给定一个有向图。任务是检查给定的图是否连通。
例子:
Input: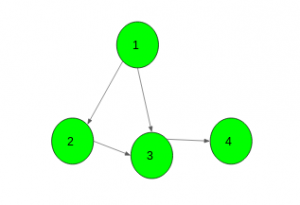
Output: Yes
Input: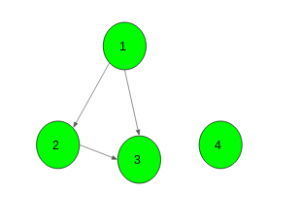
Output: No
方法:
- 取两个大小为N (图的节点数)的 bool 数组vis1和vis2 ,并在所有索引中保持 false。
- 从图 G 的随机顶点v开始,并运行 DFS(G, v)。
- 将所有访问过的顶点v设为vis1[v] = true 。
- 现在反转所有边缘的方向。
- 在步骤 2 中选择的顶点处启动 DFS。
- 将所有访问过的顶点v设为vis2[v] = true 。
- 如果任何顶点v具有vis1[v] = false和vis2[v] = false,则该图未连接。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include
using namespace std;
#define N 100000
// To keep correct and reverse direction
vector gr1[N], gr2[N];
bool vis1[N], vis2[N];
// Function to add edges
void Add_edge(int u, int v)
{
gr1[u].push_back(v);
gr2[v].push_back(u);
}
// DFS function
void dfs1(int x)
{
vis1[x] = true;
for (auto i : gr1[x])
if (!vis1[i])
dfs1(i);
}
// DFS function
void dfs2(int x)
{
vis2[x] = true;
for (auto i : gr2[x])
if (!vis2[i])
dfs2(i);
}
bool Is_Connected(int n)
{
// Call for correct direction
memset(vis1, false, sizeof vis1);
dfs1(1);
// Call for reverse direction
memset(vis2, false, sizeof vis2);
dfs2(1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
// If any vertex it not visited in any direction
// Then graph is not connected
if (!vis1[i] and !vis2[i])
return false;
}
// If graph is connected
return true;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int n = 4;
// Add edges
Add_edge(1, 2);
Add_edge(1, 3);
Add_edge(2, 3);
Add_edge(3, 4);
// Function call
if (Is_Connected(n))
cout << "Yes";
else
cout << "No";
return 0;
} Java
// Java implementation of the approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static int N = 100000;
// To keep correct and reverse direction
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
static Vector[] gr1 = new Vector[N];
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
static Vector[] gr2 = new Vector[N];
static boolean[] vis1 = new boolean[N];
static boolean[] vis2 = new boolean[N];
static {
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
gr1[i] = new Vector<>();
gr2[i] = new Vector<>();
}
}
// Function to add edges
static void Add_edge(int u, int v)
{
gr1[u].add(v);
gr2[v].add(u);
}
// DFS function
static void dfs1(int x)
{
vis1[x] = true;
for (int i : gr1[x])
if (!vis1[i])
dfs1(i);
}
// DFS function
static void dfs2(int x)
{
vis2[x] = true;
for (int i : gr2[x])
if (!vis2[i])
dfs2(i);
}
static boolean Is_connected(int n)
{
// Call for correct direction
Arrays.fill(vis1, false);
dfs1(1);
// Call for reverse direction
Arrays.fill(vis2, false);
dfs2(1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
// If any vertex it not visited in any direction
// Then graph is not connected
if (!vis1[i] && !vis2[i])
return false;
}
// If graph is connected
return true;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n = 4;
// Add edges
Add_edge(1, 2);
Add_edge(1, 3);
Add_edge(2, 3);
Add_edge(3, 4);
// Function call
if (Is_connected(n))
System.out.println("Yes");
else
System.out.println("No");
}
}
// This code is contributed by
// sanjeev2552 Python3
# Python3 implementation of the approach
N = 100000
# To keep correct and reverse direction
gr1 = {}; gr2 = {};
vis1 = [0] * N; vis2 = [0] * N;
# Function to add edges
def Add_edge(u, v) :
if u not in gr1 :
gr1[u] = [];
if v not in gr2 :
gr2[v] = [];
gr1[u].append(v);
gr2[v].append(u);
# DFS function
def dfs1(x) :
vis1[x] = True;
if x not in gr1 :
gr1[x] = {};
for i in gr1[x] :
if (not vis1[i]) :
dfs1(i)
# DFS function
def dfs2(x) :
vis2[x] = True;
if x not in gr2 :
gr2[x] = {};
for i in gr2[x] :
if (not vis2[i]) :
dfs2(i);
def Is_Connected(n) :
global vis1;
global vis2;
# Call for correct direction
vis1 = [False] * len(vis1);
dfs1(1);
# Call for reverse direction
vis2 = [False] * len(vis2);
dfs2(1);
for i in range(1, n + 1) :
# If any vertex it not visited in any direction
# Then graph is not connected
if (not vis1[i] and not vis2[i]) :
return False;
# If graph is connected
return True;
# Driver code
if __name__ == "__main__" :
n = 4;
# Add edges
Add_edge(1, 2);
Add_edge(1, 3);
Add_edge(2, 3);
Add_edge(3, 4);
# Function call
if (Is_Connected(n)) :
print("Yes");
else :
print("No");
# This code is contributed by AnkitRai01C#
// C# implementation of the approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
static int N = 100000;
// To keep correct and reverse direction
static List[] gr1 = new List[N];
static List[] gr2 = new List[N];
static bool[] vis1 = new bool[N];
static bool[] vis2 = new bool[N];
// Function to add edges
static void Add_edge(int u, int v)
{
gr1[u].Add(v);
gr2[v].Add(u);
}
// DFS function
static void dfs1(int x)
{
vis1[x] = true;
foreach (int i in gr1[x])
if (!vis1[i])
dfs1(i);
}
// DFS function
static void dfs2(int x)
{
vis2[x] = true;
foreach (int i in gr2[x])
if (!vis2[i])
dfs2(i);
}
static bool Is_connected(int n)
{
// Call for correct direction
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
vis1[i] = false;
dfs1(1);
// Call for reverse direction
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
vis2[i] = false;
dfs2(1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
// If any vertex it not visited in any direction
// Then graph is not connected
if (!vis1[i] && !vis2[i])
return false;
}
// If graph is connected
return true;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int n = 4;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
gr1[i] = new List();
gr2[i] = new List();
}
// Add edges
Add_edge(1, 2);
Add_edge(1, 3);
Add_edge(2, 3);
Add_edge(3, 4);
// Function call
if (Is_connected(n))
Console.WriteLine("Yes");
else
Console.WriteLine("No");
}
}
// This code is contributed by PrinciRaj1992 输出:
Yes
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。