可以添加到 DAG 以使其保持 DAG 的最大边数
给了我们一个 DAG,我们需要找到可以添加到该 DAG 的最大边数,之后新图仍然是 DAG,这意味着重组后的图应该有最大的边数,即使添加单个边也会创建一个图中的循环。
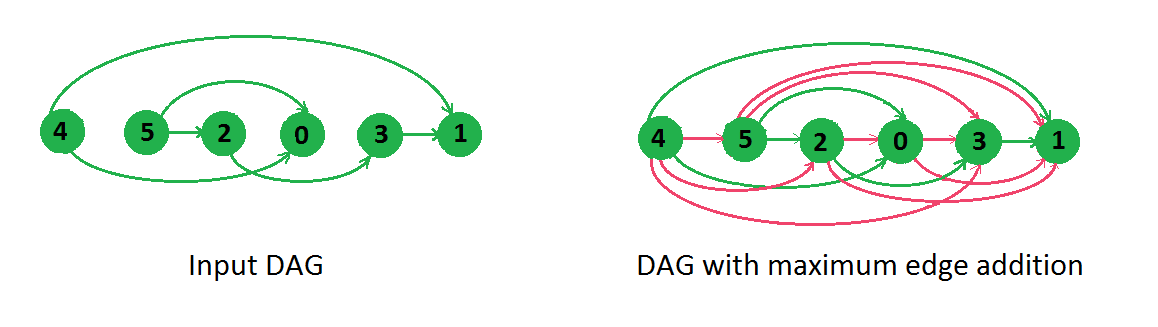
The Output for above example should be following edges in any order.
4-2, 4-5, 4-3, 5-3, 5-1, 2-0, 2-1, 0-3, 0-1如上例所示,我们在一个方向上添加了所有边,只是为了避免循环。这是解决这个问题的诀窍。我们按拓扑顺序对所有节点进行排序,并创建从节点到右侧的所有节点的边(如果还没有的话)。
我们怎么能这么说,不可能再添加任何边缘?原因是我们已经从左到右添加了所有可能的边,如果我们想添加更多的边,我们需要从右到左,但是从右到左添加边我们肯定会创建一个循环,因为它的对应部分从左到右边已经被添加到图中,创建循环不是我们需要的。
所以解决方案如下,我们按照拓扑顺序考虑节点,如果从左到右没有任何边,我们将创建它。
下面是解决方案,我们打印了所有可以添加到给定 DAG 的边,而无需进行任何循环。
C++
// C++ program to find maximum edges after adding
// which graph still remains a DAG
#include
using namespace std;
class Graph {
int V; // No. of vertices
// Pointer to a list containing adjacency list
list* adj;
// Vector to store indegree of vertices
vector indegree;
// function returns a topological sort
vector topologicalSort();
public:
Graph(int V); // Constructor
// function to add an edge to graph
void addEdge(int v, int w);
// Prints all edges that can be added without making any
// cycle
void maximumEdgeAddtion();
};
// Constructor of graph
Graph::Graph(int V)
{
this->V = V;
adj = new list[V];
// Initialising all indegree with 0
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
indegree.push_back(0);
}
// Utility function to add edge
void Graph::addEdge(int v, int w)
{
adj[v].push_back(w); // Add w to v's list.
// increasing inner degree of w by 1
indegree[w]++;
}
// Main function to print maximum edges that can be added
vector Graph::topologicalSort()
{
vector topological;
queue q;
// In starting push all node with indegree 0
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (indegree[i] == 0)
q.push(i);
while (!q.empty()) {
int t = q.front();
q.pop();
// push the node into topological vector
topological.push_back(t);
// reducing indegree of adjacent vertices
for (list::iterator j = adj[t].begin();
j != adj[t].end(); j++) {
indegree[*j]--;
// if indegree becomes 0, just push
// into queue
if (indegree[*j] == 0)
q.push(*j);
}
}
return topological;
}
// The function prints all edges that can be
// added without making any cycle
// It uses recursive topologicalSort()
void Graph::maximumEdgeAddtion()
{
bool* visited = new bool[V];
vector topo = topologicalSort();
// looping for all nodes
for (int i = 0; i < topo.size(); i++) {
int t = topo[i];
// In below loop we mark the adjacent node of t
for (list::iterator j = adj[t].begin();
j != adj[t].end(); j++)
visited[*j] = true;
// In below loop unmarked nodes are printed
for (int j = i + 1; j < topo.size(); j++) {
// if not marked, then we can make an edge
// between t and j
if (!visited[topo[j]])
cout << t << "-" << topo[j] << " ";
visited[topo[j]] = false;
}
}
}
// Driver code to test above methods
int main()
{
// Create a graph given in the above diagram
Graph g(6);
g.addEdge(5, 2);
g.addEdge(5, 0);
g.addEdge(4, 0);
g.addEdge(4, 1);
g.addEdge(2, 3);
g.addEdge(3, 1);
g.maximumEdgeAddtion();
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to find maximum edges after adding
// which graph still remains a DAG
import java.util.*;
public class Graph {
int V; // No. of vertices
ArrayList> adj; // adjacency list
// array to store indegree of vertices
int[] indegree;
// Constructor of graph
Graph(int v)
{
this.V = v;
indegree = new int[V];
adj = new ArrayList<>(V);
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
adj.add(new ArrayList());
indegree[i] = 0;
}
}
// Utility function to add edge
public void addEdge(int v,int w)
{
adj.get(v).add(w);// Add w to v's list.
