给定无向图,源顶点‘s和目标顶点‘d’ ,任务是计算从给定‘s’到‘d’的总路径。
例子
Input: s = 1, d = 4
Output: 2
Explanation:
Below are the 2 paths from 1 to 4
1 -> 3 -> 4
1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4
Input: s = 3, d = 9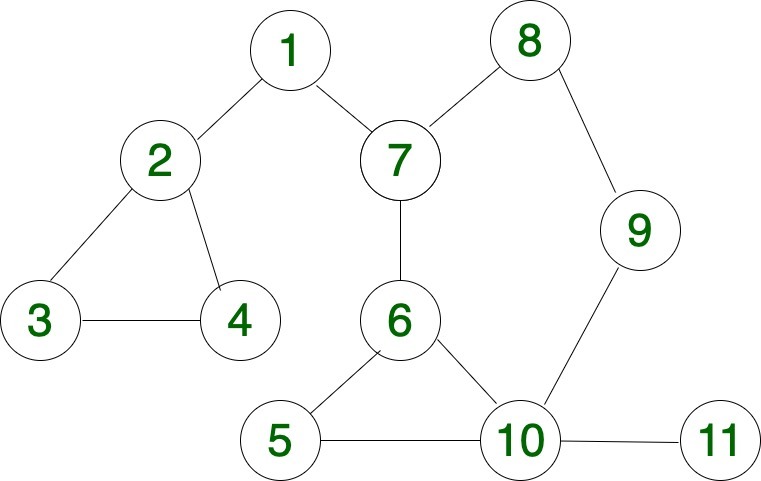
Output: 6
Explanation:
Below are the 6 paths from 3 to 9
3 -> 2 -> 1 -> 7 -> 6 -> 5 -> 10 -> 9
3 -> 2 -> 1 -> 7 -> 6 -> 10 -> 9
3 -> 2 -> 1 -> 7 -> 8 -> 9
3 -> 4 -> 2 -> 1 -> 7 -> 6 -> 5 -> 10 -> 9
3 -> 4 -> 2 -> 1 -> 7 -> 6 -> 10 -> 9
3 -> 4 -> 2 -> 1 -> 7 -> 8 -> 9
方法:
这个想法是对给定的无向图进行深度优先遍历。
- 从源开始遍历。
- 继续将访问的顶点存储在一个名为“ visited []”的数组中。
- 如果到达目标顶点,则将计数增加“ 1”。
- 重要的是将访问[]中的当前顶点标记为已访问,以使遍历不会循环进行。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program to count total number of
// ways to reach destination in a graph
#include
using namespace std;
// Utility Function to count total ways
int countWays(int mtrx[][11], int vrtx,
int i, int dest, bool visited[])
{
// Base condition
// When reach to the destination
if (i == dest) {
return 1;
}
int total = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < vrtx; j++) {
if (mtrx[i][j] == 1 && !visited[j]) {
// Make vertex visited
visited[j] = true;
// Recursive function, for count ways
total += countWays(mtrx, vrtx,
j, dest, visited);
// Backtracking
// Make vertex unvisited
visited[j] = false;
}
}
// Return total ways
return total;
}
// Function to count total ways
// to reach destination
int totalWays(int mtrx[][11], int vrtx,
int src, int dest)
{
bool visited[vrtx];
// Loop to make all vertex unvisited,
// Initially
for (int i = 0; i < vrtx; i++) {
visited[i] = false;
}
// Make source visited
visited[src] = true;
return countWays(mtrx, vrtx, src, dest,
visited);
}
int main()
{
int vrtx = 11;
int mtrx[11][11] = {
{ 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0 },
{ 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0 }
};
int src = 3;
int dest = 9;
// Print total ways
cout << totalWays(mtrx, vrtx, src - 1,
dest - 1);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to count total number of
// ways to reach destination in a graph
class GFG{
// Utility Function to count total ways
static int countWays(int mtrx[][], int vrtx,
int i, int dest, boolean visited[])
{
// Base condition
// When reach to the destination
if (i == dest) {
return 1;
}
int total = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < vrtx; j++) {
if (mtrx[i][j] == 1 && !visited[j]) {
// Make vertex visited
visited[j] = true;
// Recursive function, for count ways
total += countWays(mtrx, vrtx,
j, dest, visited);
// Backtracking
// Make vertex unvisited
visited[j] = false;
}
}
// Return total ways
return total;
}
// Function to count total ways
// to reach destination
static int totalWays(int mtrx[][], int vrtx,
int src, int dest)
{
boolean []visited = new boolean[vrtx];
// Loop to make all vertex unvisited,
// Initially
for (int i = 0; i < vrtx; i++) {
visited[i] = false;
}
// Make source visited
visited[src] = true;
return countWays(mtrx, vrtx, src, dest,
visited);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int vrtx = 11;
int mtrx[][] = {
{ 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0 },
{ 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0 }
};
int src = 3;
