在链表中查找循环的第一个节点
编写一个函数findFirstLoopNode()来检查给定的链表是否包含循环。如果存在循环,则它返回指向循环的第一个节点的点。否则它返回NULL。
例子 :
Input : Head of below linked list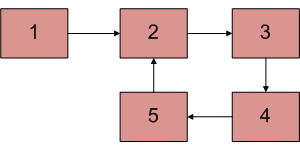
Output : Pointer to node 2我们已经讨论了 Floyd 的循环检测算法。以下是查找循环第一个节点的步骤。
1、如果找到循环,初始化一个慢指针指向头,让快指针在它的位置。
2. 一次移动一个节点的慢指针和快指针。
3. 他们相遇的点是循环的开始。
C++
// C++ program to return first node of loop.
#include
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int key;
struct Node* next;
};
Node* newNode(int key)
{
Node* temp = new Node;
temp->key = key;
temp->next = NULL;
return temp;
}
// A utility function to print a linked list
void printList(Node* head)
{
while (head != NULL) {
cout << head->key << " ";
head = head->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
// Function to detect and remove loop
// in a linked list that may contain loop
Node* detectAndRemoveLoop(Node* head)
{
// If list is empty or has only one node
// without loop
if (head == NULL || head->next == NULL)
return NULL;
Node *slow = head, *fast = head;
// Move slow and fast 1 and 2 steps
// ahead respectively.
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
// Search for loop using slow and
// fast pointers
while (fast && fast->next) {
if (slow == fast)
break;
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
// If loop does not exist
if (slow != fast)
return NULL;
// If loop exists. Start slow from
// head and fast from meeting point.
slow = head;
while (slow != fast) {
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
return slow;
}
/* Driver program to test above function*/
int main()
{
Node* head = newNode(50);
head->next = newNode(20);
head->next->next = newNode(15);
head->next->next->next = newNode(4);
head->next->next->next->next = newNode(10);
/* Create a loop for testing */
head->next->next->next->next->next = head->next->next;
Node* res = detectAndRemoveLoop(head);
if (res == NULL)
cout << "Loop does not exist";
else
cout << "Loop starting node is " << res->key;
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to return
// first node of loop.
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static class Node
{
int key;
Node next;
};
static Node newNode(int key)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.key = key;
temp.next = null;
return temp;
}
// A utility function to
// print a linked list
static void printList(Node head)
{
while (head != null)
{
System.out.print(head.key + " ");
head = head.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
// Function to detect and remove loop
// in a linked list that may contain loop
static Node detectAndRemoveLoop(Node head)
{
// If list is empty or has
// only one node without loop
if (head == null || head.next == null)
return null;
Node slow = head, fast = head;
// Move slow and fast 1
// and 2 steps ahead
// respectively.
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
// Search for loop using
// slow and fast pointers
while (fast != null &&
fast.next != null)
{
if (slow == fast)
break;
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
// If loop does not exist
if (slow != fast)
return null;
// If loop exists. Start slow from
// head and fast from meeting point.
slow = head;
while (slow != fast)
{
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
return slow;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Node head = newNode(50);
head.next = newNode(20);
head.next.next = newNode(15);
head.next.next.next = newNode(4);
head.next.next.next.next = newNode(10);
// Create a loop for testing
head.next.next.next.next.next = head.next.next;
Node res = detectAndRemoveLoop(head);
if (res == null)
System.out.print("Loop does not exist");
else
System.out.print("Loop starting node is " + res.key);
}
}
// This code is contributed by shikhasingrajputPython3
# Python3 program to return first node of loop.
class Node:
def __init__(self, key):
self.key = key
self.next = None
def newNode(key):
temp = Node(key)
return temp
# A utility function to print a linked list
def printList(head):
while (head != None):
print(head.key, end = ' ')
head = head.next
print()
# Function to detect and remove loop
# in a linked list that may contain loop
def detectAndRemoveLoop(head):
# If list is empty or has only one node
# without loop
if (head == None or head.next == None):
return None
slow = head
fast = head
# Move slow and fast 1 and 2 steps
# ahead respectively.
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
# Search for loop using slow and
# fast pointers
while (fast and fast.next):
if (slow == fast):
break
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
# If loop does not exist
if (slow != fast):
return None
# If loop exists. Start slow from
# head and fast from meeting point.
slow = head
while (slow != fast):
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next
return slow
# Driver code
if __name__=='__main__':
head = newNode(50)
head.next = newNode(20)
head.next.next = newNode(15)
head.next.next.next = newNode(4)
head.next.next.next.next = newNode(10)
# Create a loop for testing
head.next.next.next.next.next = head.next.next
res = detectAndRemoveLoop(head)
if (res == None):
print("Loop does not exist")
else:
print("Loop starting node is " +
str(res.key))
# This code is contributed by rutvik_56C#
// C# program to return
// first node of loop.
