IIR代表无限冲激响应,它是许多线性时间不变系统的显着特征之一,其特征在于其冲激响应h(t)/ h(n)在任何阶段都不会达到0,而是无限期地持续存在。
什么是IIR带通椭圆滤波器?
椭圆滤波器是一种特殊类型的滤波器,当需要从通带到阻带的快速过渡时,可用于数字信号处理。
规格如下:
- 通带频率:1400-2100 Hz
- 阻带频率:1050-24500 Hz
- 通带纹波:0.4dB
- 阻带衰减:50 dB
- 采样频率:7 kHz
- 我们将绘制滤波器的幅度和相位响应。
分步方法:
步骤1:导入所有必需的库。
Python3
# import required library
import numpy as np
import scipy.signal as signal
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltPython3
# Function to depict magnitude
# and phase plot
def mfreqz(b, a, Fs):
# Compute frequency response of the
# filter using signal.freqz function
wz, hz = signal.freqz(b, a)
# Calculate Magnitude from hz in dB
Mag = 20*np.log10(abs(hz))
# Calculate phase angle in degree from hz
Phase = np.unwrap(np.arctan2(np.imag(hz),
np.real(hz)))*(180/np.pi)
# Calculate frequency in Hz from wz
Freq = wz*Fs/(2*np.pi)
# Plot filter magnitude and phase responses using subplot.
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
# Plot Magnitude response
sub1 = plt.subplot(2, 1, 1)
sub1.plot(Freq, Mag, 'r', linewidth=2)
sub1.axis([1, Fs/2, -100, 5])
sub1.set_title('Magnitute Response', fontsize=20)
sub1.set_xlabel('Frequency [Hz]', fontsize=20)
sub1.set_ylabel('Magnitude [dB]', fontsize=20)
sub1.grid()
# Plot phase angle
sub2 = plt.subplot(2, 1, 2)
sub2.plot(Freq, Phase, 'g', linewidth=2)
sub2.set_ylabel('Phase (degree)', fontsize=20)
sub2.set_xlabel(r'Frequency (Hz)', fontsize=20)
sub2.set_title(r'Phase response', fontsize=20)
sub2.grid()
plt.subplots_adjust(hspace=0.5)
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()
# Define impz(b,a) to calculate impulse
# response and step response of a system
# input: b= an array containing numerator
# coefficients,a= an array containing
# denominator coefficients
def impz(b, a):
# Define the impulse sequence of length 60
impulse = np.repeat(0., 60)
impulse[0] = 1.
x = np.arange(0, 60)
# Compute the impulse response
response = signal.lfilter(b, a, impulse)
# Plot filter impulse and step response:
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
plt.subplot(211)
plt.stem(x, response, 'm', use_line_collection=True)
plt.ylabel('Amplitude', fontsize=15)
plt.xlabel(r'n (samples)', fontsize=15)
plt.title(r'Impulse response', fontsize=15)
plt.subplot(212)
step = np.cumsum(response)
# Compute step response of the system
plt.stem(x, step, 'g', use_line_collection=True)
plt.ylabel('Amplitude', fontsize=15)
plt.xlabel(r'n (samples)', fontsize=15)
plt.title(r'Step response', fontsize=15)
plt.subplots_adjust(hspace=0.5)
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()Python3
# Given specification
# Sampling frequency in Hz
Fs = 7000
# Pass band frequency in Hz
fp = np.array([1400, 2100])
# Stop band frequency in Hz
fs = np.array([1050, 2450])
# Pass band ripple in dB
Ap = 0.4
# Stop band attenuation in dB
As = 50Python3
# Compute pass band and stop band edge frequencies
# Normalized passband edge
# frequencies w.r.t. Nyquist rate
wp = fp/(Fs/2)
# Normalized stopband
# edge frequencies
ws = fs/(Fs/2)Python3
# Compute order of the elliptic filter
# using signal.ellipord
N, wc = signal.ellipord(wp, ws, Ap, As)
# Print the order of the filter and
# cutoff frequencies
print('Order of the filter=', N)
print('Cut-off frequency=', wc)Python3
# Design digital elliptic bandpass filter
# using signal.ellip function
z, p = signal.ellip(N, Ap, As, wc, 'bandpass')
# Print numerator and denomerator
# coefficients of the filter
print('Numerator Coefficients:', z)
print('Denominator Coefficients:', p)Python3
# Depicting visulalizations
# Call mfreqz to plot the magnitude and phase response
mfreqz(z, p, Fs)Python3
# Call impz function to plot impulse
# and step response of the filter
impz(z, p)Python3
# Import required library
import numpy as np
import scipy.signal as signal
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Function to depict magnitude
# and phase plot
def mfreqz(b, a, Fs):
# Compute frequency response of the
# filter using signal.freqz function
wz, hz = signal.freqz(b, a)
# Calculate Magnitude from hz in dB
Mag = 20*np.log10(abs(hz))
# Calculate phase angle in degree from hz
Phase = np.unwrap(np.arctan2(np.imag(hz),
np.real(hz)))*(180/np.pi)
# Calculate frequency in Hz from wz
Freq = wz*Fs/(2*np.pi)
