给定链表的成对交换元素的 C 程序
给定一个单链表,编写一个函数来成对交换元素。
Input: 1->2->3->4->5->6->NULL Output: 2->1->4->3->6->5->NULL
Input: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL Output: 2->1->4->3->5->NULL
Input: 1->NULL Output: 1->NULL
例如,如果链表是 1->2->3->4->5,则函数应将其更改为 2->1->4->3->5,如果链表是函数应将其更改为。
方法1(迭代):
从头节点开始,遍历列表。在遍历每个节点的交换数据及其下一个节点的数据时。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C
/* C program to pairwise swap elements
in a given linked list */
#include
#include
// A linked list node
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
/* Function to swap two integers
at addresses a and b */
void swap(int* a, int* b);
/* Function to pairwise swap elements
of a linked list */
void pairWiseSwap(struct Node* head)
{
struct Node* temp = head;
/* Traverse further only if there
are at-least two nodes left */
while (temp != NULL &&
temp->next != NULL)
{
/* Swap data of node with its
next node's data */
swap(&temp->data,
&temp->next->data);
// Move temp by 2 for the
// next pair
temp = temp->next->next;
}
}
// UTILITY FUNCTIONS
// Function to swap two integers
void swap(int* a, int* b)
{
int temp;
temp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = temp;
}
/* Function to add a node at the
beginning of Linked List */
void push(struct Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
// Allocate node
struct Node* new_node =
(struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
// Put in the data
new_node->data = new_data;
// Link the old list off the new node
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
// Move the head to point to the
// new node
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
/* Function to print nodes in a
given linked list */
void printList(struct Node* node)
{
while (node != NULL)
{
printf("%d ", node->data);
node = node->next;
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
struct Node* start = NULL;
/* The constructed linked list is:
1->2->3->4->5 */
push(&start, 5);
push(&start, 4);
push(&start, 3);
push(&start, 2);
push(&start, 1);
printf(
"Linked list before calling pairWiseSwap()");
printList(start);
pairWiseSwap(start);
printf(
"Linked list after calling pairWiseSwap()");
printList(start);
return 0;
} C
/* Recursive function to pairwise swap
elements of a linked list */
void pairWiseSwap(struct node* head)
{
/* There must be at-least two nodes
in the list */
if (head != NULL && head->next != NULL)
{
/* Swap the node's data with data
of next node */
swap(head->data, head->next->data);
/* Call pairWiseSwap() for rest of
the list */
pairWiseSwap(head->next->next);
}
}输出:
Linked list before calling pairWiseSwap()
1 2 3 4 5
Linked list after calling pairWiseSwap()
2 1 4 3 5 时间复杂度: O(n)
方法 2(递归):
如果链接列表中有 2 个或超过 2 个节点,则交换前两个节点并递归调用列表的其余部分。
下图是上述方法的试运行:
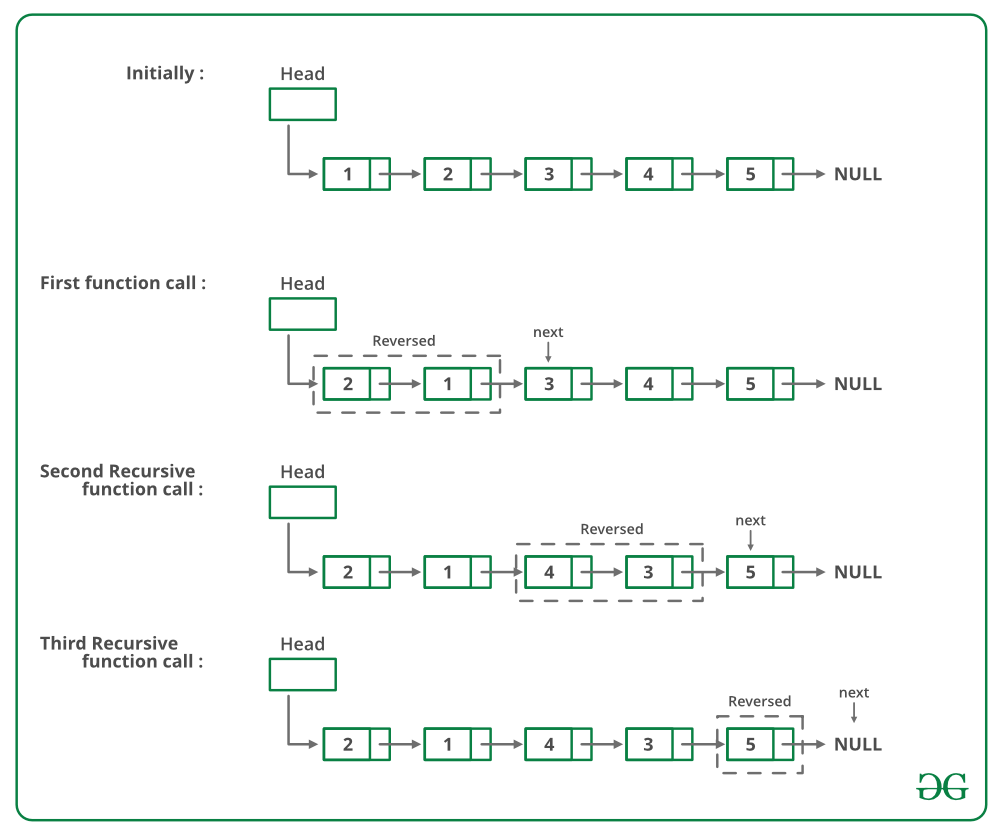
下面是上述方法的实现:
C
/* Recursive function to pairwise swap
elements of a linked list */
void pairWiseSwap(struct node* head)
{
/* There must be at-least two nodes
in the list */
if (head != NULL && head->next != NULL)
{
/* Swap the node's data with data
of next node */
swap(head->data, head->next->data);
/* Call pairWiseSwap() for rest of
the list */
pairWiseSwap(head->next->next);
}
}
时间复杂度: O(n)
那里提供的解决方案交换节点的数据。如果数据包含很多字段,就会有很多交换操作。有关更改链接而不是交换数据的实现,请参阅此内容。
有关详细信息,请参阅有关给定链表的成对交换元素的完整文章!