先决条件:高斯消除法求解线性方程组
简介: Gauss-Jordan方法,也称为Gauss-Jordan消除方法,用于求解线性方程组,是Gauss Elimination Method的改进版本。
它与高斯消除方法相似且更简单,因为我们必须在高斯消除方法中执行两个不同的过程,即
1)形成上三角矩阵,以及
2)换人
但是在高斯-乔丹消除法的情况下,我们只需要形成简化的行梯形形式(对角矩阵)。下图是高斯-乔丹消除法的流程图。
高斯-乔丹消除方法流程图: 
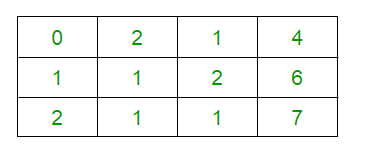
例子 :
Input : 2y + z = 4
x + y + 2z = 6
2x + y + z = 7
Output :
Final Augumented Matrix is :
1 0 0 2.2
0 2 0 2.8
0 0 -2.5 -3
Result is : 2.2 1.4 1.2
说明:下面给出的是上述示例的说明。
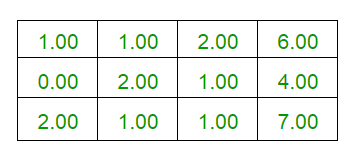
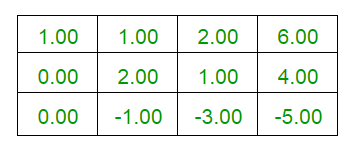
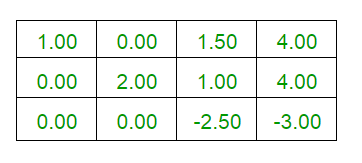


C++
// C++ Implementation for Gauss-Jordan
// Elimination Method
#include
using namespace std;
#define M 10
// Function to print the matrix
void PrintMatrix(float a[][M], int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= n; j++)
cout << a[i][j] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
}
// function to reduce matrix to reduced
// row echelon form.
int PerformOperation(float a[][M], int n)
{
int i, j, k = 0, c, flag = 0, m = 0;
float pro = 0;
// Performing elementary operations
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (a[i][i] == 0)
{
c = 1;
while ((i + c) < n && a[i + c][i] == 0)
c++;
if ((i + c) == n) {
flag = 1;
break;
}
for (j = i, k = 0; k <= n; k++)
swap(a[j][k], a[j+c][k]);
}
for (j = 0; j < n; j++) {
// Excluding all i == j
if (i != j) {
// Converting Matrix to reduced row
// echelon form(diagonal matrix)
float pro = a[j][i] / a[i][i];
for (k = 0; k <= n; k++)
a[j][k] = a[j][k] - (a[i][k]) * pro;
}
}
}
return flag;
}
// Function to print the desired result
// if unique solutions exists, otherwise
// prints no solution or infinite solutions
// depending upon the input given.
void PrintResult(float a[][M], int n, int flag)
{
cout << "Result is : ";
if (flag == 2)
cout << "Infinite Solutions Exists" << endl;
else if (flag == 3)
cout << "No Solution Exists" << endl;
// Printing the solution by dividing constants by
// their respective diagonal elements
else {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << a[i][n] / a[i][i] << " ";
}
}
// To check whether infinite solutions
// exists or no solution exists
int CheckConsistency(float a[][M], int n, int flag)
{
int i, j;
float sum;
// flag == 2 for infinite solution
// flag == 3 for No solution
flag = 3;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
sum = 0;
for (j = 0; j < n; j++)
sum = sum + a[i][j];
if (sum == a[i][j])
flag = 2;
}
return flag;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
float a[M][M] = {{ 0, 2, 1, 4 },
{ 1, 1, 2, 6 },
{ 2, 1, 1, 7 }};
// Order of Matrix(n)
int n = 3, flag = 0;
// Performing Matrix transformation
flag = PerformOperation(a, n);
if (flag == 1)
flag = CheckConsistency(a, n, flag);
// Printing Final Matrix
cout << "Final Augumented Matrix is : " << endl;
PrintMatrix(a, n);
cout << endl;
// Printing Solutions(if exist)
PrintResult(a, n, flag);
return 0;
} Java
// Java Implementation for Gauss-Jordan
// Elimination Method
class GFG {
static int M = 10;
// Function to print the matrix
static void PrintMatrix(float a[][], int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j <= n; j++)
System.out.print(a[i][j] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
// function to reduce matrix to reduced
// row echelon form.
static int PerformOperation(float a[][], int n)
{
int i, j, k = 0, c, flag = 0, m = 0;
float pro = 0;
// Performing elementary operations
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (a[i][i] == 0)
{
c = 1;
while ((i + c) < n && a[i + c][i] == 0)
c++;
if ((i + c) == n)
{
flag = 1;
break;
}
for (j = i, k = 0; k <= n; k++)
{
float temp =a[j][k];
a[j][k] = a[j+c][k];
a[j+c][k] = temp;
}
}
for (j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
// Excluding all i == j
if (i != j)
{
// Converting Matrix to reduced row
// echelon form(diagonal matrix)
float p = a[j][i] / a[i][i];
for (k = 0; k <= n; k++)
a[j][k] = a[j][k] - (a[i][k]) * p;
}
}
}
return flag;
}
// Function to print the desired result
// if unique solutions exists, otherwise
// prints no solution or infinite solutions
// depending upon the input given.