# Plot filter magnitude and phase responses using subplot.
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
# Plot Magnitude response
sub1 = plt.subplot(2, 1, 1)
sub1.plot(Freq, Mag, 'r', linewidth=2)
sub1.axis([1, Fs/2, -100, 5])
sub1.set_title('Magnitute Response', fontsize=20)
sub1.set_xlabel('Frequency [Hz]', fontsize=20)
sub1.set_ylabel('Magnitude [dB]', fontsize=20)
sub1.grid()
# Plot phase angle
sub2 = plt.subplot(2, 1, 2)
sub2.plot(Freq, Phase, 'g', linewidth=2)
sub2.set_ylabel('Phase (degree)', fontsize=20)
sub2.set_xlabel(r'Frequency (Hz)', fontsize=20)
sub2.set_title(r'Phase response', fontsize=20)
sub2.grid()
plt.subplots_adjust(hspace=0.5)
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()
# Define impz(b,a) to calculate impulse
# response and step response of a system
# input: b= an array containing numerator
# coefficients,a= an array containing
# denominator coefficients
def impz(b, a):
# Define the impulse sequence of length 60
impulse = np.repeat(0., 60)
impulse[0] = 1.
x = np.arange(0, 60)
# Compute the impulse response
response = signal.lfilter(b, a, impulse)
# Plot filter impulse and step response:
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
plt.subplot(211)
plt.stem(x, response, 'm', use_line_collection=True)
plt.ylabel('Amplitude', fontsize=15)
plt.xlabel(r'n (samples)', fontsize=15)
plt.title(r'Impulse response', fontsize=15)
plt.subplot(212)
step = np.cumsum(response)
# Compute step response of the system
plt.stem(x, step, 'g', use_line_collection=True)
plt.ylabel('Amplitude', fontsize=15)
plt.xlabel(r'n (samples)', fontsize=15)
plt.title(r'Step response', fontsize=15)
plt.subplots_adjust(hspace=0.5)
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()
# Given specification
# Sampling frequency in Hz
Fs = 7000
# Pass band frequency in Hz
fp = np.array([1400, 2100])
# Stop band frequency in Hz
fs = np.array([1050, 2450])
# Pass band ripple in dB
Ap = 0.4
# Stop band attenuation in dB
As = 50
# Compute pass band and
# stop band edge frequencies
# Normalized passband edge frequencies
# w.r.t. Nyquist rate
wp = fp/(Fs/2)
# Normalized stopband edge frequencies
ws = fs/(Fs/2)
# Compute order of the elliptic filter
# using signal.ellipord
N, wc = signal.ellipord(wp, ws, Ap, As)
# Print the order of the filter and cutoff frequencies
print('Order of the filter=', N)
print('Cut-off frequency=', wc)
# Design digital elliptic bandpass filter
# using signal.ellip() function
z, p = signal.ellip(N, Ap, As, wc, 'bandpass')
# Print numerator and denomerator coefficients of the filter
print('Numerator Coefficients:', z)
print('Denominator Coefficients:', p)
# Depicting visulalizations
# Call mfreqz to plot the magnitude and
# phase response
mfreqz(z, p, Fs)
# Call impz function to plot impulse and
# step response of the filter
impz(z, p)步骤2:定义用户定义的函数mfreqz()和impz() 。该mfreqz为幅度和相位图的函数和impz为脉冲和阶跃响应]的函数。
Python3
# Function to depict magnitude
# and phase plot
def mfreqz(b, a, Fs):
# Compute frequency response of the
# filter using signal.freqz function
wz, hz = signal.freqz(b, a)
# Calculate Magnitude from hz in dB
Mag = 20*np.log10(abs(hz))
# Calculate phase angle in degree from hz
Phase = np.unwrap(np.arctan2(np.imag(hz),
np.real(hz)))*(180/np.pi)
# Calculate frequency in Hz from wz
Freq = wz*Fs/(2*np.pi)