using System;
class GFG{
class Node
{
public int key;
public Node next;
};
static Node newNode(int key)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.key = key;
temp.next = null;
return temp;
}
// A utility function to
// print a linked list
static void printList(Node head)
{
while (head != null)
{
Console.Write(head.key + " ");
head = head.next;
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
// Function to detect and remove loop
// in a linked list that may contain loop
static Node detectAndRemoveLoop(Node head)
{
// If list is empty or has
// only one node without loop
if (head == null || head.next == null)
return null;
Node slow = head, fast = head;
// Move slow and fast 1
// and 2 steps ahead
// respectively.
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
// Search for loop using
// slow and fast pointers
while (fast != null &&
fast.next != null)
{
if (slow == fast)
break;
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
// If loop does not exist
if (slow != fast)
return null;
// If loop exists. Start slow from
// head and fast from meeting point.
slow = head;
while (slow != fast)
{
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
return slow;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
Node head = newNode(50);
head.next = newNode(20);
head.next.next = newNode(15);
head.next.next.next = newNode(4);
head.next.next.next.next = newNode(10);
// Create a loop for testing
head.next.next.next.next.next =
head.next.next;
Node res = detectAndRemoveLoop(head);
if (res == null)
Console.Write("Loop does not exist");
else
Console.Write("Loop starting node is " +
res.key);
}
}
// This code is contributed by shikhasingrajputJavascript
C++
// C++ program to return first node of loop
#include
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int key;
struct Node* next;
};
Node* newNode(int key)
{
Node* temp = new Node;
temp->key = key;
temp->next = NULL;
return temp;
}
// A utility function to print a linked list
void printList(Node* head)
{
while (head != NULL) {
cout << head->key << " ";
head = head->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
// Function to detect first node of loop
// in a linked list that may contain loop
Node* detectLoop(Node* head)
{
// Create a temporary node
Node* temp = new Node;
while (head != NULL) {
// This condition is for the case
// when there is no loop
if (head->next == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
// Check if next is already
// pointing to temp
if (head->next == temp) {
break;
}
// Store the pointer to the next node
// in order to get to it in the next step
Node* nex = head->next;
// Make next point to temp
head->next = temp;
// Get to the next node in the list
head = nex;
}
return head;
}
/* Driver program to test above function*/
int main()
{
Node* head = newNode(50);
head->next = newNode(20);
head->next->next = newNode(15);
head->next->next->next = newNode(4);
head->next->next->next->next = newNode(10);
/* Create a loop for testing */
head->next->next->next->next->next = head->next->next;
Node* res = detectLoop(head);
if (res == NULL)
cout << "Loop does not exist";
else
cout << "Loop starting node is " << res->key;
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to return first node of loop
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static class Node
{
int key;
Node next;
};
static Node newNode(int key)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.key = key;
temp.next = null;
return temp;
}
// A utility function to print a linked list
static void printList(Node head)
{
while (head != null)
{
System.out.print(head.key + " ");
head = head.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
// Function to detect first node of loop
// in a linked list that may contain loop
static Node detectLoop(Node head)
{
// Create a temporary node
Node temp = new Node();
while (head != null)
{
// This condition is for the case
// when there is no loop
if (head.next == null)
{
return null;
}
// Check if next is already
// pointing to temp
if (head.next == temp)
{
break;
}
// Store the pointer to the next node
// in order to get to it in the next step
Node nex = head.next;
// Make next point to temp
head.next = temp;
// Get to the next node in the list
head = nex;
}
return head;
}
/* Driver program to test above function*/
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Node head = newNode(50);
head.next = newNode(20);
head.next.next = newNode(15);
head.next.next.next = newNode(4);
head.next.next.next.next = newNode(10);
/* Create a loop for testing */
head.next.next.next.next.next = head.next.next;
Node res = detectLoop(head);
if (res == null)
System.out.print("Loop does not exist");
else
System.out.print("Loop starting node is " +
res.key);
}
}