// increasing inner degree of w by 1
indegree[w]++;
}
// Main function to print maximum edges that can be added
public List topologicalSort()
{
List topological = new ArrayList<>(V);
Queue q = new LinkedList<>();
// In starting push all node with indegree 0
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
if(indegree[i] == 0)
{
q.add(i);
}
}
while(!q.isEmpty())
{
int t=q.poll();
// push the node into topological list
topological.add(t);
// reducing inDegree of adjacent vertical
for(int j: adj.get(t))
{
indegree[j]--;
// if inDegree becomes 0, just push
// into queue
if(indegree[j] == 0)
{
q.add(j);
}
}
}
return topological;
}
// The function prints all edges that can be
// added without making any cycle
// It uses recursive topologicalSort()
public void maximumEdgeAddtion()
{
boolean[] visited = new boolean[V];
List topo=topologicalSort();
// looping for all nodes
for(int i = 0; i < topo.size(); i++)
{
int t = topo.get(i);
// In below loop we mark the adjacent node of t
for( Iterator j = adj.get(t).listIterator();j.hasNext();)
{
visited[j.next()] = true;
}
for(int j = i + 1; j < topo.size(); j++)
{
// if not marked, then we can make an edge
// between t and j
if(!visited[topo.get(j)])
{
System.out.print( t + "-" + topo.get(j) + " ");
}
visited[topo.get(j)] = false;
}
}
}
// Driver code to test above methods
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Create a graph given in the above diagram
Graph g = new Graph(6);
g.addEdge(5, 2);
g.addEdge(5, 0);
g.addEdge(4, 0);
g.addEdge(4, 1);
g.addEdge(2, 3);
g.addEdge(3, 1);
g.maximumEdgeAddtion();
return ;
}
}
// This code is contributed by sameergupta22. Python3
# Python3 program to find maximum
# edges after adding which graph
# still remains a DAG
class Graph:
def __init__(self, V):
# No. of vertices
self.V = V
# Pointer to a list containing
# adjacency list
self.adj = [[] for i in range(V)]
# Vector to store indegree of vertices
self.indegree = [0 for i in range(V)]
# Utility function to add edge
def addEdge(self, v, w):
# Add w to v's list.
self.adj[v].append(w)
# Increasing inner degree of w by 1
self.indegree[w] += 1
# Main function to print maximum
# edges that can be added
def topologicalSort(self):
topological = []
q = []
# In starting append all node
# with indegree 0
for i in range(self.V):
if (self.indegree[i] == 0):
q.append(i)
while (len(q) != 0):
t = q[0]
q.pop(0)
# Append the node into topological
# vector
topological.append(t)
# Reducing indegree of adjacent
# vertices
for j in self.adj[t]:
self.indegree[j] -= 1
# If indegree becomes 0, just
# append into queue
if (self.indegree[j] == 0):
q.append(j)
return topological
# The function prints all edges that
# can be added without making any cycle
# It uses recursive topologicalSort()
def maximumEdgeAddtion(self):
visited = [False for i in range(self.V)]
topo = self.topologicalSort()
# Looping for all nodes
for i in range(len(topo)):
t = topo[i]
# In below loop we mark the
# adjacent node of t
for j in self.adj[t]:
visited[j] = True
# In below loop unmarked nodes
# are printed
for j in range(i + 1, len(topo)):
# If not marked, then we can make
# an edge between t and j
if (not visited[topo[j]]):
print(str(t) + '-' +
str(topo[j]), end=' ')
visited[topo[j]] = False
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Create a graph given in the
# above diagram
g = Graph(6)
g.addEdge(5, 2)
g.addEdge(5, 0)
g.addEdge(4, 0)
g.addEdge(4, 1)
g.addEdge(2, 3)
g.addEdge(3, 1)
g.maximumEdgeAddtion()
# This code is contributed by rutvik_56输出:
4-5, 4-2, 4-3, 5-3, 5-1, 2-0, 2-1, 0-3, 0-1