图中的桥梁
无向连通图中的一条边是一座桥,如果移除它会断开该图。对于断开连接的无向图,定义类似,桥是一个边去除,它增加了断开连接组件的数量。
与连接点一样,网桥代表连接网络中的漏洞,对于设计可靠的网络很有用。例如,在有线计算机网络中,连接点表示关键计算机,网桥表示关键线路或连接。
以下是一些示例图,其中以红色突出显示的桥梁。
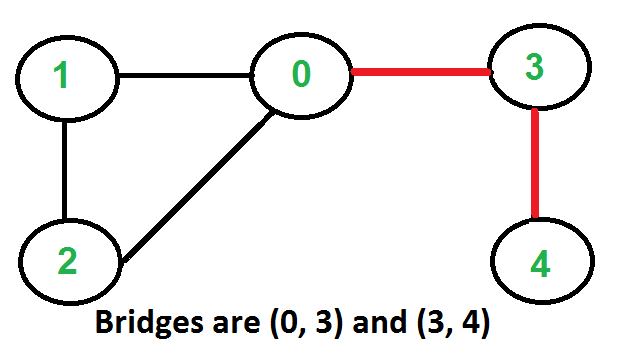
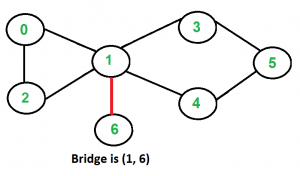
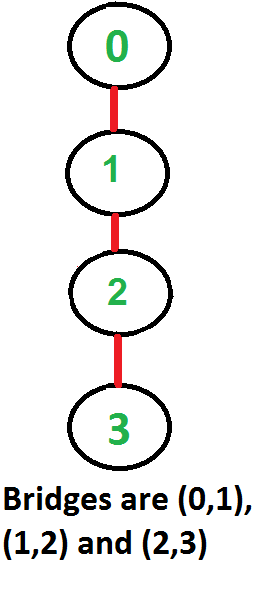
如何找到给定图中的所有桥梁?
一个简单的方法是,将所有的边一个一个地去掉,看看去掉一个边是否会导致图不连贯。以下是连接图的简单方法的步骤。
1) 对于每条边 (u, v),执行以下操作
.....a) 从图中删除 (u, v)
.....b) 查看图是否保持连接(我们可以使用 BFS 或 DFS)
.....c) 将 (u, v) 添加回图表。
对于使用邻接表表示的图,上述方法的时间复杂度为 O(E*(V+E))。我们能做得更好吗?
AO(V+E) 算法查找所有桥
这个想法类似于 Articulation Points 的 O(V+E) 算法。我们对给定的图进行 DFS 遍历。在 DFS 树中,如果不存在任何其他替代方法可以从以 v 为根的子树到达 u 或 u 的祖先,则边 (u, v)(u 是 DFS 树中 v 的父级)是桥接。如上一篇文章中所述,值low[v]表示从以v为根的子树可到达的最早访问的顶点。边(u,v)成为桥的条件是“low[v] > disc[u]” 。
以下是上述方法的实现。
C++
// A C++ program to find bridges in a given undirected graph
#include
#include
#define NIL -1
using namespace std;
// A class that represents an undirected graph
class Graph
{
int V; // No. of vertices
list *adj; // A dynamic array of adjacency lists
void bridgeUtil(int v, bool visited[], int disc[], int low[],
int parent[]);
public:
Graph(int V); // Constructor
void addEdge(int v, int w); // to add an edge to graph
void bridge(); // prints all bridges
};
Graph::Graph(int V)
{
this->V = V;
adj = new list[V];
}
void Graph::addEdge(int v, int w)
{
adj[v].push_back(w);
adj[w].push_back(v); // Note: the graph is undirected
}
// A recursive function that finds and prints bridges using
// DFS traversal
// u --> The vertex to be visited next
// visited[] --> keeps track of visited vertices
// disc[] --> Stores discovery times of visited vertices
// parent[] --> Stores parent vertices in DFS tree
void Graph::bridgeUtil(int u, bool visited[], int disc[],
int low[], int parent[])
{
// A static variable is used for simplicity, we can
// avoid use of static variable by passing a pointer.
static int time = 0;
// Mark the current node as visited
visited[u] = true;
// Initialize discovery time and low value
disc[u] = low[u] = ++time;
// Go through all vertices adjacent to this
list::iterator i;
for (i = adj[u].begin(); i != adj[u].end(); ++i)
{
int v = *i; // v is current adjacent of u
// If v is not visited yet, then recur for it
if (!visited[v])
{
parent[v] = u;
bridgeUtil(v, visited, disc, low, parent);
// Check if the subtree rooted with v has a
// connection to one of the ancestors of u
low[u] = min(low[u], low[v]);
// If the lowest vertex reachable from subtree
// under v is below u in DFS tree, then u-v
// is a bridge
if (low[v] > disc[u])
cout << u <<" " << v << endl;
}
// Update low value of u for parent function calls.
else if (v != parent[u])
low[u] = min(low[u], disc[v]);
}
}
// DFS based function to find all bridges. It uses recursive
// function bridgeUtil()
void Graph::bridge()
{
// Mark all the vertices as not visited
bool *visited = new bool[V];
int *disc = new int[V];
int *low = new int[V];
int *parent = new int[V];
// Initialize parent and visited arrays
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
parent[i] = NIL;
visited[i] = false;
}
// Call the recursive helper function to find Bridges
// in DFS tree rooted with vertex 'i'
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (visited[i] == false)
bridgeUtil(i, visited, disc, low, parent);
}
// Driver program to test above function
int main()
{
// Create graphs given in above diagrams
cout << "\nBridges in first graph \n";
Graph g1(5);
g1.addEdge(1, 0);
g1.addEdge(0, 2);
g1.addEdge(2, 1);
g1.addEdge(0, 3);
g1.addEdge(3, 4);
g1.bridge();
cout << "\nBridges in second graph \n";
Graph g2(4);
g2.addEdge(0, 1);
g2.addEdge(1, 2);
g2.addEdge(2, 3);
g2.bridge();
cout << "\nBridges in third graph \n";
Graph g3(7);
g3.addEdge(0, 1);
g3.addEdge(1, 2);
g3.addEdge(2, 0);
g3.addEdge(1, 3);
g3.addEdge(1, 4);
g3.addEdge(1, 6);
g3.addEdge(3, 5);
g3.addEdge(4, 5);
g3.bridge();
return 0;
}
Java
// A Java program to find bridges in a given undirected graph
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.LinkedList;
// This class represents a undirected graph using adjacency list
// representation
class Graph
{
private int V; // No. of vertices
// Array of lists for Adjacency List Representation
private LinkedList adj[];
int time = 0;
static final int NIL = -1;
// Constructor
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")Graph(int v)
{
V = v;
adj = new LinkedList[v];
for (int i=0; i The vertex to be visited next
// visited[] --> keeps track of visited vertices
// disc[] --> Stores discovery times of visited vertices
// parent[] --> Stores parent vertices in DFS tree
void bridgeUtil(int u, boolean visited[], int disc[],
int low[], int parent[])
{
// Mark the current node as visited
visited[u] = true;
// Initialize discovery time and low value
disc[u] = low[u] = ++time;
// Go through all vertices adjacent to this
Iterator i = adj[u].iterator();
while (i.hasNext())
{
int v = i.next(); // v is current adjacent of u
// If v is not visited yet, then make it a child
// of u in DFS tree and recur for it.
// If v is not visited yet, then recur for it
if (!visited[v])
{
parent[v] = u;
bridgeUtil(v, visited, disc, low, parent);
// Check if the subtree rooted with v has a
// connection to one of the ancestors of u
low[u] = Math.min(low[u], low[v]);
// If the lowest vertex reachable from subtree
// under v is below u in DFS tree, then u-v is
// a bridge
if (low[v] > disc[u])
System.out.println(u+" "+v);
}
// Update low value of u for parent function calls.
else if (v != parent[u])
low[u] = Math.min(low[u], disc[v]);
}
}
// DFS based function to find all bridges. It uses recursive
// function bridgeUtil()
void bridge()
{
// Mark all the vertices as not visited
boolean visited[] = new boolean[V];
int disc[] = new int[V];
int low[] = new int[V];
int parent[] = new int[V];
// Initialize parent and visited, and ap(articulation point)
// arrays
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
parent[i] = NIL;
visited[i] = false;
}
// Call the recursive helper function to find Bridges
// in DFS tree rooted with vertex 'i'
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (visited[i] == false)
bridgeUtil(i, visited, disc, low, parent);
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Create graphs given in above diagrams
System.out.println("Bridges in first graph ");
Graph g1 = new Graph(5);
g1.addEdge(1, 0);
g1.addEdge(0, 2);
g1.addEdge(2, 1);
g1.addEdge(0, 3);
g1.addEdge(3, 4);
g1.bridge();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Bridges in Second graph");
Graph g2 = new Graph(4);
g2.addEdge(0, 1);
g2.addEdge(1, 2);
g2.addEdge(2, 3);
g2.bridge();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Bridges in Third graph ");
Graph g3 = new Graph(7);
g3.addEdge(0, 1);
g3.addEdge(1, 2);
g3.addEdge(2, 0);
g3.addEdge(1, 3);
g3.addEdge(1, 4);
g3.addEdge(1, 6);
g3.addEdge(3, 5);
g3.addEdge(4, 5);
g3.bridge();
}
}
// This code is contributed by Aakash Hasija Python3
# Python program to find bridges in a given undirected graph
#Complexity : O(V+E)
from collections import defaultdict
#This class represents an undirected graph using adjacency list representation
class Graph:
def __init__(self,vertices):
self.V= vertices #No. of vertices
self.graph = defaultdict(list) # default dictionary to store graph
self.Time = 0
# function to add an edge to graph
def addEdge(self,u,v):
self.graph[u].append(v)
self.graph[v].append(u)
'''A recursive function that finds and prints bridges
using DFS traversal
u --> The vertex to be visited next
visited[] --> keeps track of visited vertices
disc[] --> Stores discovery times of visited vertices
parent[] --> Stores parent vertices in DFS tree'''
def bridgeUtil(self,u, visited, parent, low, disc):
# Mark the current node as visited and print it
visited[u]= True
# Initialize discovery time and low value
disc[u] = self.Time
low[u] = self.Time
self.Time += 1
#Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex
for v in self.graph[u]:
# If v is not visited yet, then make it a child of u
# in DFS tree and recur for it
if visited[v] == False :
parent[v] = u
self.bridgeUtil(v, visited, parent, low, disc)
# Check if the subtree rooted with v has a connection to
# one of the ancestors of u
low[u] = min(low[u], low[v])
''' If the lowest vertex reachable from subtree
under v is below u in DFS tree, then u-v is
a bridge'''
if low[v] > disc[u]:
print ("%d %d" %(u,v))
elif v != parent[u]: # Update low value of u for parent function calls.
low[u] = min(low[u], disc[v])
# DFS based function to find all bridges. It uses recursive
# function bridgeUtil()
def bridge(self):
# Mark all the vertices as not visited and Initialize parent and visited,
# and ap(articulation point) arrays
visited = [False] * (self.V)
disc = [float("Inf")] * (self.V)
low = [float("Inf")] * (self.V)
parent = [-1] * (self.V)
# Call the recursive helper function to find bridges
# in DFS tree rooted with vertex 'i'
for i in range(self.V):
if visited[i] == False:
self.bridgeUtil(i, visited, parent, low, disc)
# Create a graph given in the above diagram
g1 = Graph(5)
g1.addEdge(1, 0)
g1.addEdge(0, 2)
g1.addEdge(2, 1)
g1.addEdge(0, 3)
g1.addEdge(3, 4)
print ("Bridges in first graph ")
g1.bridge()
g2 = Graph(4)
g2.addEdge(0, 1)
g2.addEdge(1, 2)
g2.addEdge(2, 3)
print ("\nBridges in second graph ")
g2.bridge()
g3 = Graph (7)
g3.addEdge(0, 1)
g3.addEdge(1, 2)
g3.addEdge(2, 0)
g3.addEdge(1, 3)
g3.addEdge(1, 4)
g3.addEdge(1, 6)
g3.addEdge(3, 5)
g3.addEdge(4, 5)
print ("\nBridges in third graph ")
g3.bridge()
#This code is contributed by Neelam YadavC#
// A C# program to find bridges
// in a given undirected graph
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
// This class represents a undirected graph
// using adjacency list representation
public class Graph
{
private int V; // No. of vertices
// Array of lists for Adjacency List Representation
private List []adj;
int time = 0;
static readonly int NIL = -1;
// Constructor
Graph(int v)
{
V = v;
adj = new List[v];
for (int i = 0; i < v; ++i)
adj[i] = new List();
}
// Function to add an edge into the graph
void addEdge(int v, int w)
{
adj[v].Add(w); // Add w to v's list.