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1Python3
# Python3 program to return first node of loop
class Node:
def __init__(self, x):
self.key = x
self.next = None
# A utility function to print a linked list
def printList(head):
while (head != None):
print(head.key, end = " ")
head = head.next
# Function to detect first node of loop
# in a linked list that may contain loop
def detectLoop(head):
# Create a temporary node
temp = Node(-1)
while (head != None):
# This condition is for the case
# when there is no loop
if (head.next == None):
return None
# Check if next is already
# pointing to temp
if (head.next == temp):
break
# Store the pointer to the next node
# in order to get to it in the next step
nex = head.next
# Make next point to temp
head.next = temp
# Get to the next node in the list
head = nex
return head
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
head = Node(50)
head.next = Node(20)
head.next.next = Node(15)
head.next.next.next = Node(4)
head.next.next.next.next = Node(10)
# Create a loop for testing
head.next.next.next.next.next = head.next.next
res = detectLoop(head)
if (res == None):
print("Loop does not exist")
else:
print("Loop starting node is ", res.key)
# This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29C#
// C# program to return first node of loop
using System;
class GFG{
class Node
{
public int key;
public Node next;
};
static Node newNode(int key)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.key = key;
temp.next = null;
return temp;
}
// A utility function to print a linked list
static void printList(Node head)
{
while (head != null)
{
Console.Write(head.key + " ");
head = head.next;
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
// Function to detect first node of loop
// in a linked list that may contain loop
static Node detectLoop(Node head)
{
// Create a temporary node
Node temp = new Node();
while (head != null)
{
// This condition is for the case
// when there is no loop
if (head.next == null)
{
return null;
}
// Check if next is already
// pointing to temp
if (head.next == temp)
{
break;
}
// Store the pointer to the next node
// in order to get to it in the next step
Node nex = head.next;
// Make next point to temp
head.next = temp;
// Get to the next node in the list
head = nex;
}
return head;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
Node head = newNode(50);
head.next = newNode(20);
head.next.next = newNode(15);
head.next.next.next = newNode(4);
head.next.next.next.next = newNode(10);
// Create a loop for testing
head.next.next.next.next.next = head.next.next;
Node res = detectLoop(head);
if (res == null)
Console.Write("Loop does not exist");
else
Console.Write("Loop starting node is " +
res.key);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Amit KatiyarJavascript
C++14
// The below function take head of Linked List as
// input and return Address of first node in
// the loop if present else return NULL.
/* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };*/
ListNode* detectCycle(ListNode* A)
{
// declaring map to store node address
unordered_set uset;
ListNode *ptr = A;
// Default consider that no cycle is present
while (ptr != NULL) {
// checking if address is already present in map
if (uset.find(ptr) != uset.end())
return ptr;
// if address not present then insert into the set
else
uset.insert(ptr);
ptr = ptr->next;
}
return NULL;
}
// This code is contributed by Pankaj_Joshi Java
// The below function take head of Linked List as
// input and return Address of first node in
// the loop if present else return NULL.
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static Node detectCycle(Node A)
{
// declaring map to store node address
Set uset = new HashSet();
Node = A;
// Default consider that no cycle is present
while (ptr != NULL)
{
// checking if address is already present in map
if(uset.contains(ptr))
{
return ptr;
}
// if address not present then insert into the set
else
{
uset.add(ptr);
}
ptr = ptr.next;
}
return null;
}
}
// This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155 Python3
# The below function take head of Linked List as
# input and return Address of first node in
# the loop if present else return NULL.
''' Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode:
* def __init__(self, x):
* self.val=x
* self.next=None
* '''
def detectCycle(A):
# Declaring map to store node
# address
uset = set()
ptr = A
# Default consider that no cycle
# is present
while (ptr != None):
# Checking if address is already
# present in map
if (ptr in uset):
return ptr
# If address not present then
# insert into the set
else:
uset.add(ptr)
ptr = ptr.next
return None
# This code is contributed by pratham76Javascript
Loop starting node is 15这种方法是如何工作的?
