找到要从树中删除的边以最大化组件的 XOR 乘积
给定一棵以节点0为根的N个节点的树,以及一个表示每个节点的值的数组val[] ,任务是在从树中删除一条边和边后找到连通分量的 XOR 的最大可能乘积被删除。
注意:如果有多个边给出最大值,则以任何顺序打印它们。
例子:
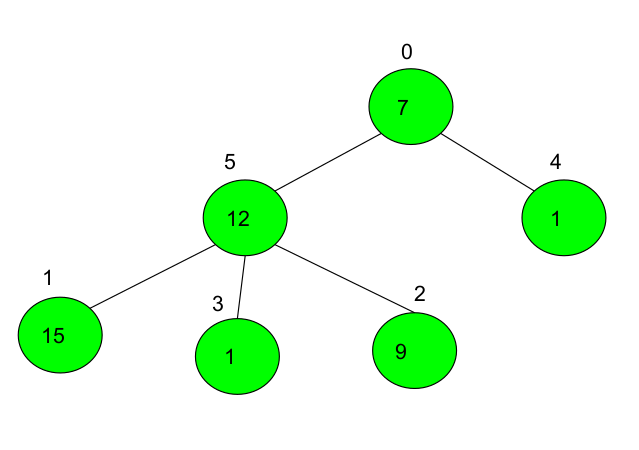
Input: edges[][] = { {0, 5}, {0, 4}, {5, 1}, {5, 3}, {5, 2} }, val[ ] = { 7, 15, 9, 1, 1, 12}
Output: max_xor_product = 66
Edges: {0, 5}
Explanation: If we delete an edge {0, 5} then the tree will divide into two components.
The XOR of the first component is (1^7) = 6.
And the XOR of the second component is ( 12^15^1^9) = 11.
The product of xor of those components is ( 6*11) = 66.
Similarly, if we delete an edge { 5, 1} tree again divide into two-component.
The XOR of the first component is ( 15 ) ( because it has only one node)
and XOR of the second component is ( 7^1^12^9^1) = 2.
And the product of XOR of those components is ( 15 * 2 ) = 30.
If this is repeated the maximum value of the product of XOR of components will be 66,
which can be achieved if we delete the edge {0, 5}.
See the image below to understand it better
Input: edges[][] = { {0, 1}, {0, 2}}, val[ ]={ 17, 17, 17}
Output: max_xor_product = 0
Edges: {{0, 1}, {0, 2}}
朴素方法:删除每条边并遍历组件,并对这些组件中的节点的值进行异或,然后做异或的乘积,存储最大值和与该值对应的边。
时间复杂度: O(N*N)
辅助空间: O(N)
有效方法:这个问题可以通过 预先计算每个节点的子树的 XOR 并使用按位 XOR 属性,如下所示:
If an edge of a tree is deleted, then the tree will always divide into two components. The XOR of one component will be same as the XOR of the subtree (say X) and the other component will have XOR = (total XOR of all nodes ^ X).
For each edge, consider it to be removed and then find the XOR of both the components (using above observation) and their product. Keep track of the maximum and removing which edge results in that.
请按照下图所示进行更好的理解。
插图:
Consider the first example given below
edges[][] = { {0, 5}, {0, 4}, {5, 1}, {5, 3}, {5, 2} }, val[ ] = { 7, 15, 9, 1, 1, 12}
Remove edge {0, 4}:
=> Two components are {1} and {7, 12, 15, 1, 9}
=> XOR values are 1 and 12
=> Product = 1*12 = 12
Remove edge {0, 5}:
=> Two components are {1, 7} and {12, 15, 1, 9}
=> XOR values are 6 and 11
=> Product = 6*11 = 66
Remove edge {5, 1}:
=> Two components are {1, 7, 12, 1, 9} and {15}
=> XOR values are 2 and 15
=> Product = 2*15 = 30
Remove edge {5, 2}:
=> Two components are {1, 7, 12, 15, 1} and {9}
=> XOR values are 4 and 9
=> Product = 4*9 = 36
Remove edge {5, 3}:
=> Two components are {1, 7, 12, 15, 9} and {1}
=> XOR values are 1 and 12
=> Product = 1*12 = 12
So the maximum value is 66 which is achieved when the edge {0, 5} is removed
请按照以下步骤解决此问题:
- 计算所有树节点的所有给定值的异或(比如tot_xor )
- 创建一个数组(比如subtree_xor[] )并使用 DFS 存储第 i 个节点的子树的按位异或。
- 现在使用 DFS 遍历树并针对每个节点:
- 考虑当前节点与其父节点之间的边被删除。
- 这两个组件将是:当前节点及其子树和树的剩余部分。
- 如上述观察中所述,计算当前节点及其子树和剩余树的按位异或。
- 求 XOR 值的乘积。
- 相应地更新最大值并移除边缘。
- 返回最大值和删除的边缘。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ code to implement the approach
#include
using namespace std;
const int mxx = 1e6 + 7;
int subtree_xor[mxx];
unordered_map > >
store;
// To add edges in tree
void addEdge(vector tree[], int u, int v)
{
tree[u].push_back(v);
tree[v].push_back(u);
}
// To precompute xor value of each subtree
void dfs(vector tree[], int val[],
int cur_node, int par)
{
// assign value of current node
subtree_xor[cur_node] = val[cur_node];
for (auto& child : tree[cur_node]) {
if (child == par)
continue;
dfs(tree, val, child, cur_node);
// take xor of all child node
subtree_xor[cur_node]
^= subtree_xor[child];
}
}
// To store all xor_product
// and it's corresponding edges
void store_xor_product(vector tree[],
int cur_node,
int par, int tot_xor)
{
for (auto& child : tree[cur_node]) {
if (child == par)
continue;
// Xor of first component
int first_comp_xor
= subtree_xor[child];
// Xor of second component
int second_comp_xor
= tot_xor ^ first_comp_xor;
// Product can exceed int range
// so store it in long long data type
long long xor_product
= first_comp_xor * 1LL
* second_comp_xor;
// Store edges corresponding
// to its product
store[xor_product].push_back({ cur_node,
child });
store_xor_product(tree, child,
cur_node, tot_xor);
}
}
// To print edges corresponding
// to max_xor_product of components
void print_edges(long long mx_product)
{
for (auto edges : store[mx_product]) {
cout << edges.first << " "
<< edges.second << "\n";
}
}
// Driver code
int findVal(int N, int val[],
vector >& edges)
{
int tot_xor = 0;
// Store the xor of all values
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
tot_xor ^= val[i];
vector tree[N];
// Create a tree from given edges
for (int i = 0; i < N - 1; i++)
addEdge(tree, edges[i][0],
edges[i][1]);
// Dfs travel to store subtree xor
dfs(tree, val, 0, -1);
// To store edges corresponding
// to xor_product
store_xor_product(tree, 0, -1, tot_xor);
// Find maximum xor_product
long long mx_product = -1;
for (auto ele : store) {
long long cur_product = ele.first;
mx_product
= max(mx_product, cur_product);
}
return mx_product;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int N = 6;
vector > edges = {
{ 0, 5 }, { 0, 4 }, { 5, 1 }, { 5, 3 }, { 5, 2 }
};
int val[] = { 7, 15, 9, 1, 1, 12 };
int mx_product = findVal(N, val, edges);
cout << mx_product << "\n";
// To print edges corresponding
// to maximum xor_product
print_edges(mx_product);
return 0;
} 66
0 5时间复杂度:O(N)
辅助空间:O(N)