static void PrintResult(float a[][], int n, int flag)
{
System.out.print("Result is : ");
if (flag == 2)
System.out.println("Infinite Solutions Exists");
else if (flag == 3)
System.out.println("No Solution Exists");
// Printing the solution by dividing constants by
// their respective diagonal elements
else {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
System.out.print(a[i][n] / a[i][i] +" ");
}
}
// To check whether infinite solutions
// exists or no solution exists
static int CheckConsistency(float a[][], int n, int flag)
{
int i, j;
float sum;
// flag == 2 for infinite solution
// flag == 3 for No solution
flag = 3;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
sum = 0;
for (j = 0; j < n; j++)
sum = sum + a[i][j];
if (sum == a[i][j])
flag = 2;
}
return flag;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
float a[][] = {{ 0, 2, 1, 4 },
{ 1, 1, 2, 6 },
{ 2, 1, 1, 7 }};
// Order of Matrix(n)
int n = 3, flag = 0;
// Performing Matrix transformation
flag = PerformOperation(a, n);
if (flag == 1)
flag = CheckConsistency(a, n, flag);
// Printing Final Matrix
System.out.println("Final Augumented Matrix is : ");
PrintMatrix(a, n);
System.out.println("");
// Printing Solutions(if exist)
PrintResult(a, n, flag);
}
}
/* This code contributed by PrinciRaj1992 */C#
// C# Implementation for Gauss-Jordan
// Elimination Method
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
static int M = 10;
// Function to print the matrix
static void PrintMatrix(float [,]a, int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j <= n; j++)
Console.Write(a[i, j] + " ");
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
// function to reduce matrix to reduced
// row echelon form.
static int PerformOperation(float [,]a, int n)
{
int i, j, k = 0, c, flag = 0;
// Performing elementary operations
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (a[i, i] == 0)
{
c = 1;
while ((i + c) < n && a[i + c, i] == 0)
c++;
if ((i + c) == n)
{
flag = 1;
break;
}
for (j = i, k = 0; k <= n; k++)
{
float temp = a[j, k];
a[j, k] = a[j + c, k];
a[j + c, k] = temp;
}
}
for (j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
// Excluding all i == j
if (i != j)
{
// Converting Matrix to reduced row
// echelon form(diagonal matrix)
float p = a[j, i] / a[i, i];
for (k = 0; k <= n; k++)
a[j, k] = a[j, k] - (a[i, k]) * p;
}
}
}
return flag;
}
// Function to print the desired result
// if unique solutions exists, otherwise
// prints no solution or infinite solutions
// depending upon the input given.
static void PrintResult(float [,]a,
int n, int flag)
{
Console.Write("Result is : ");
if (flag == 2)
Console.WriteLine("Infinite Solutions Exists");
else if (flag == 3)
Console.WriteLine("No Solution Exists");
// Printing the solution by dividing
// constants by their respective
// diagonal elements
else
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
Console.Write(a[i, n] / a[i, i] + " ");
}
}
// To check whether infinite solutions
// exists or no solution exists
static int CheckConsistency(float [,]a,
int n, int flag)
{
int i, j;
float sum;
// flag == 2 for infinite solution
// flag == 3 for No solution
flag = 3;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
sum = 0;
for (j = 0; j < n; j++)
sum = sum + a[i, j];
if (sum == a[i, j])
flag = 2;
}
return flag;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
float [,]a = {{ 0, 2, 1, 4 },
{ 1, 1, 2, 6 },
{ 2, 1, 1, 7 }};
// Order of Matrix(n)
int n = 3, flag = 0;
// Performing Matrix transformation
flag = PerformOperation(a, n);
if (flag == 1)
flag = CheckConsistency(a, n, flag);
// Printing Final Matrix
Console.WriteLine("Final Augumented Matrix is : ");
PrintMatrix(a, n);
Console.WriteLine("");
// Printing Solutions(if exist)
PrintResult(a, n, flag);
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar输出:
Final Augumented Matrix is :
1 0 0 2.2
0 2 0 2.8
0 0 -2.5 -3
Result is : 2.2 1.4 1.2
应用范围:
- 线性方程组的求解:高斯-乔丹消除法可用于找到在整个数学中都应用的线性方程组的解。
- 查找行列式:高斯消除法可以应用于方矩阵,以便找到矩阵的行列式。
- 查找矩阵的逆:高斯-乔丹消除法可用于确定平方矩阵的逆。
- 查找等级和底数:使用简化的行梯形形式,可以通过高斯消除法计算平方矩阵的等级和底数。