在弗洛伊德循环查找算法之后的某个时间点让慢速和快速相遇。下图显示了找到循环时的情况。

我们可以从上图中得出以下结论
Distance traveled by fast pointer = 2 * (Distance traveled
by slow pointer)
(m + n*x + k) = 2*(m + n*y + k)
Note that before meeting the point shown above, fast
was moving at twice speed.
x --> Number of complete cyclic rounds made by
fast pointer before they meet first time
y --> Number of complete cyclic rounds made by
slow pointer before they meet first time从上面的等式,我们可以得出以下结论
m + k = (x-2y)*n
Which means m+k is a multiple of n.因此,如果我们再次以相同的速度移动两个指针,使得一个指针(比如慢)从链表的头节点开始,而其他指针(比如快)从会合点开始。当慢指针到达循环的开头(已经走了 m 步)时,快指针也会移动 m 步,因为它们现在以相同的速度移动。由于 m+k 是 n 的倍数并且从 k 开始快速开始,因此它们会在开始时相遇。他们之前也能见面吗?不会,因为慢指针在 m 步后第一次进入循环。
方法二:
在此方法中,创建了一个临时节点。遍历的每个节点的下一个指针指向这个临时节点。这样,我们使用节点的下一个指针作为标志来指示该节点是否已被遍历。检查每个节点以查看下一个节点是否指向临时节点。在循环的第一个节点的情况下,我们第二次遍历它时,此条件为真,因此我们返回该节点。
代码以 O(n) 时间复杂度运行并使用恒定内存空间。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program to return first node of loop
#include
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int key;
struct Node* next;
};
Node* newNode(int key)
{
Node* temp = new Node;
temp->key = key;
temp->next = NULL;
return temp;
}
// A utility function to print a linked list
void printList(Node* head)
{
while (head != NULL) {
cout << head->key << " ";
head = head->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
// Function to detect first node of loop
// in a linked list that may contain loop
Node* detectLoop(Node* head)
{
// Create a temporary node
Node* temp = new Node;
while (head != NULL) {
// This condition is for the case
// when there is no loop
if (head->next == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
// Check if next is already
// pointing to temp
if (head->next == temp) {
break;
}
// Store the pointer to the next node
// in order to get to it in the next step
Node* nex = head->next;
// Make next point to temp
head->next = temp;
// Get to the next node in the list
head = nex;
}
return head;
}
/* Driver program to test above function*/
int main()
{
Node* head = newNode(50);
head->next = newNode(20);
head->next->next = newNode(15);
head->next->next->next = newNode(4);
head->next->next->next->next = newNode(10);
/* Create a loop for testing */
head->next->next->next->next->next = head->next->next;
Node* res = detectLoop(head);
if (res == NULL)
cout << "Loop does not exist";
else
cout << "Loop starting node is " << res->key;
return 0;
}
Java
// Java program to return first node of loop
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static class Node
{
int key;
Node next;
};
static Node newNode(int key)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.key = key;
temp.next = null;
return temp;
}
// A utility function to print a linked list
static void printList(Node head)
{
while (head != null)
{
System.out.print(head.key + " ");
head = head.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
// Function to detect first node of loop
// in a linked list that may contain loop
static Node detectLoop(Node head)
{
// Create a temporary node
Node temp = new Node();
while (head != null)
{
// This condition is for the case
// when there is no loop
if (head.next == null)
{
return null;
}
// Check if next is already
// pointing to temp
if (head.next == temp)
{
break;
}
// Store the pointer to the next node
// in order to get to it in the next step
Node nex = head.next;
// Make next point to temp
head.next = temp;
// Get to the next node in the list
head = nex;
}
return head;
}
/* Driver program to test above function*/
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Node head = newNode(50);
head.next = newNode(20);
head.next.next = newNode(15);
head.next.next.next = newNode(4);
head.next.next.next.next = newNode(10);
/* Create a loop for testing */
head.next.next.next.next.next = head.next.next;
Node res = detectLoop(head);
if (res == null)
System.out.print("Loop does not exist");
else
System.out.print("Loop starting node is " +
res.key);
}
}
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1
蟒蛇3
# Python3 program to return first node of loop
class Node:
def __init__(self, x):
self.key = x
self.next = None
# A utility function to print a linked list
def printList(head):
while (head != None):
print(head.key, end = " ")
head = head.next
# Function to detect first node of loop
# in a linked list that may contain loop
def detectLoop(head):
# Create a temporary node
temp = Node(-1)
while (head != None):
# This condition is for the case
# when there is no loop
if (head.next == None):