# Plot filter magnitude and phase responses using subplot.
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
# Plot Magnitude response
sub1 = plt.subplot(2, 1, 1)
sub1.plot(Freq, Mag, 'r', linewidth=2)
sub1.axis([1, Fs/2, -100, 5])
sub1.set_title('Magnitute Response', fontsize=20)
sub1.set_xlabel('Frequency [Hz]', fontsize=20)
sub1.set_ylabel('Magnitude [dB]', fontsize=20)
sub1.grid()
# Plot phase angle
sub2 = plt.subplot(2, 1, 2)
sub2.plot(Freq, Phase, 'g', linewidth=2)
sub2.set_ylabel('Phase (degree)', fontsize=20)
sub2.set_xlabel(r'Frequency (Hz)', fontsize=20)
sub2.set_title(r'Phase response', fontsize=20)
sub2.grid()
plt.subplots_adjust(hspace=0.5)
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()
# Define impz(b,a) to calculate impulse
# response and step response of a system
# input: b= an array containing numerator
# coefficients,a= an array containing
# denominator coefficients
def impz(b, a):
# Define the impulse sequence of length 60
impulse = np.repeat(0., 60)
impulse[0] = 1.
x = np.arange(0, 60)
# Compute the impulse response
response = signal.lfilter(b, a, impulse)
# Plot filter impulse and step response:
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
plt.subplot(211)
plt.stem(x, response, 'm', use_line_collection=True)
plt.ylabel('Amplitude', fontsize=15)
plt.xlabel(r'n (samples)', fontsize=15)
plt.title(r'Impulse response', fontsize=15)
plt.subplot(212)
step = np.cumsum(response)
# Compute step response of the system
plt.stem(x, step, 'g', use_line_collection=True)
plt.ylabel('Amplitude', fontsize=15)
plt.xlabel(r'n (samples)', fontsize=15)
plt.title(r'Step response', fontsize=15)
plt.subplots_adjust(hspace=0.5)
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()
步骤3:使用过滤器的给定规格定义变量。
Python3
# Given specification
# Sampling frequency in Hz
Fs = 7000
# Pass band frequency in Hz
fp = np.array([1400, 2100])
# Stop band frequency in Hz
fs = np.array([1050, 2450])
# Pass band ripple in dB
Ap = 0.4
# Stop band attenuation in dB
As = 50
步骤4:计算截止频率
Python3
# Compute pass band and stop band edge frequencies
# Normalized passband edge
# frequencies w.r.t. Nyquist rate
wp = fp/(Fs/2)
# Normalized stopband
# edge frequencies
ws = fs/(Fs/2)
步骤5:计算椭圆带通数字滤波器的阶数。
Python3
# Compute order of the elliptic filter
# using signal.ellipord
N, wc = signal.ellipord(wp, ws, Ap, As)
# Print the order of the filter and
# cutoff frequencies
print('Order of the filter=', N)
print('Cut-off frequency=', wc)

步骤6:设计数字椭圆带通滤波器。
Python3
# Design digital elliptic bandpass filter
# using signal.ellip function
z, p = signal.ellip(N, Ap, As, wc, 'bandpass')
# Print numerator and denomerator
# coefficients of the filter
print('Numerator Coefficients:', z)
print('Denominator Coefficients:', p)

步骤7:绘制幅度和相位响应。
Python3
# Depicting visulalizations
# Call mfreqz to plot the magnitude and phase response
mfreqz(z, p, Fs)

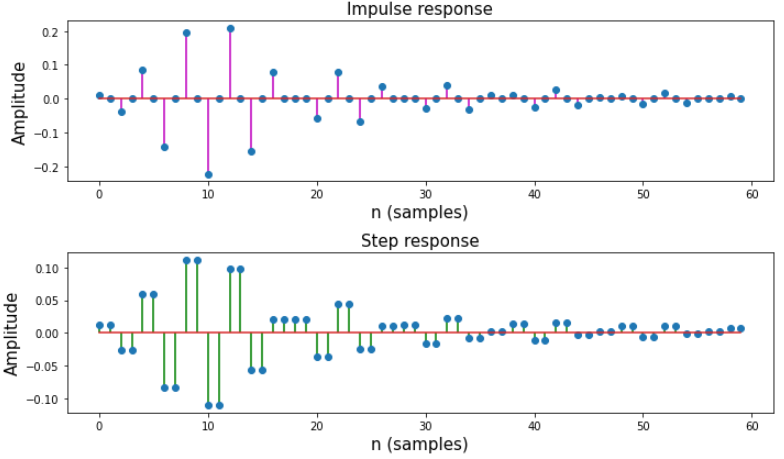
步骤8:绘制滤波器的脉冲和阶跃响应。
Python3
# Call impz function to plot impulse
# and step response of the filter
impz(z, p)
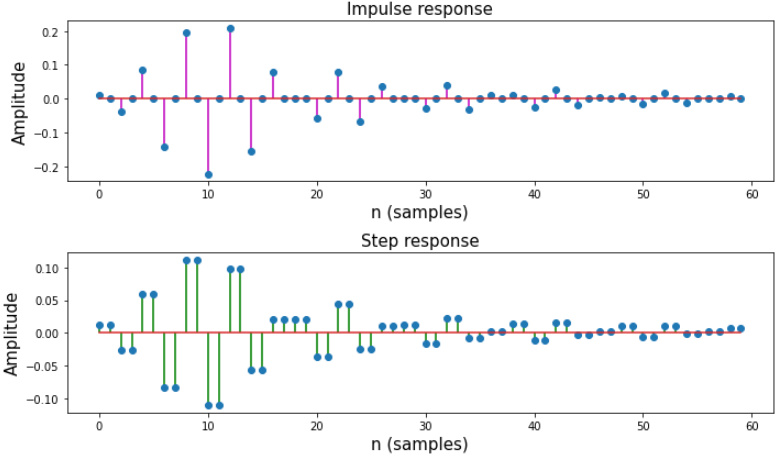
以下是上述逐步方法的完整实现:
Python3
# Import required library
import numpy as np
import scipy.signal as signal
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Function to depict magnitude
