给定一个数组A [] ,该数组由0、1和2组成。任务是编写一个对给定数组进行排序的函数。函数应将全0放在最前面,然后将全1放在最后,并将全2放在最后。
例子:
Input: {0, 1, 2, 0, 1, 2}
Output: {0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 2}
Input: {0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 2, 1, 2, 0, 0, 0, 1}
Output: {0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2}在这篇文章(对0、1、2和2的数组进行排序(简单计数))中讨论了一种简单的解决方案。
方法1
- 方法:该问题类似于我们的旧帖子将数组0和1分开,并且这两个问题都是著名的荷兰国旗问题的变体。
问题是由三种颜色构成的,这里是“ 0”,“ 1”和“ 2”。该数组分为四个部分:- a [1..Lo-1]零(红色)
- a [Lo..Mid-1]个(白色)
- 一个[Mid..Hi]未知
- a [Hi + 1..N]两位(蓝色)
- 如果第ith个元素为0,则将该元素交换到较低范围,从而缩小未知范围。
- 同样,如果元素为1,则保持原样,但缩小未知范围。
- 如果元素为2,则将其与高范围的元素交换。
- 算法:
- 保持三个索引为低= 1,中= 1和高= N,并且有四个范围,从1到低(包含0的范围),低到中(包含1的范围),中到高(包含未知元素的范围)和高到N(包含2的范围)。
- 从头到尾遍历数组,中间值不高。 (循环计数器是i)
- 如果元素为0,则将其与索引为低的元素交换,并更新low = low + 1和mid = mid + 1
- 如果元素为1,则更新mid = mid + 1
- 如果元素为2,则将其与索引为高的元素交换,并更新high = high – 1并更新i = i –1。因为未处理交换的元素
- 打印输出数组。
- 空运行:
在此过程的一部分过程中,一些红色,白色和蓝色元素是已知的,并且位于“正确的”位置。通过检查a [Mid]缩小未知元素部分a [Mid..Hi]:
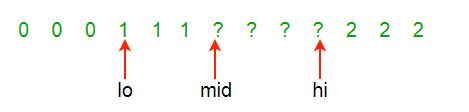
Examine a[Mid]. There are three possibilities:
a[Mid] is (0) red, (1) white or (2) blue.
Case (0) a[Mid] is red, swap a[Lo] and a[Mid]; Lo++; Mid++
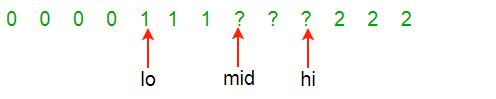
Case (1) a[Mid] is white, Mid++
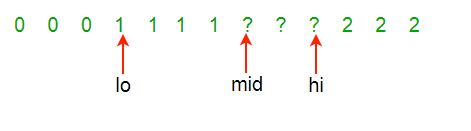
Case (2) a[Mid] is blue, swap a[Mid] and a[Hi]; Hi–
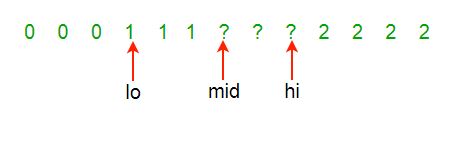
Continue until Mid>Hi.
- 执行:
C++
// C++ program to sort an array
// with 0, 1 and 2 in a single pass
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to sort the input array,
// the array is assumed
// to have values in {0, 1, 2}
void sort012(int a[], int arr_size)
{
int lo = 0;
int hi = arr_size - 1;
int mid = 0;
// Iterate till all the elements
// are sorted
while (mid <= hi) {
switch (a[mid]) {
// If the element is 0
case 0:
swap(a[lo++], a[mid++]);
break;
// If the element is 1 .