return None
# Check if next is already
# pointing to temp
if (head.next == temp):
break
# Store the pointer to the next node
# in order to get to it in the next step
nex = head.next
# Make next point to temp
head.next = temp
# Get to the next node in the list
head = nex
return head
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
head = Node(50)
head.next = Node(20)
head.next.next = Node(15)
head.next.next.next = Node(4)
head.next.next.next.next = Node(10)
# Create a loop for testing
head.next.next.next.next.next = head.next.next
res = detectLoop(head)
if (res == None):
print("Loop does not exist")
else:
print("Loop starting node is ", res.key)
# This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29
C#
// C# program to return first node of loop
using System;
class GFG{
class Node
{
public int key;
public Node next;
};
static Node newNode(int key)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.key = key;
temp.next = null;
return temp;
}
// A utility function to print a linked list
static void printList(Node head)
{
while (head != null)
{
Console.Write(head.key + " ");
head = head.next;
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
// Function to detect first node of loop
// in a linked list that may contain loop
static Node detectLoop(Node head)
{
// Create a temporary node
Node temp = new Node();
while (head != null)
{
// This condition is for the case
// when there is no loop
if (head.next == null)
{
return null;
}
// Check if next is already
// pointing to temp
if (head.next == temp)
{
break;
}
// Store the pointer to the next node
// in order to get to it in the next step
Node nex = head.next;
// Make next point to temp
head.next = temp;
// Get to the next node in the list
head = nex;
}
return head;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
Node head = newNode(50);
head.next = newNode(20);
head.next.next = newNode(15);
head.next.next.next = newNode(4);
head.next.next.next.next = newNode(10);
// Create a loop for testing
head.next.next.next.next.next = head.next.next;
Node res = detectLoop(head);
if (res == null)
Console.Write("Loop does not exist");
else
Console.Write("Loop starting node is " +
res.key);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Amit Katiyar
Javascript
Loop starting node is 15方法三:
我们还可以使用散列的概念来检测循环的第一个节点。这个想法很简单,只需遍历整个链表并将节点地址一个一个地存储在一个集合( C++ STL )中,同时将节点地址添加到集合中,检查它是否已经包含该特定节点地址,如果没有,则将节点地址添加到set 如果它已经存在于集合中,则当前节点是循环的第一个节点。
C++14
// The below function take head of Linked List as
// input and return Address of first node in
// the loop if present else return NULL.
/* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };*/
ListNode* detectCycle(ListNode* A)
{
// declaring map to store node address
unordered_set uset;
ListNode *ptr = A;
// Default consider that no cycle is present
while (ptr != NULL) {
// checking if address is already present in map
if (uset.find(ptr) != uset.end())
return ptr;
// if address not present then insert into the set
else
uset.insert(ptr);
ptr = ptr->next;
}
return NULL;
}
// This code is contributed by Pankaj_Joshi
Java
// The below function take head of Linked List as
// input and return Address of first node in
// the loop if present else return NULL.
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static Node detectCycle(Node A)
{
// declaring map to store node address
Set uset = new HashSet();
Node = A;
// Default consider that no cycle is present
while (ptr != NULL)
{
// checking if address is already present in map
if(uset.contains(ptr))
{
return ptr;
}
// if address not present then insert into the set
else
{
uset.add(ptr);
}
ptr = ptr.next;
}
return null;
}
}
// This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155
蟒蛇3
# The below function take head of Linked List as
# input and return Address of first node in
# the loop if present else return NULL.
''' Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode:
* def __init__(self, x):
* self.val=x
* self.next=None
* '''
def detectCycle(A):
# Declaring map to store node
# address
uset = set()
ptr = A
# Default consider that no cycle
# is present
while (ptr != None):
# Checking if address is already
# present in map
if (ptr in uset):
return ptr
# If address not present then
# insert into the set
else:
uset.add(ptr)
ptr = ptr.next
return None
# This code is contributed by pratham76
Javascript
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。