给定 N 条线和一个二维空间中的起点和终点。这 N 行将空间分成一些块。我们需要打印从起点到达目的地点的最小跳跃次数。只有当它们共享一侧时,我们才能从一个块跳到另一个块。
例子:
输入:Lines = [x = 0, y = 0, x + y – 2 = 0] 起点 = [1, 1], 终点 = [-2, -1] 输出:2 我们需要跳跃 2 次( B4 -> B3 然后 B3 -> B5 或 B4 -> B6 然后 B6 -> B5) 从下图所示的起点到达目的地。图中的每个块 i 都有一个 id Bi。 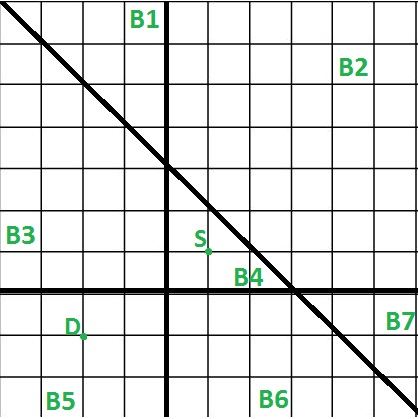
我们可以使用线和点的属性来解决这个问题,如果我们将两个点放在线方程中,那么如果两个点位于同一侧,它们将具有相同的符号,即评估值的正负或负负线,在不同符号的情况下,即正负它们将位于线的不同侧。
现在我们可以使用上面的属性来解决这个问题,对于每条线,我们将检查起点和终点是否在同一侧。如果他们位于一条线的另一侧,则必须跳过该线以靠近。如上图中起点和终点在x + y – 2 = 0 线的同一侧,因此该线不需要跳线,其余两条线需要跳线,因为这两个点位于相反的一侧。
最后,我们将检查每条线的点评估符号,并且每当我们发现相反的符号时,我们将增加跳跃计数。这个问题的总时间复杂度将是线性的。
C++
// C++ program to find minimum jumps to reach
// a given destination from a given source
#include
using namespace std;
// To represent point in 2D space
struct point
{
int x, y;
point(int x, int y) : x(x), y(y)
{}
};
// To represent line of (ax + by + c)format
struct line
{
int a, b, c;
line(int a, int b, int c) : a(a), b(b), c(c)
{}
line()
{}
};
// Returns 1 if evaluation is greater > 0,
// else returns -1
int evalPointOnLine(point p, line curLine)
{
int eval = curLine.a* p.x +
curLine.b * p.y +
curLine.c;
if (eval > 0)
return 1;
return -1;
}
// Returns minimum jumps to reach
// dest point from start point
int minJumpToReachDestination(point start,
point dest, line lines[], int N)
{
int jumps = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
// get sign of evaluation from point
// co-ordinate and line equation
int signStart = evalPointOnLine(start, lines[i]);
int signDest = evalPointOnLine(dest, lines[i]);
// if both evaluation are of opposite sign,
// increase jump by 1
if (signStart * signDest < 0)
jumps++;
}
return jumps;
}
// Driver code to test above methods
int main()
{
point start(1, 1);
point dest(-2, -1);
line lines[3];
lines[0] = line(1, 0, 0);
lines[1] = line(0, 1, 0);
lines[2] = line(1, 1, -2);
cout << minJumpToReachDestination(start, dest, lines, 3);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to find minimum jumps to reach
// a given destination from a given source
class GFG
{
// To represent point in 2D space
static class point
{
int x, y;
public point(int x, int y)
{
super();
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
};
// To represent line of (ax + by + c)format
static class line
{
public line(int a, int b, int c)
{
this.a = a;
this.b = b;
this.c = c;
}
int a, b, c;
line()
{}
};
// Returns 1 if evaluation is greater > 0,
// else returns -1
static int evalPointOnLine(point p, line curLine)
{
int eval = curLine.a* p.x +
curLine.b * p.y +
curLine.c;
if (eval > 0)
return 1;
return -1;
}
// Returns minimum jumps to reach
// dest point from start point
static int minJumpToReachDestination(point start,
point dest, line lines[], int N)
{
int jumps = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
// get sign of evaluation from point
// co-ordinate and line equation
int signStart = evalPointOnLine(start, lines[i]);
int signDest = evalPointOnLine(dest, lines[i]);
// if both evaluation are of opposite sign,
// increase jump by 1
if (signStart * signDest < 0)
jumps++;
}
return jumps;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
point start = new point(1, 1);
point dest = new point(-2, -1);
line []lines = new line[3];
lines[0] = new line(1, 0, 0);
lines[1] = new line(0, 1, 0);
lines[2] = new line(1, 1, -2);
System.out.print(minJumpToReachDestination(start, dest, lines, 3));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-JiC#
// C# program to find minimum jumps to reach
// a given destination from a given source
using System;
class GFG
{
// To represent point in 2D space
class point
{
public int x, y;
public point(int x, int y)
{
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
};
// To represent line of (ax + by + c)format
class line
{
public int a, b, c;
line()
{}
public line(int a, int b, int c)
{
this.a = a;
this.b = b;
this.c = c;
}
};
// Returns 1 if evaluation is greater > 0,
// else returns -1
static int evalPointOnLine(point p, line curLine)
{
int eval = curLine.a* p.x +
curLine.b * p.y +
curLine.c;
if (eval > 0)
return 1;
return -1;
}
// Returns minimum jumps to reach
// dest point from start point
static int minJumpToReachDestination(point start,
point dest, line []lines, int N)
{
int jumps = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
// get sign of evaluation from point
// co-ordinate and line equation
int signStart = evalPointOnLine(start, lines[i]);
int signDest = evalPointOnLine(dest, lines[i]);
// if both evaluation are of opposite sign,
// increase jump by 1
if (signStart * signDest < 0)
jumps++;
}
return jumps;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
point start = new point(1, 1);
point dest = new point(-2, -1);
line []lines = new line[3];
lines[0] = new line(1, 0, 0);
lines[1] = new line(0, 1, 0);
lines[2] = new line(1, 1, -2);
Console.Write(minJumpToReachDestination(start, dest, lines, 3));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji输出:
2
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。