int dest = 9;
// Print total ways
System.out.print(totalWays(mtrx, vrtx, src - 1,
dest - 1));
}
}
// This code contributed by Rajput-JiPython 3
# Python 3 program to count total number of
# ways to reach destination in a graph
# Utility Function to count total ways
def countWays(mtrx, vrtx, i, dest, visited):
# Base condition
# When reach to the destination
if (i == dest):
return 1
total = 0
for j in range(vrtx):
if (mtrx[i][j] == 1 and not visited[j]):
# Make vertex visited
visited[j] = True;
# Recursive function, for count ways
total += countWays(mtrx, vrtx, j, dest, visited);
# Backtracking
# Make vertex unvisited
visited[j] = False;
# Return total ways
return total
# Function to count total ways
# to reach destination
def totalWays(mtrx, vrtx, src, dest):
visited = [False]*vrtx
# Loop to make all vertex unvisited,
# Initially
for i in range(vrtx):
visited[i] = False
# Make source visited
visited[src] = True;
return countWays(mtrx, vrtx, src, dest,visited)
# Driver function
vrtx = 11
mtrx = [
[0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0 ],
[ 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 ],
[ 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 ],
[ 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 ],
[ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0 ],
[ 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0 ],
[ 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0 ],
[ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0 ],
[ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0 ],
[ 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0 ],
[ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0 ]
]
src = 3
dest = 9
# Print total ways
print(totalWays(mtrx, vrtx, src - 1,dest - 1))
# This code is contributed by atul kumar shrivastavaC#
// C# program to count total number of
// ways to reach destination in a graph
using System;
class GFG{
// Utility Function to count total ways
static int countWays(int[,] mtrx, int vrtx,
int i, int dest, bool[] visited)
{
// Base condition
// When reach to the destination
if (i == dest) {
return 1;
}
int total = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < vrtx; j++) {
if (mtrx[i,j] == 1 && !visited[j]) {
// Make vertex visited
visited[j] = true;
// Recursive function, for count ways
total += countWays(mtrx, vrtx,
j, dest, visited);
// Backtracking
// Make vertex unvisited
visited[j] = false;
}
}
// Return total ways
return total;
}
// Function to count total ways
// to reach destination
static int totalWays(int[,] mtrx, int vrtx,
int src, int dest)
{
bool[]visited = new bool[vrtx];
// Loop to make all vertex unvisited,
// Initially
for (int i = 0; i < vrtx; i++) {
visited[i] = false;
}
// Make source visited
visited[src] = true;
return countWays(mtrx, vrtx, src, dest,
visited);
}
public static void Main()
{
int vrtx = 11;
int[,] mtrx = {
{ 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0 },
{ 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0 }
};
int src = 3;
int dest = 9;
// Print total ways
Console.Write(totalWays(mtrx, vrtx, src - 1,
dest - 1));
}
}输出:
6
性能分析:
- 时间复杂度:在上述方法中,对于给定的顶点,我们检查所有顶点,因此时间复杂度为O(N * N) ,其中N是没有顶点。
- 辅助空间复杂度:在上述方法中,我们使用大小为N的访问数组,其中N是顶点数,因此辅助空间复杂度为O(N) 。