length = len(N)
for i in range(0, length):
# Increment the count of
# digit occured
count[int(N[i])] += 1
# Assign the factorial of
# length of input
result = factorial[int(length)]
# Multiplying result with the
# modulo multiplicative inverse of
# factorial of count of i
for i in range(0, 10):
result = (result *
modInverse(
factorial[int(count[i])], m)) % m
# Print the result
print(result)
# Driver code
# Given number as string
N = "0223";
# Function call
countNumbers(N)
# This code is contributed by Stream_CipherC#
// C# program for the above approach
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System;
class GFG{
// Recursive function to return the value
// of (x ^ n) % m
static long modexp(long x, long n, long m)
{
// Base Case
if (n == 0)
{
return 1;
}
// If N is even
else if (n % 2 == 0)
{
return modexp((x * x) % m,
n / 2, m);
}
// Else N is odd
else
{
return (x * modexp((x * x) % m,
(n - 1) / 2, m) % m);
}
}
// Function to find modular inverse
// of a number x under modulo m
static long modInverse(long x, long m)
{
// Using Fermat's little theorem
return modexp(x, m - 2, m);
}
// Function to count of numbers formed by
// shuffling the digits of a large number N
static void countNumbers(string N)
{
// Modulo value
long m = 1000000007;
// Array to store the factorials
// upto the maximum value of N
long []factorial = new long [100001];
// Store factorial of i at index i
factorial[0] = 1;
for(int i = 1; i < 100001; i++)
{
factorial[i] = (factorial[i - 1] * i) % m;
}
// To store count of occurrence
// of a digit
long []count = new long [10];
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
count[i] = 0;
}
long length = N.Length;
for(int i = 0; i < length; i++)
// Increment the count of
// digit occured
count[N[i] - '0']++;
// Assign the factorial of
// length of input
long result = factorial[(int)length];
// Multiplying result with the
// modulo multiplicative inverse of
// factorial of count of i
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
result = (result *
modInverse(
factorial[(int)count[i]], m)) % m;
}
// Print the result
Console.WriteLine(result);
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
// Given number as string
string N = "0223";
// Function call
countNumbers(N);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Stream_Cipher输出:
12
时间复杂度: O(K + log(M))。 O(K)用于计算数N的阶乘,根据费马小定理,需要O(log(M))来计算模m下任意数量x的模乘逆。
辅助空间: O(log 10 N),其中N是给定的数字N。