具有 N 个节点且最大深度等于 H 的 BST 的计数
给定两个整数N和H ,任务是找到由N个节点组成的不同二叉搜索树的计数,其中树的最大深度或高度等于H 。
注意:只有根节点的 BST 高度为0 。
例子:
Input: N = 2, H = 1
Output: 2
Explanation: The two BST’s are :
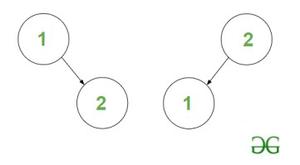
BST’s of height H = 1 and nodes N = 2
Input: N = 3, H = 2
Output: 4
Explanation: The four BST are :
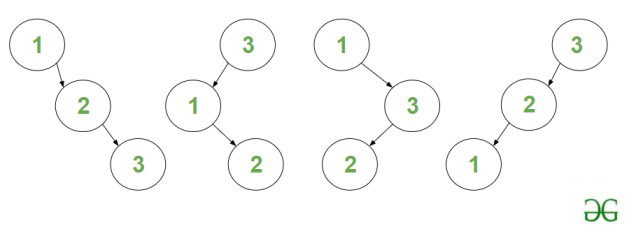
BST’s of height H = 2 and nodes N = 3
朴素的方法:可以使用递归来解决问题,可以记住递归以获得基于以下思想的动态规划解决方案:
The problem can be efficiently solved by finding the count of BST’s having maximum depth upto H (i.e., [0 – H]) instead of exactly H.
Let f(N, H) represent the count of BST’s consisting of ‘N’ nodes and having maximum depth upto ‘H’. Then the solution for the above problem: count of BST’s having maximum depth of exactly ‘H’ is equal to f(N, H) – f(N, H – 1).
请按照下图更好地理解。
插图:
Consider: N = 3, H = 2
The answer for this example is : count of BST’s of maximum depth upto 2 – count of BST’s of maximum depth upto 1.
- Count of BST’s of maximum depth upto 2 is 5, they are:
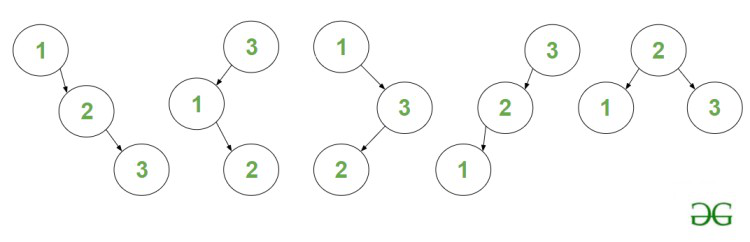
5 – BST’s of maximum depth upto 2
- Count of BST’s of maximum depth upto 1 is 1, it is :
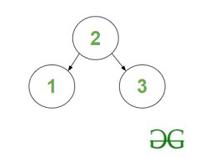
1 – BST of maximum depth upto 1
- Hence the count of BST’s of maximum depth equal to ‘2’ is 4.
请按照以下步骤解决问题。
- 节点i的 BST 计数为 根节点 等于由节点 1 到i-1形成的左子树和由节点i+1到N形成的右子树的 BST 计数的乘积。
- 为了找到左子树的 BST 计数,我们可以递归调用深度H-1和N=i – 1的相同函数。要找到右子树的 BST 计数,递归调用深度H-1和N=Ni的函数。
- 从[1, N]作为根节点循环i的所有值,并将左右子树计数的乘积添加到结果中。
时间复杂度: O(N * 2 N )
辅助空间: O(1)
有效方法:上述方法可以通过使用动态规划进行优化,因为上述问题具有重叠子问题和最优子结构。子问题可以存储在dp[][]表记忆中,其中dp[N][H]存储由N个节点组成的最大深度为H的 BST 的计数。请按照以下步骤解决问题:
- 初始化一个全局多维数组dp[105][105] ,所有值都为 -1,存储每个递归调用的结果。
- 定义一个递归函数,比如countOfBST(N, H)并执行以下步骤。
- 情况 1:如果N = 0 ,则返回1 。
- 情况 2:如果H = 0 ,则返回 true 如果N = 1 。
- 如果已计算状态dp[N][H]的结果,则返回此值dp[N][H] 。
- 使用变量“ i ”作为根迭代范围[1, N]并执行以下操作。
- 将递归函数countOfBST(i – 1, H – 1)和countOfBST(N – i, H – 1)的值相乘。这两个函数分别计算左子树和右子树的 BST 计数。
- 将术语添加到最终答案中,该答案存储[1, N]中所有根可能的 BST 总数。
- 打印函数countOfBST(N, H)返回的值。
以下是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ code to implement the approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Declaring a dp-array
int dp[105][105];
const int mod = 1000000007;
// Function to find the count of
// BST upto height 'H' consisting
// of 'N' nodes.
int countOfBST(int N, int H)
{
// Base Case1 : If N == 0, return
// 1 as a valid BST has been formed
if (N == 0) {
return 1;
}
// Base Case2 : If H == 0, return true
// if N == 1
if (H == 0) {
return N == 1;
}
// If the current state has already
// been computed, then return it.
if (dp[N][H] != -1) {
return dp[N][H];
}
// Initialize answer to 0.
int ans = 0;
// Iterate over all numbers from
// [1, N], with 'i' as root.
for (int i = 1; i <= N; ++i) {
// Call the recursive functions to
// find count of BST of left and right
// subtrees. Add the product of
// both terms to the answer.
ans += (countOfBST(i - 1, H - 1) * 1LL
* countOfBST(N - i, H - 1))
% mod;
// Take modulo 1000000007
ans %= mod;
}
// Return ans
return dp[N][H] = ans;
}
// Utility function to find the count
// of BST upto height 'H' consisting
// of 'N' nodes.
