给定两个整数N和K 。任务是找到一个具有N个顶点的连通图,使得恰好有K对(i, j) ,其中它们之间的最短距离为2 。如果不存在这样的图,则打印-1 。
笔记:
- 第一行输出应该是图中的边数(比如 m),接下来的 m 行应该包含两个数字,代表顶点之间的边。
- 如果有多个答案,请打印其中任何一个。
例子:
Input: N = 5, K = 3
Output: 7
1 2
1 3
1 4
1 5
3 4
3 5
4 5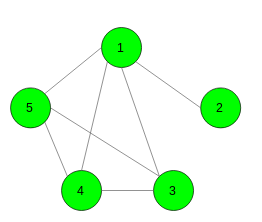
Input: N = 5, K = 8
Output: -1
方法:一个有 N 个顶点的连通图至少有N-1 条边。每对的最短距离等于1 。很明显,如果K > N * (N – 1) / 2 – (N – 1) = (N – 1) * (N – 2) / 2 ,显然不存在解。
反之,通过构造满足条件的图,可以证明如果K ≤ (N – 1) * (N – 2) / 2存在解。首先,让我们考虑每个顶点与所有其他顶点连接的图,然后任何两个顶点之间的最短顶点是1 。现在删除任何K 个边,那么就存在正好K 个这样的对。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to find the required graph
void connected_graph(int n, int k)
{
// If no such graph exists
if (k > (n - 1) * (n - 2) / 2) {
cout << -1 << endl;
return;
}
// Consider edge between all vertices
bool isEdge[n][n] = {};
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
isEdge[i][j] = true;
}
// Remove K vertices
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
if (cnt < k) {
isEdge[i][j] = false;
cnt++;
}
}
}
// Store all the edges
vector > vec;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
if (isEdge[i][j])
vec.emplace_back(i, j);
}
}
// Print all the edges
cout << vec.size() << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < vec.size(); i++) {
cout << vec[i].first + 1 << " "
<< vec[i].second + 1 << endl;
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int n = 5, k = 3;
// Function call
connected_graph(n, k);
return 0;
} Java
// Java implementation of the approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static class pair
{
int first, second;
public pair(int first, int second)
{
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
}
// Function to find the required graph
static void connected_graph(int n, int k)
{
// If no such graph exists
if (k > (n - 1) * (n - 2) / 2)
{
System.out.println(-1);
return;
}
// Consider edge between all vertices
boolean [][]isEdge = new boolean[n][n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
isEdge[i][j] = true;
}
// Remove K vertices
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
{
if (cnt < k)
{
isEdge[i][j] = false;
cnt++;
}
}
}
// Store all the edges
Vector vec = new Vector<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
{
if (isEdge[i][j])
vec.add(new pair(i, j));
}
}
// Print all the edges
System.out.println(vec.size());
for (int i = 0; i < vec.size(); i++)
{
System.out.println(vec.get(i).first + 1 +
" " + (vec.get(i).second + 1));
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n = 5, k = 3;
// Function call
connected_graph(n, k);
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar Python3
# Python3 implementation of the approach
import numpy as np;
# Function to find the required graph
def connected_graph(n, k) :
# If no such graph exists
if (k > (n - 1) * (n - 2) / 2) :
print(-1) ;
return;
# Consider edge between all vertices
isEdge = np.zeros((n, n));
for i in range(n) :
for j in range(i + 1, n) :
isEdge[i][j] = True;
# Remove K vertices
cnt = 0;
for i in range(1, n) :
for j in range(i + 1 , n) :
if (cnt < k) :
isEdge[i][j] = False;
cnt += 1;
# Store all the edges
vec = [];
for i in range(n) :
for j in range(i + 1, n) :
if (isEdge[i][j]) :
vec.append([i, j]);
# Print all the edges
print(len(vec));
for i in range(len(vec)) :
print(vec[i][0] + 1, vec[i][1] + 1);
# Driver code
if __name__ == "__main__" :
n = 5; k = 3;
# Function call
connected_graph(n, k);
# This code is contributed by Ankit RaiC#
// C# implementation of the approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
public class pair
{
public int first, second;
public pair(int first, int second)
{
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
}
// Function to find the required graph
static void connected_graph(int n, int k)
{
// If no such graph exists
if (k > (n - 1) * (n - 2) / 2)
{
Console.WriteLine(-1);
return;
}
// Consider edge between all vertices
bool [,]isEdge = new bool[n, n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
isEdge[i, j] = true;
}
// Remove K vertices
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
{
if (cnt < k)
{
isEdge[i, j] = false;
cnt++;
}
}
}
// Store all the edges
List vec = new List();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
{
if (isEdge[i, j])
vec.Add(new pair(i, j));
}
}
// Print all the edges
Console.WriteLine(vec.Count);
for (int i = 0; i < vec.Count; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(vec[i].first + 1 +
" " + (vec[i].second + 1));
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int n = 5, k = 3;
// Function call
connected_graph(n, k);
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar 输出:
7
1 2
1 3
1 4
1 5
3 4
3 5
4 5
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。