给定一棵树,有N 个节点,编号从 1 到 N 和N – 1 个边和数组colours[] ,其中 colours[i] 表示 第 i个节点的颜色。任务是找到一个节点,使得连接到该节点的每个相邻树都包含相同颜色的节点。如果不存在这样的节点,则打印 -1。
Input: N = 8, colours[] = {1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 1, 3} edges = {(1, 2) (1, 3) (2, 4) (2, 7) (3, 5) (3, 6) (6, 8)}
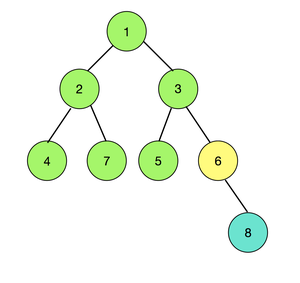
Visualizing the tree
Output: 6
Explanation:
Consider the node 6, it has 2 trees connected to it. One of them is rooted at 3 and the other is rooted at 8. Clearly, the tree rooted at 3 has nodes of same color and the tree rooted at 8 has only one node. Therefore, node 6 is one such node.
Input: N = 4, colors[] = {1, 2, 3, 4}, edges = {(1, 3) (1, 2 ) (2, 4)}
Output: -1
Explanation:
There is no such node.
方法:想法是检查所有节点是否具有相同的颜色,那么任何节点都可以是根。否则,选取任意两个相邻且颜色不同的节点,并通过执行 DFS 检查这些节点的子树。如果这些节点中的任何一个满足条件,则该节点可以是根。如果这两个节点都不满足条件,则不存在这样的根并打印 -1。
- 遍历树并找到彼此相邻的前两个不同颜色的节点,比如root1和root2 。如果没有找到这样的节点,那么所有节点都是相同的颜色,任何节点都可以作为root 。
- 通过将root1视为树的根来检查每个子树的所有节点的 是否具有相同的颜色。如果满足条件,则root1就是答案。
- 如果root1不满足条件,则对root2重复步骤 2。
- 如果root2不满足条件,则不存在这样的根,输出为 -1。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
const int NN = 1e5 + 5;
// Vector to store the tree
vector G[NN];
// Function to perform dfs
void dfs(int node, int parent,
bool& check,
int current_colour,
int* colours)
{
// Check is assigned to false if either it
// is already false or the current_colour
// is not same as the node colour
check = check
&& (colours[node] == current_colour);
// Iterate over the neighbours of node
for (auto a : G[node]) {
// If the neighbour is
// not the parent node
if (a != parent) {
// call the function
// for the neighbour
dfs(a, node, check,
current_colour,
colours);
}
}
}
// Function to check whether all the
// nodes in each subtree of the given
// node have same colour
bool checkPossibility(
int root, int* colours)
{
// Initialise the boolean answer
bool ans = true;
// Iterate over the neighbours
// of selected root
for (auto a : G[root]) {
// Initialise the colour
// for this subtree
// as the colour of
// first neighbour
int current_colour = colours[a];
// Variable to check
// condition of same
// colour for each subtree
bool check = true;
// dfs function call
dfs(a, root, check,
current_colour, colours);
// Check if any one subtree
// does not have all
// nodes of same colour
// then ans will become false
ans = ans && check;
}
// Return the answer
return ans;
}
// Function to add edges to the tree
void addedge(int x, int y)
{
// y is added as a neighbour of x
G[x].push_back(y);
// x is added as a neighbour of y
G[y].push_back(x);
}
// Function to find the node
void solve(int* colours, int N)
{
// Initialise root1 as -1
int root1 = -1;
// Initialise root2 as -1
int root2 = -1;
// Find the first two nodes of
// different colour which are adjacent
// to each other
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
for (auto a : G[i]) {
if (colours[a] != colours[i]) {
root1 = a;
root2 = i;
break;
}
}
}
// If no two nodes of different
// colour are found
if (root1 == -1) {
// make any node (say 1)
// as the root
cout << endl
<< "1" << endl;
}
// Check if making root1
// as the root of the
// tree solves the purpose
else if (
checkPossibility(root1, colours)) {
cout << root1 << endl;
}
// check for root2
else if (
checkPossibility(root2, colours)) {
cout << root2 << endl;
}
// otherwise no such root exist
else {
cout << "-1" << endl;
}
}
// Driver code
int32_t main()
{
// Number of nodes
int N = 8;
// add edges
addedge(1, 2);
addedge(1, 3);
addedge(2, 4);
addedge(2, 7);
addedge(3, 5);
addedge(3, 6);
addedge(6, 8);
// Node colours
// 0th node is extra to make
// the array 1 indexed
int colours[9] = { 0, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 2, 1, 3 };
solve(colours, N);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static int NN = (int)(1e5 + 5);
// Vector to store the tree
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
static Vector []G = new Vector[NN];
// Function to perform dfs
