给定两个整数N和K ,任务是找到将K个主教放在N×N棋盘上的方式的数目,以使没有两个主教互相攻击。
Here is an example for a 5×5 chessboard.
例子:
Input: N = 2, K = 2
Output: 4
The different ways to place 2 bishops in a 2 * 2 chessboard are :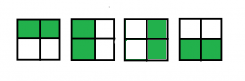
Input: N = 4, K = 3
Output: 232
方法:可以使用动态编程解决此问题。
- 令dp [i] [j]表示将j个主教放在对角线最多i的对角线上的方式的数目,这些对角线的颜色与对角线i相同。那么i = 1…2N-1 , j = 0…K 。
- 我们可以仅使用dp [i-2]的值来计算dp [i] [j] (我们减去2是因为我们只考虑与i相同颜色的对角线)。有两种获取dp [i] [j]的方法。要么将所有j个主教都放在前面的对角线上:然后有dp [i-2] [j]种方法来实现。或者我们将一个主教放在对角线i上,将j-1主教放在对角线上。这样做的方法数量等于对角线i –(j – 1)中的正方形数,因为放置在先前对角线上的j-1个主教中的每个主教都将阻塞当前对角线上的一个正方形。
- 基本情况很简单: dp [i] [0] = 1,dp [1] [1] = 1 。
- 一旦我们计算了dp [i] [j]的所有值,就可以得到以下答案:考虑放置在黑色对角线i = 0…K上的所有主教的可能数量,以及白色对角线Ki上的主教的相应数量。放置在黑色和白色对角线上的主教永远不会互相攻击,因此可以独立进行放置。最后一个黑色对角线的索引是2N-1 ,最后一个白色对角线的索引是2N-2 。对于每个i,我们将dp [2N-1] [i] * dp [2N-2] [Ki]加到答案中。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// CPP implementation of the approach
#include
using namespace std;
// returns the number of squares in diagonal i
int squares(int i)
{
if ((i & 1) == 1)
return i / 4 * 2 + 1;
else
return (i - 1) / 4 * 2 + 2;
}
// returns the number of ways to fill a
// n * n chessboard with k bishops so
// that no two bishops attack each other.
long bishop_placements(int n, int k)
{
// return 0 if the number of valid places to be
// filled is less than the number of bishops
if (k > 2 * n - 1)
return 0;
// dp table to store the values
long dp[n * 2][k + 1];
// Setting the base conditions
for(int i = 0; i < n * 2; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < k + 1; j++)
{
dp[i][j] = 0;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n * 2; i++)
dp[i][0] = 1;
dp[1][1] = 1;
// calculate the required number of ways
for (int i = 2; i < n * 2; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= k; j++)
{
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 2][j]
+ dp[i - 2][j - 1] * (squares(i) - j + 1);
}
}
// stores the answer
long ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= k; i++)
{
ans += dp[n * 2 - 1][i] * dp[n * 2 - 2][k - i];
}
return ans;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int n = 2;
int k = 2;
long ans = bishop_placements(n, k);
cout << (ans);
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji Java
// Java implementation of the approach
class GFG {
// returns the number of squares in diagonal i
static int squares(int i)
{
if ((i & 1) == 1)
return i / 4 * 2 + 1;
else
return (i - 1) / 4 * 2 + 2;
}
// returns the number of ways to fill a
// n * n chessboard with k bishops so
// that no two bishops attack each other.