int UtilCountOfBST(int N, int H)
{
// Initialize dp-array with -1.
memset(dp, -1, sizeof dp);
// If height is 0, return true if
// only one node is present.
if (H == 0) {
return (N == 1);
}
// Function call.
return (countOfBST(N, H)
- countOfBST(N, H - 1)
+ mod)
% mod;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// Number of nodes
int N = 3;
// Height of tree
int H = 2;
cout << UtilCountOfBST(N, H) << endl;
return 0;
} Java
// Java implementation of above approach
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
// Declaring a dp-array
static int[][] dp = new int[105][105];
static int mod = 1000000007;
// Function to find the count of
// BST upto height 'H' consisting
// of 'N' nodes.
static int countOfBST(int N, int H)
{
// Base Case1 : If N == 0, return
// 1 as a valid BST has been formed
if (N == 0) {
return 1;
}
// Base Case2 : If H == 0, return true
// if N == 1
if (H == 0) {
if (N == 1)
return 1;
return 0;
}
// If the current state has already
// been computed, then return it.
if (dp[N][H] != -1) {
return dp[N][H];
}
// Initialize answer to 0.
int ans = 0;
// Iterate over all numbers from
// [1, N], with 'i' as root.
for (int i = 1; i <= N; ++i) {
// Call the recursive functions to
// find count of BST of left and right
// subtrees. Add the product of
// both terms to the answer.
ans += (countOfBST(i - 1, H - 1)
* countOfBST(N - i, H - 1))
% mod;
// Take modulo 1000000007
ans %= mod;
}
// Return ans
dp[N][H] = ans;
return dp[N][H];
}
// Utility function to find the count
// of BST upto height 'H' consisting
// of 'N' nodes.
static int UtilCountOfBST(int N, int H)
{
// Initialize dp-array with -1.
for (int i = 0; i < 105; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < 105; j++)
dp[i][j] = -1;
// If height is 0, return true if
// only one node is present.
if (H == 0) {
if (N == 1)
return 1;
return 0;
}
// Function call.
return (countOfBST(N, H) - countOfBST(N, H - 1)
+ mod)
% mod;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Number of nodes
int N = 3;
// Height of tree
int H = 2;
System.out.print(UtilCountOfBST(N, H));
}
}
// This code is contributed by code_hunt.Python3
# python3 code to implement the approach
# Declaring a dp-array
dp = [[-1 for _ in range(105)] for _ in range(105)]
mod = 1000000007
# Function to find the count of
# BST upto height 'H' consisting
# of 'N' nodes.
def countOfBST(N, H):
# Base Case1 : If N == 0, return
# 1 as a valid BST has been formed
if (N == 0):
return 1
# Base Case2 : If H == 0, return true
# if N == 1
if (H == 0):
return N == 1
# If the current state has already
# been computed, then return it.
if (dp[N][H] != -1):
return dp[N][H]
# Initialize answer to 0.
ans = 0
# Iterate over all numbers from
# [1, N], with 'i' as root.
for i in range(1, N+1):
# Call the recursive functions to
# find count of BST of left and right
# subtrees. Add the product of
# both terms to the answer.
ans += (countOfBST(i - 1, H - 1) * countOfBST(N - i, H - 1)) % mod
# Take modulo 1000000007
ans %= mod
# Return ans
dp[N][H] = ans
return dp[N][H]
# Utility function to find the count
# of BST upto height 'H' consisting
# of 'N' nodes.
def UtilCountOfBST(N, H):
# Initialize dp-array with -1.
# If height is 0, return true if
# only one node is present.
if (H == 0):
return (N == 1)
# Function call.
return (countOfBST(N, H)
- countOfBST(N, H - 1)
+ mod) % mod
# Driver code
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Number of nodes
N = 3
# Height of tree
H = 2
print(UtilCountOfBST(N, H))
# This code is contributed by rakeshsahniC#
// C# code to implement the approach
using System;
class GFG {
// Declaring a dp-array
static int[, ] dp = new int[105, 105];
const int mod = 1000000007;
// Function to find the count of
// BST upto height 'H' consisting
// of 'N' nodes.
static int countOfBST(int N, int H)
{
// Base Case1 : If N == 0, return
// 1 as a valid BST has been formed
if (N == 0) {
return 1;
}
// Base Case2 : If H == 0, return true
// if N == 1
if (H == 0) {
if (N == 1)
return 1;
return 0;
}
// If the current state has already
// been computed, then return it.
if (dp[N, H] != -1) {
return dp[N, H];
}
// Initialize answer to 0.
int ans = 0;
// Iterate over all numbers from
// [1, N], with 'i' as root.
for (int i = 1; i <= N; ++i) {
// Call the recursive functions to
// find count of BST of left and right
// subtrees. Add the product of
// both terms to the answer.
ans += (countOfBST(i - 1, H - 1)
* countOfBST(N - i, H - 1))
% mod;
// Take modulo 1000000007
ans %= mod;
}
// Return ans
dp[N, H] = ans;
return dp[N, H];
}
// Utility function to find the count
// of BST upto height 'H' consisting
// of 'N' nodes.
static int UtilCountOfBST(int N, int H)
{
// Initialize dp-array with -1.
for (int i = 0; i < 105; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < 105; j++)
dp[i, j] = -1;
// If height is 0, return true if
// only one node is present.
if (H == 0) {
if (N == 1)
return 1;
return 0;
}
// Function call.
return (countOfBST(N, H) - countOfBST(N, H - 1)
+ mod)
% mod;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
// Number of nodes
int N = 3;
// Height of tree
int H = 2;
Console.Write(UtilCountOfBST(N, H));
}
}
// This code is contributed by ukasp.Javascript
4时间复杂度: O(N 2 * H)
辅助空间: O(N * H)