static void dfs(int node, int parent,
boolean check,
int current_colour,
int[] colours)
{
// Check is assigned to false if either it
// is already false or the current_colour
// is not same as the node colour
check = check &&
(colours[node] == current_colour);
// Iterate over the neighbours of node
for(int a : G[node])
{
// If the neighbour is
// not the parent node
if (a != parent)
{
// Call the function
// for the neighbour
dfs(a, node, check,
current_colour,
colours);
}
}
}
// Function to check whether all the
// nodes in each subtree of the given
// node have same colour
static boolean checkPossibility(int root,
int[] colours)
{
// Initialise the boolean answer
boolean ans = true;
// Iterate over the neighbours
// of selected root
for(int a : G[root])
{
// Initialise the colour
// for this subtree
// as the colour of
// first neighbour
int current_colour = colours[a];
// Variable to check
// condition of same
// colour for each subtree
boolean check = true;
// dfs function call
dfs(a, root, check,
current_colour, colours);
// Check if any one subtree
// does not have all
// nodes of same colour
// then ans will become false
ans = ans && check;
}
// Return the answer
return ans;
}
// Function to add edges to the tree
static void addedge(int x, int y)
{
// y is added as a neighbour of x
G[x].add(y);
// x is added as a neighbour of y
G[y].add(x);
}
// Function to find the node
static void solve(int[] colours, int N)
{
// Initialise root1 as -1
int root1 = -1;
// Initialise root2 as -1
int root2 = -1;
// Find the first two nodes of
// different colour which are adjacent
// to each other
for(int i = 1; i <= N; i++)
{
for(int a : G[i])
{
if (colours[a] != colours[i])
{
root1 = a;
root2 = i;
break;
}
}
}
// If no two nodes of different
// colour are found
if (root1 == -1)
{
// Make any node (say 1)
// as the root
System.out.println("1" + "\n");
}
// Check if making root1
// as the root of the
// tree solves the purpose
else if (checkPossibility(root1, colours))
{
System.out.print(root1 + "\n");
}
// Check for root2
else if (checkPossibility(root2, colours))
{
System.out.print(root2 + "\n");
}
// Otherwise no such root exist
else
{
System.out.print("-1" + "\n");
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Number of nodes
int N = 8;
for(int i = 0; i < G.length; i++)
G[i] = new Vector();
// Add edges
addedge(1, 2);
addedge(1, 3);
addedge(2, 4);
addedge(2, 7);
addedge(3, 5);
addedge(3, 6);
addedge(6, 8);
// Node colours 0th node is extra
// to make the array 1 indexed
int colours[] = { 0, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 2, 1, 3 };
solve(colours, N);
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach
NN = 1e5 + 5
# Vector to store tree
G = []
for i in range(int(NN)):
G.append([])
# Function to perform dfs
def dfs(node, parent, check,
current_colour, colours):
# Check is assigned to false if
# either it is already false or
# the current_colour is not same
# as the node colour
check[0] = check[0] & (colours[node] ==
current_colour)
# Iterate over the neighbours of node
for a in G[node]:
# If the neighbour is
# not the parent node
if a != parent:
# Call the function
# for the neighbour
dfs(a, node, check,
current_colour, colours)
# Function to check whether all the
# nodes in each subtree of the given
# node have same colour
def checkPossibility(root, colours):
# Initialise the boolean answer
ans = True
for a in G[root]:
# Initialise the colour
# for this subtree
# as the colour of
# first neighbour
current_colour = colours[a]
# Variable to check
# condition of same
# colour for each subtree
check = [True]
# dfs function call
dfs(a, root, check,
current_colour, colours)
# Check if any one subtree
# does not have all
# nodes of same colour
# then ans will become false
ans = ans & check[0]
# Return the ans
return ans
# Function to add edges to the tree
def addedge(x, y):
# y is added as a neighbour of x
G[x].append(y)
# x is added as a neighbour of y
G[y].append(x)
