给定链表的成对交换元素
给定一个单链表,编写一个函数来成对交换元素。
Input : 1->2->3->4->5->6->NULL
Output : 2->1->4->3->6->5->NULL
Input : 1->2->3->4->5->NULL
Output : 2->1->4->3->5->NULL
Input : 1->NULL
Output : 1->NULL
例如,如果链表是 1->2->3->4->5 那么函数应该将其更改为 2->1->4->3->5,如果链表是函数应将其更改为。
方法一(迭代)
从头节点开始,遍历链表。在遍历每个节点的数据与其下一个节点的数据时。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program to pairwise swap elements
// in a given linked list
#include
using namespace std;
/* A linked list node */
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node* next;
};
/* Function to pairwise swap elements
of a linked list */
void pairWiseSwap(Node* head)
{
Node* temp = head;
/* Traverse further only if
there are at-least two nodes left */
while (temp != NULL && temp->next != NULL) {
/* Swap data of node with
its next node's data */
swap(temp->data,
temp->next->data);
/* Move temp by 2 for the next pair */
temp = temp->next->next;
}
}
/* Function to add a node at the
beginning of Linked List */
void push(Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
/* allocate node */
Node* new_node = new Node();
/* put in the data */
new_node->data = new_data;
/* link the old list off the new node */
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
/* move the head to point
to the new node */
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
/* Function to print nodes
in a given linked list */
void printList(Node* node)
{
while (node != NULL) {
cout << node->data << " ";
node = node->next;
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
Node* start = NULL;
/* The constructed linked list is:
1->2->3->4->5 */
push(&start, 5);
push(&start, 4);
push(&start, 3);
push(&start, 2);
push(&start, 1);
cout << "Linked list "
<< "before calling pairWiseSwap()\n";
printList(start);
pairWiseSwap(start);
cout << "\nLinked list "
<< "after calling pairWiseSwap()\n";
printList(start);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed
// by rathbhupendra C
/* C program to pairwise swap elements in a given linked list */
#include
#include
/* A linked list node */
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
/*Function to swap two integers at addresses a and b */
void swap(int* a, int* b);
/* Function to pairwise swap elements of a linked list */
void pairWiseSwap(struct Node* head)
{
struct Node* temp = head;
/* Traverse further only if there are at-least two nodes left */
while (temp != NULL && temp->next != NULL) {
/* Swap data of node with its next node's data */
swap(&temp->data, &temp->next->data);
/* Move temp by 2 for the next pair */
temp = temp->next->next;
}
}
/* UTILITY FUNCTIONS */
/* Function to swap two integers */
void swap(int* a, int* b)
{
int temp;
temp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = temp;
}
/* Function to add a node at the beginning of Linked List */
void push(struct Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
/* allocate node */
struct Node* new_node = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
/* put in the data */
new_node->data = new_data;
/* link the old list off the new node */
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
/* move the head to point to the new node */
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
/* Function to print nodes in a given linked list */
void printList(struct Node* node)
{
while (node != NULL) {
printf("%d ", node->data);
node = node->next;
}
}
/* Driver program to test above function */
int main()
{
struct Node* start = NULL;
/* The constructed linked list is:
1->2->3->4->5 */
push(&start, 5);
push(&start, 4);
push(&start, 3);
push(&start, 2);
push(&start, 1);