# and phase plot
def mfreqz(b, a, Fs):
# Compute frequency response of the
# filter using signal.freqz function
wz, hz = signal.freqz(b, a)
# Calculate Magnitude from hz in dB
Mag = 20*np.log10(abs(hz))
# Calculate phase angle in degree from hz
Phase = np.unwrap(np.arctan2(np.imag(hz),
np.real(hz)))*(180/np.pi)
# Calculate frequency in Hz from wz
Freq = wz*Fs/(2*np.pi)
# Plot filter magnitude and phase responses using subplot.
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
# Plot Magnitude response
sub1 = plt.subplot(2, 1, 1)
sub1.plot(Freq, Mag, 'r', linewidth=2)
sub1.axis([1, Fs/2, -100, 5])
sub1.set_title('Magnitute Response', fontsize=20)
sub1.set_xlabel('Frequency [Hz]', fontsize=20)
sub1.set_ylabel('Magnitude [dB]', fontsize=20)
sub1.grid()
# Plot phase angle
sub2 = plt.subplot(2, 1, 2)
sub2.plot(Freq, Phase, 'g', linewidth=2)
sub2.set_ylabel('Phase (degree)', fontsize=20)
sub2.set_xlabel(r'Frequency (Hz)', fontsize=20)
sub2.set_title(r'Phase response', fontsize=20)
sub2.grid()
plt.subplots_adjust(hspace=0.5)
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()
# Define impz(b,a) to calculate impulse
# response and step response of a system
# input: b= an array containing numerator
# coefficients,a= an array containing
# denominator coefficients
def impz(b, a):
# Define the impulse sequence of length 60
impulse = np.repeat(0., 60)
impulse[0] = 1.
x = np.arange(0, 60)
# Compute the impulse response
response = signal.lfilter(b, a, impulse)
# Plot filter impulse and step response:
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
plt.subplot(211)
plt.stem(x, response, 'm', use_line_collection=True)
plt.ylabel('Amplitude', fontsize=15)
plt.xlabel(r'n (samples)', fontsize=15)
plt.title(r'Impulse response', fontsize=15)
plt.subplot(212)
step = np.cumsum(response)
# Compute step response of the system
plt.stem(x, step, 'g', use_line_collection=True)
plt.ylabel('Amplitude', fontsize=15)
plt.xlabel(r'n (samples)', fontsize=15)
plt.title(r'Step response', fontsize=15)
plt.subplots_adjust(hspace=0.5)
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()
# Given specification
# Sampling frequency in Hz
Fs = 7000
# Pass band frequency in Hz
fp = np.array([1400, 2100])
# Stop band frequency in Hz
fs = np.array([1050, 2450])
# Pass band ripple in dB
Ap = 0.4
# Stop band attenuation in dB
As = 50
# Compute pass band and
# stop band edge frequencies
# Normalized passband edge frequencies
# w.r.t. Nyquist rate
wp = fp/(Fs/2)
# Normalized stopband edge frequencies
ws = fs/(Fs/2)
# Compute order of the elliptic filter
# using signal.ellipord
N, wc = signal.ellipord(wp, ws, Ap, As)
# Print the order of the filter and cutoff frequencies
print('Order of the filter=', N)
print('Cut-off frequency=', wc)
# Design digital elliptic bandpass filter
# using signal.ellip() function
z, p = signal.ellip(N, Ap, As, wc, 'bandpass')
# Print numerator and denomerator coefficients of the filter
print('Numerator Coefficients:', z)
print('Denominator Coefficients:', p)
# Depicting visulalizations
# Call mfreqz to plot the magnitude and
# phase response
mfreqz(z, p, Fs)
# Call impz function to plot impulse and
# step response of the filter
impz(z, p)
输出: