具有相同数量的 1 和 0 的最大子树
给定一棵树,每个节点的值都是0或1 ,任务是找到给定树中具有相等数量 0 和 1 的子树的最大大小,如果不存在这样的子树,则打印-1 .
例子:
Input:
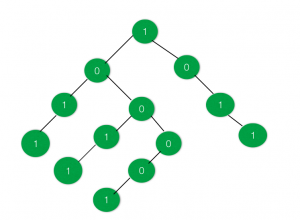
Output: 6
Input:
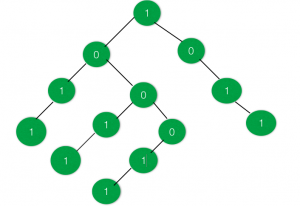
Output: -1
方法:
- 将树的所有节点更改为0到-1 。现在问题被简化为找到其节点为0的子树和的最大大小。
- 更新树的所有节点,使它们代表以当前节点为根的子树中所有节点的总和。
- 现在找到以值为0的节点为根的最大子树的大小。如果没有找到这样的节点,则打印-1
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include
using namespace std;
// To store the size of the maximum sub-tree
// with equal number of 0's and 1's
int maxSize = -1;
// Represents a node of the tree
struct node {
int data;
struct node *right, *left;
};
// To create a new node
struct node* newnode(int key)
{
struct node* temp = new node;
temp->data = key;
temp->right = NULL;
temp->left = NULL;
return temp;
}
// Function to perform inorder traversal on
// the tree and print the nodes in that order
void inorder(struct node* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
inorder(root->left);
cout << root->data << endl;
inorder(root->right);
}
// Function to return the maximum size of
// the sub-tree having equal number of 0's and 1's
int maxsize(struct node* root)
{
int a = 0, b = 0;
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
// Max size in the right sub-tree
a = maxsize(root->right);
// 1 is added for the parent
a = a + 1;
// Max size in the left sub-tree
b = maxsize(root->left);
// Total size of the tree
// rooted at the current node
a = b + a;
// If the current tree has equal
// number of 0's and 1's
if (root->data == 0)
// If the total size exceeds
// the current max
if (a >= maxSize)
maxSize = a;
return a;
}
// Function to update and return the sum
// of all the tree nodes rooted at
// the passed node
int sum_tree(struct node* root)
{
if (root != NULL)
// If current node's value is 0
// then update it to -1
if (root->data == 0)
root->data = -1;
int a = 0, b = 0;
// If left child exists
if (root->left != NULL)
a = sum_tree(root->left);
// If right child exists
if (root->right != NULL)
b = sum_tree(root->right);
root->data += (a + b);
return root->data;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
struct node* root = newnode(1);
root->right = newnode(0);
root->right->right = newnode(1);
root->right->right->right = newnode(1);
root->left = newnode(0);
root->left->left = newnode(1);
root->left->left->left = newnode(1);
root->left->right = newnode(0);
root->left->right->left = newnode(1);
root->left->right->left->left = newnode(1);
root->left->right->right = newnode(0);
root->left->right->right->left = newnode(0);
root->left->right->right->left->left = newnode(1);
sum_tree(root);
maxsize(root);
cout << maxSize;
return 0;
} Java
// Java implementation of the approach
class GFG
{
// To store the size of the maximum sub-tree
// with equal number of 0's and 1's
static int maxSize = -1;
// Represents a node of the tree
static class node
{
int data;
node right, left;
};
// To create a new node
static node newnode(int key)
{
node temp = new node();
temp.data = key;
temp.right = null;
temp.left = null;
return temp;
}
// Function to perform inorder traversal on
// the tree and print the nodes in that order
static void inorder(node root)
{
if (root == null)
return;
inorder(root.left);
System.out.print(root.data +"\n");
inorder(root.right);
}
// Function to return the maximum size of
// the sub-tree having equal number of 0's and 1's
static int maxsize(node root)
{
int a = 0, b = 0;
if (root == null)
return 0;
// Max size in the right sub-tree
a = maxsize(root.right);
// 1 is added for the parent
a = a + 1;
// Max size in the left sub-tree
b = maxsize(root.left);
// Total size of the tree
// rooted at the current node
a = b + a;
// If the current tree has equal
// number of 0's and 1's
if (root.data == 0)
// If the total size exceeds
// the current max
if (a >= maxSize)
maxSize = a;
return a;
}
// Function to update and return the sum
// of all the tree nodes rooted at
// the passed node
static int sum_tree(node root)
{
if (root != null)
// If current node's value is 0
// then update it to -1
if (root.data == 0)
root.data = -1;
int a = 0, b = 0;
// If left child exists
if (root.left != null)
a = sum_tree(root.left);
// If right child exists
if (root.right != null)
b = sum_tree(root.right);
root.data += (a + b);
return root.data;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
node root = newnode(1);
root.right = newnode(0);
root.right.right = newnode(1);
root.right.right.right = newnode(1);
root.left = newnode(0);
root.left.left = newnode(1);
root.left.left.left = newnode(1);
root.left.right = newnode(0);
root.left.right.left = newnode(1);
root.left.right.left.left = newnode(1);
root.left.right.right = newnode(0);
root.left.right.right.left = newnode(0);
root.left.right.right.left.left = newnode(1);
sum_tree(root);
maxsize(root);
System.out.print(maxSize);
}
}
// This code is contributed by PrinciRaj1992C#
// C# implementation of the approach
using System;
class GFG
{
// To store the size of the maximum sub-tree
// with equal number of 0's and 1's
static int maxSize = -1;
// Represents a node of the tree
public class node
{
public int data;
public node right, left;
};
// To create a new node
static node newnode(int key)
{
node temp = new node();
temp.data = key;
temp.right = null;
temp.left = null;
return temp;
}
// Function to perform inorder traversal on
// the tree and print the nodes in that order
static void inorder(node root)
{
if (root == null)
return;
inorder(root.left);
Console.Write(root.data +"\n");
inorder(root.right);
}
// Function to return the maximum size of
// the sub-tree having equal number of 0's and 1's
static int maxsize(node root)
{
int a = 0, b = 0;
if (root == null)
return 0;
// Max size in the right sub-tree
a = maxsize(root.right);
// 1 is added for the parent
a = a + 1;
// Max size in the left sub-tree
b = maxsize(root.left);
// Total size of the tree
// rooted at the current node
a = b + a;
// If the current tree has equal
// number of 0's and 1's
if (root.data == 0)
// If the total size exceeds
// the current max
if (a >= maxSize)
maxSize = a;
return a;
}
// Function to update and return the sum
// of all the tree nodes rooted at
// the passed node
static int sum_tree(node root)
{
if (root != null)
// If current node's value is 0
// then update it to -1
if (root.data == 0)
root.data = -1;
int a = 0, b = 0;
// If left child exists
if (root.left != null)
a = sum_tree(root.left);
// If right child exists
if (root.right != null)
b = sum_tree(root.right);
root.data += (a + b);
return root.data;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
node root = newnode(1);
root.right = newnode(0);
root.right.right = newnode(1);
root.right.right.right = newnode(1);
root.left = newnode(0);
root.left.left = newnode(1);
root.left.left.left = newnode(1);
root.left.right = newnode(0);
root.left.right.left = newnode(1);
root.left.right.left.left = newnode(1);
root.left.right.right = newnode(0);
root.left.right.right.left = newnode(0);
root.left.right.right.left.left = newnode(1);
sum_tree(root);
maxsize(root);
Console.Write(maxSize);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-JiJavascript
输出:
6