printf("Linked list before calling pairWiseSwap()\n");
printList(start);
pairWiseSwap(start);
printf("\nLinked list after calling pairWiseSwap()\n");
printList(start);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to pairwise swap elements of a linked list
class LinkedList {
Node head; // head of list
/* Linked list Node*/
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
void pairWiseSwap()
{
Node temp = head;
/* Traverse only till there are atleast 2 nodes left */
while (temp != null && temp.next != null) {
/* Swap the data */
int k = temp.data;
temp.data = temp.next.data;
temp.next.data = k;
temp = temp.next.next;
}
}
/* Utility functions */
/* Inserts a new Node at front of the list. */
public void push(int new_data)
{
/* 1 & 2: Allocate the Node &
Put in the data*/
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
/* 3. Make next of new Node as head */
new_node.next = head;
/* 4. Move the head to point to new Node */
head = new_node;
}
/* Function to print linked list */
void printList()
{
Node temp = head;
while (temp != null) {
System.out.print(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
/* Driver program to test above functions */
public static void main(String args[])
{
LinkedList llist = new LinkedList();
/* Created Linked List 1->2->3->4->5 */
llist.push(5);
llist.push(4);
llist.push(3);
llist.push(2);
llist.push(1);
System.out.println("Linked List before calling pairWiseSwap() ");
llist.printList();
llist.pairWiseSwap();
System.out.println("Linked List after calling pairWiseSwap() ");
llist.printList();
}
}
/* This code is contributed by Rajat Mishra */Python
# Python program to swap the elements of linked list pairwise
# Node class
class Node:
# Constructor to initialize the node object
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
# Function to initialize head
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
# Function to pairwise swap elements of a linked list
def pairwiseSwap(self):
temp = self.head
# There are no nodes in linked list
if temp is None:
return
# Traverse furthur only if there are at least two
# left
while(temp and temp.next):
# If both nodes are same,
# no need to swap data
if(temp.data != temp.next.data):
# Swap data of node with its next node's data
temp.data, temp.next.data = temp.next.data, temp.data
# Move temp by 2 to the next pair
temp = temp.next.next
# Function to insert a new node at the beginning
def push(self, new_data):
new_node = Node(new_data)
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
# Utility function to prit the linked LinkedList
def printList(self):
temp = self.head
while(temp):
print temp.data,
temp = temp.next
# Driver program
llist = LinkedList()
llist.push(5)
llist.push(4)
llist.push(3)
llist.push(2)
llist.push(1)
print "Linked list before calling pairWiseSwap() "
llist.printList()
llist.pairwiseSwap()
print "\nLinked list after calling pairWiseSwap()"
llist.printList()
# This code is contributed by Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007)C#
// C# program to pairwise swap elements of a linked list
using System;
class LinkedList {
Node head; // head of list
/* Linked list Node*/
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node next;
public Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
void pairWiseSwap()
{
Node temp = head;
/* Traverse only till there are atleast 2 nodes left */
while (temp != null && temp.next != null) {
/* Swap the data */
int k = temp.data;
temp.data = temp.next.data;
temp.next.data = k;
temp = temp.next.next;
}
}
/* Utility functions */
/* Inserts a new Node at front of the list. */
public void push(int new_data)
{
/* 1 & 2: Allocate the Node &
Put in the data*/
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
/* 3. Make next of new Node as head */
new_node.next = head;
/* 4. Move the head to point to new Node */
head = new_node;
}
/* Function to print linked list */
void printList()
{
Node temp = head;
while (temp != null) {
Console.Write(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
/* Driver program to test above functions */
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList llist = new LinkedList();
/* Created Linked List 1->2->3->4->5 */
llist.push(5);
llist.push(4);
llist.push(3);
llist.push(2);
llist.push(1);
Console.WriteLine("Linked List before calling pairWiseSwap() ");
llist.printList();
llist.pairWiseSwap();
Console.WriteLine("Linked List after calling pairWiseSwap() ");
llist.printList();
}
}
// This code is contributed by Arnab KunduJavascript
C
/* Recursive function to pairwise swap elements
of a linked list */
void pairWiseSwap(struct node* head)
{
/* There must be at-least two nodes in the list */
if (head != NULL && head->next != NULL) {
/* Swap the node's data with data of next node */
swap(head->data, head->next->data);
/* Call pairWiseSwap() for rest of the list */
pairWiseSwap(head->next->next);
}
}Java
/* Recursive function to pairwise swap elements
of a linked list */
static void pairWiseSwap(node head)
{
/* There must be at-least two nodes in the list */
if (head != null && head.next != null) {
/* Swap the node's data with data of next node */
swap(head.data, head.next.data);
/* Call pairWiseSwap() for rest of the list */
pairWiseSwap(head.next.next);
}
}
// This code contributed by aashish1995C#
/* Recursive function to pairwise swap elements
of a linked list */
static void pairWiseSwap(node head)
{
/* There must be at-least two nodes in the list */
if (head != null && head.next != null) {
/* Swap the node's data with data of next node */
swap(head.data, head.next.data);
/* Call pairWiseSwap() for rest of the list */
pairWiseSwap(head.next.next);
}
}
// This code contributed by aashish1995Javascript
输出
Linked list before calling pairWiseSwap()
1 2 3 4 5
Linked list after calling pairWiseSwap()
2 1 4 3 5 时间复杂度: O(n)
方法 2(递归)
如果链表中有 2 个或 2 个以上的节点,则交换前两个节点并递归调用列表的其余部分。
下图是上述方法的试运行:
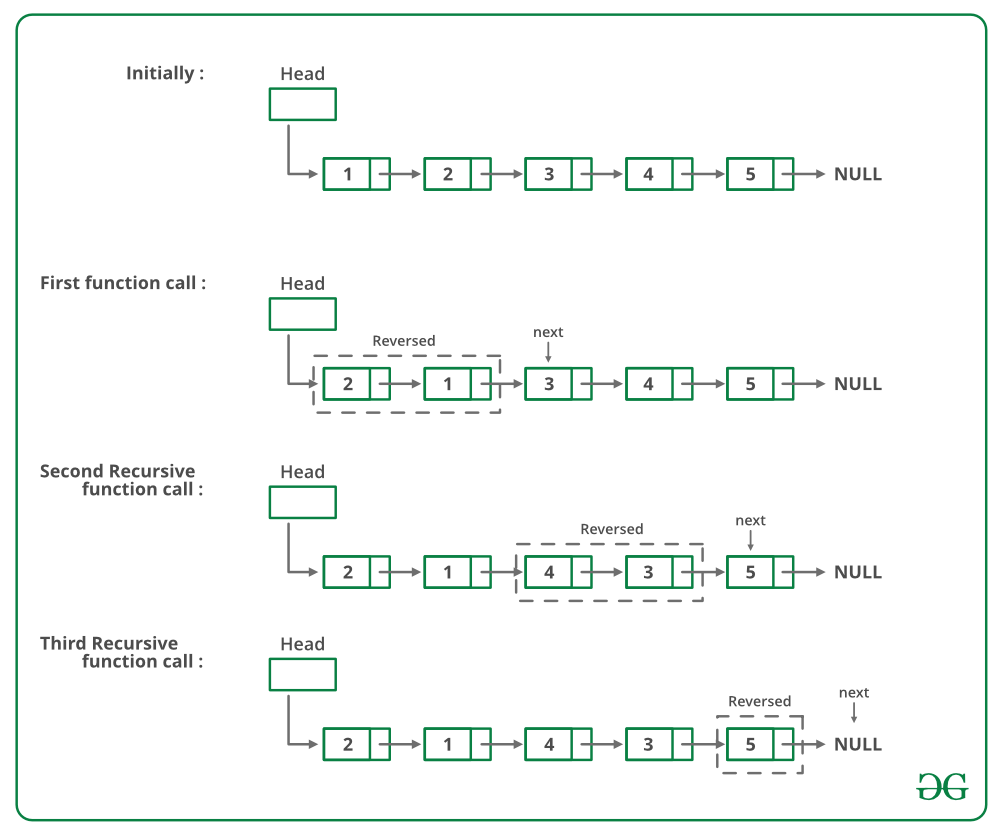
下面是上述方法的实现:
C
/* Recursive function to pairwise swap elements
of a linked list */
void pairWiseSwap(struct node* head)
{
/* There must be at-least two nodes in the list */
if (head != NULL && head->next != NULL) {
/* Swap the node's data with data of next node */
swap(head->data, head->next->data);
/* Call pairWiseSwap() for rest of the list */
pairWiseSwap(head->next->next);
}
}
Java
/* Recursive function to pairwise swap elements
of a linked list */
static void pairWiseSwap(node head)
{
/* There must be at-least two nodes in the list */
if (head != null && head.next != null) {
/* Swap the node's data with data of next node */
swap(head.data, head.next.data);
/* Call pairWiseSwap() for rest of the list */
pairWiseSwap(head.next.next);
}
}
// This code contributed by aashish1995
C#
/* Recursive function to pairwise swap elements
of a linked list */
static void pairWiseSwap(node head)
{
/* There must be at-least two nodes in the list */
if (head != null && head.next != null) {
/* Swap the node's data with data of next node */
swap(head.data, head.next.data);
/* Call pairWiseSwap() for rest of the list */
pairWiseSwap(head.next.next);
}
}
// This code contributed by aashish1995
Javascript
时间复杂度: O(n)
那里提供的解决方案交换节点的数据。如果数据包含很多字段,就会有很多交换操作。有关更改链接而不是交换数据的实现,请参阅this 。
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。