static long bishop_placements(int n, int k)
{
// return 0 if the number of valid places to be
// filled is less than the number of bishops
if (k > 2 * n - 1)
return 0;
// dp table to store the values
long[][] dp = new long[n * 2][k + 1];
// Setting the base conditions
for (int i = 0; i < n * 2; i++)
dp[i][0] = 1;
dp[1][1] = 1;
// calculate the required number of ways
for (int i = 2; i < n * 2; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= k; j++)
dp[i][j]
= dp[i - 2][j]
+ dp[i - 2][j - 1] * (squares(i) - j + 1);
}
// stores the answer
long ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= k; i++) {
ans += dp[n * 2 - 1][i] * dp[n * 2 - 2][k - i];
}
return ans;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n = 2;
int k = 2;
long ans = bishop_placements(n, k);
System.out.println(ans);
}
}Python3
# Python 3 implementation of the approach
# returns the number of squares in
# diagonal i
def squares(i):
if ((i & 1) == 1):
return int(i / 4) * 2 + 1
else:
return int((i - 1) / 4) * 2 + 2
# returns the number of ways to fill a
# n * n chessboard with k bishops so
# that no two bishops attack each other.
def bishop_placements(n, k):
# return 0 if the number of valid places
# to be filled is less than the number
# of bishops
if (k > 2 * n - 1):
return 0
# dp table to store the values
dp = [[0 for i in range(k + 1)]
for i in range(n * 2)]
# Setting the base conditions
for i in range(n * 2):
dp[i][0] = 1
dp[1][1] = 1
# calculate the required number of ways
for i in range(2, n * 2, 1):
for j in range(1, k + 1, 1):
dp[i][j] = (dp[i - 2][j] +
dp[i - 2][j - 1] *
(squares(i) - j + 1))
# stores the answer
ans = 0
for i in range(0, k + 1, 1):
ans += (dp[n * 2 - 1][i] *
dp[n * 2 - 2][k - i])
return ans
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
n = 2
k = 2
ans = bishop_placements(n, k)
print(ans)
# This code is contributed by
# Sanjit_PrasadC#
// C# implementation of the approach
using System;
class GFG
{
// returns the number of squares
// in diagonal i
static int squares(int i)
{
if ((i & 1) == 1)
return i / 4 * 2 + 1;
else
return (i - 1) / 4 * 2 + 2;
}
// returns the number of ways to fill a
// n * n chessboard with k bishops so
// that no two bishops attack each other.
static long bishop_placements(int n, int k)
{
// return 0 if the number of valid
// places to be filled is less than
// the number of bishops
if (k > 2 * n - 1)
return 0;
// dp table to store the values
long[,] dp = new long[n * 2, k + 1];
// Setting the base conditions
for (int i = 0; i < n * 2; i++)
dp[i, 0] = 1;
dp[1, 1] = 1;
// calculate the required
// number of ways
for (int i = 2; i < n * 2; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= k; j++)
dp[i, j] = dp[i - 2, j] +
dp[i - 2, j - 1] *
(squares(i) - j + 1);
}
// stores the answer
long ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= k; i++)
{
ans += dp[n * 2 - 1, i] *
dp[n * 2 - 2, k - i];
}
return ans;
}
// Driver code
static public void Main ()
{
int n = 2;
int k = 2;
long ans = bishop_placements(n, k);
Console.WriteLine(ans);
}
}
// This code is contributed by akt_mitPHP
2 * $n - 1)
return 0;
// dp table to store the values
$dp = array_fill(0, $n * 2,
array_fill(0, $k + 1, NULL));
// Setting the base conditions
for ($i = 0; $i < $n * 2; $i++)
$dp[$i][0] = 1;
$dp[1][1] = 1;
// calculate the required number of ways
for ($i = 2; $i < $n * 2; $i++)
{
for ($j = 1; $j <= $k; $j++)
$dp[$i][$j] = $dp[$i - 2][$j] +
$dp[$i - 2][$j - 1] *
(squares($i) - $j + 1);
}
// stores the answer
$ans = 0;
for ($i = 0; $i <= $k; $i++)
{
$ans += $dp[$n * 2 - 1][$i] *
$dp[$n * 2 - 2][$k - $i];
}
return $ans;
}
// Driver code
$n = 2;
$k = 2;
$ans = bishop_placements($n, $k);
echo $ans;
// This code is contributed by ita_c
?>输出:
4