case 1:
mid++;
break;
// If the element is 2
case 2:
swap(a[mid], a[hi--]);
break;
}
}
}
// Function to print array arr[]
void printArray(int arr[], int arr_size)
{
// Iterate and print every element
for (int i = 0; i < arr_size; i++)
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 2, 1, 2, 0, 0, 0, 1 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
sort012(arr, n);
cout << "array after segregation ";
printArray(arr, n);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Shivi_Aggarwal C
// C program to sort an array with 0, 1 and 2
// in a single pass
#include
/* Function to swap *a and *b */
void swap(int* a, int* b);
// Sort the input array, the array is assumed to
// have values in {0, 1, 2}
void sort012(int a[], int arr_size)
{
int lo = 0;
int hi = arr_size - 1;
int mid = 0;
while (mid <= hi) {
switch (a[mid]) {
case 0:
swap(&a[lo++], &a[mid++]);
break;
case 1:
mid++;
break;
case 2:
swap(&a[mid], &a[hi--]);
break;
}
}
}
/* UTILITY FUNCTIONS */
void swap(int* a, int* b)
{
int temp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = temp;
}
/* Utility function to print array arr[] */
void printArray(int arr[], int arr_size)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < arr_size; i++)
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
printf("n");
}
/* driver program to test */
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 2, 1, 2, 0, 0, 0, 1 };
int arr_size = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int i;
sort012(arr, arr_size);
printf("array after segregation ");
printArray(arr, arr_size);
getchar();
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to sort an array of 0, 1 and 2
import java.io.*;
class countzot {
// Sort the input array, the array is assumed to
// have values in {0, 1, 2}
static void sort012(int a[], int arr_size)
{
int lo = 0;
int hi = arr_size - 1;
int mid = 0, temp = 0;
while (mid <= hi) {
switch (a[mid]) {
case 0: {
temp = a[lo];
a[lo] = a[mid];
a[mid] = temp;
lo++;
mid++;
break;
}
case 1:
mid++;
break;
case 2: {
temp = a[mid];
a[mid] = a[hi];
a[hi] = temp;
hi--;
break;
}
}
}
}
/* Utility function to print array arr[] */
static void printArray(int arr[], int arr_size)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < arr_size; i++)
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
System.out.println("");
}
/*Driver function to check for above functions*/
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 2, 1, 2, 0, 0, 0, 1 };
int arr_size = arr.length;
sort012(arr, arr_size);
System.out.println("Array after seggregation ");
printArray(arr, arr_size);
}
}
/*This code is contributed by Devesh Agrawal*/Python
# Python program to sort an array with
# 0, 1 and 2 in a single pass
# Function to sort array
def sort012( a, arr_size):
lo = 0
hi = arr_size - 1
mid = 0
while mid <= hi:
if a[mid] == 0:
a[lo], a[mid] = a[mid], a[lo]
lo = lo + 1
mid = mid + 1
elif a[mid] == 1:
mid = mid + 1
else:
a[mid], a[hi] = a[hi], a[mid]
hi = hi - 1
return a
# Function to print array
def printArray( a):
for k in a:
print k,
# Driver Program
arr = [0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 2, 1, 2, 0, 0, 0, 1]
arr_size = len(arr)
arr = sort012( arr, arr_size)
print "Array after segregation :\n",
printArray(arr)
# Contributed by Harshit AgrawalC#
// C# program to sort an
// array of 0, 1 and 2
using System;
class GFG {
// Sort the input array, the array is assumed to
// have values in {0, 1, 2}
static void sort012(int[] a, int arr_size)
{
int lo = 0;
int hi = arr_size - 1;
int mid = 0, temp = 0;
while (mid <= hi) {
switch (a[mid]) {
case 0: {
temp = a[lo];
a[lo] = a[mid];
a[mid] = temp;
lo++;
mid++;
break;
}
case 1:
mid++;
break;
case 2: {
temp = a[mid];
a[mid] = a[hi];
a[hi] = temp;
hi--;
break;
}
}
}
}
/* Utility function to print array arr[] */
static void printArray(int[] arr, int arr_size)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < arr_size; i++)
Console.Write(arr[i] + " ");
Console.WriteLine("");
}
/*Driver function to check for above functions*/
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr = { 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 2, 1, 2, 0, 0, 0, 1 };
int arr_size = arr.Length;
sort012(arr, arr_size);
Console.Write("Array after seggregation ");
printArray(arr, arr_size);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Sam007PHP
Javascript
C++
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Utility function to print the contents of an array
void printArr(int arr[], int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
// Function to sort the array of 0s, 1s and 2s
void sortArr(int arr[], int n)
{
int i, cnt0 = 0, cnt1 = 0, cnt2 = 0;
// Count the number of 0s, 1s and 2s in the array
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
switch (arr[i]) {
case 0:
cnt0++;
break;
case 1:
cnt1++;
break;
case 2:
cnt2++;
break;
}
}
// Update the array
i = 0;
// Store all the 0s in the beginning
while (cnt0 > 0) {
arr[i++] = 0;
cnt0--;
}
// Then all the 1s
while (cnt1 > 0) {
arr[i++] = 1;
cnt1--;
}
// Finally all the 2s
while (cnt2 > 0) {
arr[i++] = 2;
cnt2--;
}
// Print the sorted array
printArr(arr, n);
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 2, 1, 2, 0, 0, 0, 1 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(int);
sortArr(arr, n);
return 0;
} Java
// Java implementation of the approach
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
// Utility function to print the contents of an array
static void printArr(int arr[], int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
// Function to sort the array of 0s, 1s and 2s
static void sortArr(int arr[], int n)
{
int i, cnt0 = 0, cnt1 = 0, cnt2 = 0;
// Count the number of 0s, 1s and 2s in the array
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
switch (arr[i]) {
case 0:
cnt0++;
break;
case 1:
cnt1++;
break;
case 2:
cnt2++;
break;
}
}
// Update the array
i = 0;
// Store all the 0s in the beginning
while (cnt0 > 0) {
arr[i++] = 0;
cnt0--;
}
// Then all the 1s
while (cnt1 > 0) {
arr[i++] = 1;
cnt1--;
}
// Finally all the 2s
while (cnt2 > 0) {
arr[i++] = 2;
cnt2--;
}
// Print the sorted array
printArr(arr, n);
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 2, 1, 2, 0, 0, 0, 1 };
int n = arr.length;
sortArr(arr, n);
}
}
// This code is contributed by shubhamsingh10Python
# Python implementation of the approach
# Utility function to print contents of an array
def printArr(arr, n):
for i in range(n):
print(arr[i],end=" ")
# Function to sort the array of 0s, 1s and 2s
def sortArr(arr, n):
cnt0 = 0
cnt1 = 0
cnt2 = 0
# Count the number of 0s, 1s and 2s in the array
for i in range(n):
if arr[i] == 0:
cnt0+=1
elif arr[i] == 1:
cnt1+=1
elif arr[i] == 2:
cnt2+=1
# Update the array
i = 0
# Store all the 0s in the beginning
while (cnt0 > 0):
arr[i] = 0
i+=1
cnt0-=1
# Then all the 1s
while (cnt1 > 0):
arr[i] = 1
i+=1
cnt1-=1
# Finally all the 2s
while (cnt2 > 0):
arr[i] = 2
i+=1
cnt2-=1
# Prthe sorted array
printArr(arr, n)
# Driver code
arr = [0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 2, 1, 2, 0, 0, 0, 1]
n = len(arr)
sortArr(arr, n)
#This code is contributed by shubhamsingh10C#
// C# implementation of the approach
using System;
class GFG {
// Utility function to print the contents of an array
static void printArr(int[] arr, int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
Console.Write(arr[i] + " ");
}
// Function to sort the array of 0s, 1s and 2s
static void sortArr(int[] arr, int n)
{
int i, cnt0 = 0, cnt1 = 0, cnt2 = 0;
// Count the number of 0s, 1s and 2s in the array
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
switch (arr[i]) {
case 0:
cnt0++;
break;
case 1:
cnt1++;
break;
case 2:
cnt2++;
break;
}
}
// Update the array
i = 0;
// Store all the 0s in the beginning
while (cnt0 > 0) {
arr[i++] = 0;
cnt0--;
}
// Then all the 1s
while (cnt1 > 0) {
arr[i++] = 1;
cnt1--;
}
// Finally all the 2s
while (cnt2 > 0) {
arr[i++] = 2;
cnt2--;
}
// Print the sorted array
printArr(arr, n);
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr = { 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 2, 1, 2, 0, 0, 0, 1 };
int n = arr.Length;
sortArr(arr, n);
}
}
// This code is contributed by shubhamsingh10Javascript
- 输出:
array after segregation
0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 - 复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O(n)。
只需要遍历数组一次。 - 空间复杂度: O(1)。
不需要额外的空间。 - 方法:计算给定数组中0、1、2的数量。然后在开始时存储所有0,然后存储所有1,然后存储所有2。