# Function to find the node
def solve(colours, N):
# Initialise the root1 as -1
root1 = -1
# Initialise the root 2 as -1
root2 = -1
# Find the first two nodes of
# different colour which are adjacent
# to each other
for i in range(1, N + 1):
for a in G[i]:
if colours[a] != colours[i]:
root1 = a
root2 = i
break
# If no two nodes of different
# colour are found
if root1 == -1:
# make any node (say 1)
# as the root
print(1)
# Check if making root1
# as the root of the
# tree solves the purpose
elif checkPossibility(root1, colours):
print(root1)
# Check for root2
elif checkPossibility(root2, colours):
print(root2)
# Otherwise no such root exist
else:
print(-1)
# Driver code
# Number of nodes
N = 8
# add edges
addedge(1, 2)
addedge(1, 3)
addedge(2, 4)
addedge(2, 7)
addedge(3, 5)
addedge(3, 6)
addedge(6, 8)
# Node colours
# 0th node is extra to make
# the array 1 indexed
colours = [ 0, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 2, 1, 3 ]
solve(colours, N)
# This code is contributed by Stuti PathakC#
// C# program for the above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
static int NN = (int)(1e5 + 5);
// List to store the tree
static List[] G = new List[ NN ];
// Function to perform dfs
static void dfs(int node, int parent, bool check,
int current_colour, int[] colours)
{
// Check is assigned to false if either it
// is already false or the current_colour
// is not same as the node colour
check = check && (colours[node] == current_colour);
// Iterate over the neighbours of node
foreach(int a in G[node])
{
// If the neighbour is
// not the parent node
if (a != parent)
{
// Call the function
// for the neighbour
dfs(a, node, check,
current_colour, colours);
}
}
}
// Function to check whether all the
// nodes in each subtree of the given
// node have same colour
static bool checkPossibility(int root, int[] colours)
{
// Initialise the bool answer
bool ans = true;
// Iterate over the neighbours
// of selected root
foreach(int a in G[root])
{
// Initialise the colour
// for this subtree
// as the colour of
// first neighbour
int current_colour = colours[a];
// Variable to check
// condition of same
// colour for each subtree
bool check = true;
// dfs function call
dfs(a, root, check, current_colour, colours);
// Check if any one subtree
// does not have all
// nodes of same colour
// then ans will become false
ans = ans && check;
}
// Return the answer
return ans;
}
// Function to add edges to the tree
static void addedge(int x, int y)
{
// y is added as a neighbour of x
G[x].Add(y);
// x is added as a neighbour of y
G[y].Add(x);
}
// Function to find the node
static void solve(int[] colours, int N)
{
// Initialise root1 as -1
int root1 = -1;
// Initialise root2 as -1
int root2 = -1;
// Find the first two nodes of
// different colour which are adjacent
// to each other
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++)
{
foreach(int a in G[i])
{
if (colours[a] != colours[i])
{
root1 = a;
root2 = i;
break;
}
}
}
// If no two nodes of different
// colour are found
if (root1 == -1)
{
// Make any node (say 1)
// as the root
Console.WriteLine("1" + "\n");
}
// Check if making root1
// as the root of the
// tree solves the purpose
else if (checkPossibility(root1, colours))
{
Console.Write(root1 + "\n");
}
// Check for root2
else if (checkPossibility(root2, colours))
{
Console.Write(root2 + "\n");
}
// Otherwise no such root exist
else
{
Console.Write("-1" + "\n");
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Number of nodes
int N = 8;
for (int i = 0; i < G.Length; i++)
G[i] = new List();
// Add edges
addedge(1, 2);
addedge(1, 3);
addedge(2, 4);
addedge(2, 7);
addedge(3, 5);
addedge(3, 6);
addedge(6, 8);
// Node colours 0th node is extra
// to make the array 1 indexed
int[] colours = {0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 1, 3};
solve(colours, N);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji 6
时间复杂度: O(N) 在哪里 N 是树中的节点数。
辅助空间: O(1)
如果您想与行业专家一起参加直播课程,请参阅Geeks Classes Live