adj[w].Add(v); //Add v to w's list
}
// A recursive function that finds and prints bridges
// using DFS traversal
// u --> The vertex to be visited next
// visited[] --> keeps track of visited vertices
// disc[] --> Stores discovery times of visited vertices
// parent[] --> Stores parent vertices in DFS tree
void bridgeUtil(int u, bool []visited, int []disc,
int []low, int []parent)
{
// Mark the current node as visited
visited[u] = true;
// Initialize discovery time and low value
disc[u] = low[u] = ++time;
// Go through all vertices adjacent to this
foreach(int i in adj[u])
{
int v = i; // v is current adjacent of u
// If v is not visited yet, then make it a child
// of u in DFS tree and recur for it.
// If v is not visited yet, then recur for it
if (!visited[v])
{
parent[v] = u;
bridgeUtil(v, visited, disc, low, parent);
// Check if the subtree rooted with v has a
// connection to one of the ancestors of u
low[u] = Math.Min(low[u], low[v]);
// If the lowest vertex reachable from subtree
// under v is below u in DFS tree, then u-v is
// a bridge
if (low[v] > disc[u])
Console.WriteLine(u + " " + v);
}
// Update low value of u for parent function calls.
else if (v != parent[u])
low[u] = Math.Min(low[u], disc[v]);
}
}
// DFS based function to find all bridges. It uses recursive
// function bridgeUtil()
void bridge()
{
// Mark all the vertices as not visited
bool []visited = new bool[V];
int []disc = new int[V];
int []low = new int[V];
int []parent = new int[V];
// Initialize parent and visited,
// and ap(articulation point) arrays
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
parent[i] = NIL;
visited[i] = false;
}
// Call the recursive helper function to find Bridges
// in DFS tree rooted with vertex 'i'
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (visited[i] == false)
bridgeUtil(i, visited, disc, low, parent);
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String []args)
{
// Create graphs given in above diagrams
Console.WriteLine("Bridges in first graph ");
Graph g1 = new Graph(5);
g1.addEdge(1, 0);
g1.addEdge(0, 2);
g1.addEdge(2, 1);
g1.addEdge(0, 3);
g1.addEdge(3, 4);
g1.bridge();
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("Bridges in Second graph");
Graph g2 = new Graph(4);
g2.addEdge(0, 1);
g2.addEdge(1, 2);
g2.addEdge(2, 3);
g2.bridge();
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("Bridges in Third graph ");
Graph g3 = new Graph(7);
g3.addEdge(0, 1);
g3.addEdge(1, 2);
g3.addEdge(2, 0);
g3.addEdge(1, 3);
g3.addEdge(1, 4);
g3.addEdge(1, 6);
g3.addEdge(3, 5);
g3.addEdge(4, 5);
g3.bridge();
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji Javascript
输出:
Bridges in first graph
3 4
0 3
Bridges in second graph
2 3
1 2
0 1
Bridges in third graph
1 6时间复杂度:上述函数是带有附加数组的简单 DFS。因此,时间复杂度与 DFS 相同,即图的邻接表表示的 O(V+E)。
辅助空间: O(B^M),其中 B 是搜索树的最大分支因子,M 是状态空间的最大深度。