- 算法:
- 保持三个计数器c0计数0s,c1计数1s,c2计数2s
- 遍历数组并增加c0的数量是0,增加c1的数量是1,增加c2的数量是2
- 现在再次遍历数组,将第一个c0元素替换为0,将下一个c1元素替换为1,将下一个c2元素替换为2。
- 执行:
- 时间复杂度: O(n)。
C++
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Utility function to print the contents of an array
void printArr(int arr[], int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
// Function to sort the array of 0s, 1s and 2s
void sortArr(int arr[], int n)
{
int i, cnt0 = 0, cnt1 = 0, cnt2 = 0;
// Count the number of 0s, 1s and 2s in the array
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
switch (arr[i]) {
case 0:
cnt0++;
break;
case 1:
cnt1++;
break;
case 2:
cnt2++;
break;
}
}
// Update the array
i = 0;
// Store all the 0s in the beginning
while (cnt0 > 0) {
arr[i++] = 0;
cnt0--;
}
// Then all the 1s
while (cnt1 > 0) {
arr[i++] = 1;
cnt1--;
}
// Finally all the 2s
while (cnt2 > 0) {
arr[i++] = 2;
cnt2--;
}
// Print the sorted array
printArr(arr, n);
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 2, 1, 2, 0, 0, 0, 1 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(int);
sortArr(arr, n);
return 0;
}
Java
// Java implementation of the approach
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
// Utility function to print the contents of an array
static void printArr(int arr[], int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
// Function to sort the array of 0s, 1s and 2s
static void sortArr(int arr[], int n)
{
int i, cnt0 = 0, cnt1 = 0, cnt2 = 0;
// Count the number of 0s, 1s and 2s in the array
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
switch (arr[i]) {
case 0:
cnt0++;
break;
case 1:
cnt1++;
break;
case 2:
cnt2++;
break;
}
}
// Update the array
i = 0;
// Store all the 0s in the beginning
while (cnt0 > 0) {
arr[i++] = 0;
cnt0--;
}
// Then all the 1s
while (cnt1 > 0) {
arr[i++] = 1;
cnt1--;
}
// Finally all the 2s
while (cnt2 > 0) {
arr[i++] = 2;
cnt2--;
}
// Print the sorted array
printArr(arr, n);
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 2, 1, 2, 0, 0, 0, 1 };
int n = arr.length;
sortArr(arr, n);
}
}
// This code is contributed by shubhamsingh10
Python
# Python implementation of the approach
# Utility function to print contents of an array
def printArr(arr, n):
for i in range(n):
print(arr[i],end=" ")
# Function to sort the array of 0s, 1s and 2s
def sortArr(arr, n):
cnt0 = 0
cnt1 = 0
cnt2 = 0
# Count the number of 0s, 1s and 2s in the array
for i in range(n):
if arr[i] == 0:
cnt0+=1
elif arr[i] == 1:
cnt1+=1
elif arr[i] == 2:
cnt2+=1
# Update the array
i = 0
# Store all the 0s in the beginning
while (cnt0 > 0):
arr[i] = 0
i+=1
cnt0-=1
# Then all the 1s
while (cnt1 > 0):
arr[i] = 1
i+=1
cnt1-=1
# Finally all the 2s
while (cnt2 > 0):
arr[i] = 2
i+=1
cnt2-=1
# Prthe sorted array
printArr(arr, n)
# Driver code
arr = [0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 2, 1, 2, 0, 0, 0, 1]
n = len(arr)
sortArr(arr, n)
#This code is contributed by shubhamsingh10
C#
// C# implementation of the approach
using System;
class GFG {
// Utility function to print the contents of an array
static void printArr(int[] arr, int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
Console.Write(arr[i] + " ");
}
// Function to sort the array of 0s, 1s and 2s
static void sortArr(int[] arr, int n)
{
int i, cnt0 = 0, cnt1 = 0, cnt2 = 0;
// Count the number of 0s, 1s and 2s in the array
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
switch (arr[i]) {
case 0:
cnt0++;
break;
case 1:
cnt1++;
break;
case 2:
cnt2++;
break;
}
}
// Update the array
i = 0;
// Store all the 0s in the beginning
while (cnt0 > 0) {
arr[i++] = 0;
cnt0--;
}
// Then all the 1s
while (cnt1 > 0) {
arr[i++] = 1;
cnt1--;
}
// Finally all the 2s
while (cnt2 > 0) {
arr[i++] = 2;
cnt2--;
}
// Print the sorted array
printArr(arr, n);
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr = { 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 2, 1, 2, 0, 0, 0, 1 };
int n = arr.Length;
sortArr(arr, n);
}
}
// This code is contributed by shubhamsingh10
Java脚本
输出:
0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 2 2- 复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O(n)。
仅需要两次遍历数组。 - 空间复杂度: O(1)。
由于不需要额外的空间。
- 时间复杂度: O(n)。