打印二叉树的左视图
给定一棵二叉树,打印它的左视图。二叉树的左视图是从左侧访问树时可见的一组节点。
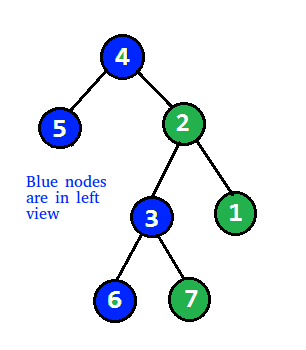
例子:
Input :
1
/ \
2 3
/ \ \
4 5 6
Output : 1 2 4
Input :
1
/ \
2 3
\
4
\
5
\
6
Output :1 2 4 5 6方法一(使用递归)
左视图包含作为其级别中的第一个节点的所有节点。一个简单的解决方案是进行级别顺序遍历 并打印每个级别的第一个节点。
该问题也可以使用简单的递归遍历来解决。我们可以通过将参数传递给所有递归调用来跟踪节点的级别。这个想法也是为了跟踪最高水平。每当我们看到一个节点的级别超过迄今为止的最大级别时,我们打印该节点,因为这是其级别中的第一个节点(请注意,我们在右子树之前遍历左子树)。
下面是上述想法的实现——
C++
// C++ program to print left view of Binary Tree
#include
using namespace std;
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *left, *right;
};
// A utility function to
// create a new Binary Tree Node
struct Node *newNode(int item)
{
struct Node *temp = (struct Node *)malloc(
sizeof(struct Node));
temp->data = item;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
// Recursive function to print
// left view of a binary tree.
void leftViewUtil(struct Node *root,
int level, int *max_level)
{
// Base Case
if (root == NULL) return;
// If this is the first Node of its level
if (*max_level < level)
{
cout << root->data << " ";
*max_level = level;
}
// Recur for left subtree first,
// then right subtree
leftViewUtil(root->left, level + 1, max_level);
leftViewUtil(root->right, level + 1, max_level);
}
// A wrapper over leftViewUtil()
void leftView(struct Node *root)
{
int max_level = 0;
leftViewUtil(root, 1, &max_level);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
Node* root = newNode(10);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(7);
root->left->right = newNode(8);
root->right->right = newNode(15);
root->right->left = newNode(12);
root->right->right->left = newNode(14);
leftView(root);
return 0;
} C
// C program to print left view of Binary Tree
#include
#include
struct node {
int data;
struct node *left, *right;
};
// A utility function to create a new Binary Tree node
struct node* newNode(int item)
{
struct node* temp
= (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
temp->data = item;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
// Recursive function to print left view of a binary tree.
void leftViewUtil(struct node* root, int level,
int* max_level)
{
// Base Case
if (root == NULL)
return;
// If this is the first node of its level
if (*max_level < level) {
printf("%d\t", root->data);
*max_level = level;
}
// Recur for left and right subtrees
leftViewUtil(root->left, level + 1, max_level);
leftViewUtil(root->right, level + 1, max_level);
}
// A wrapper over leftViewUtil()
void leftView(struct node* root)
{
int max_level = 0;
leftViewUtil(root, 1, &max_level);
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
struct node* root = newNode(10);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(7);
root->left->right = newNode(8);
root->right->right = newNode(15);
root->right->left = newNode(12);
root->right->right->left = newNode(14);
leftView(root);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to print left view of binary tree
/* Class containing left and right child of current
node and key value*/
class Node {
int data;
Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
/* Class to print the left view */
class BinaryTree {
Node root;
static int max_level = 0;
// recursive function to print left view
void leftViewUtil(Node node, int level)
{
// Base Case
if (node == null)
return;
// If this is the first node of its level
if (max_level < level) {
System.out.print(" " + node.data);
max_level = level;
}
// Recur for left and right subtrees
leftViewUtil(node.left, level + 1);
leftViewUtil(node.right, level + 1);
}
// A wrapper over leftViewUtil()
void leftView()
{
leftViewUtil(root, 1);
}
/* testing for example nodes */
public static void main(String args[])
{
/* creating a binary tree and entering the nodes */
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(10);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(7);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(8);
tree.root.right.right = new Node(15);
tree.root.right.left = new Node(12);
tree.root.right.right.left = new Node(14);
tree.leftView();
}
}Python
# Python program to print left view of Binary Tree
# A binary tree node
class Node:
# Constructor to create a new node
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.left = None
self.right = None
# Recursive function print left view of a binary tree
def leftViewUtil(root, level, max_level):
# Base Case
if root is None:
return
# If this is the first node of its level
if (max_level[0] < level):
print "% d\t" %(root.data),
max_level[0] = level
# Recur for left and right subtree
leftViewUtil(root.left, level + 1, max_level)
leftViewUtil(root.right, level + 1, max_level)
# A wrapper over leftViewUtil()
def leftView(root):
max_level = [0]
leftViewUtil(root, 1, max_level)
# Driver program to test above function
root = Node(10)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.left.left = Node(7)
root.left.right = Node(8)
root.right.right = Node(15)
root.right.left = Node(12)
root.right.right.left = Node(14)
leftView(root)
# This code is contributed by Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007)C#
using System;
// C# program to print left view of binary tree
/* Class containing left and right child of current
node and key value*/
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
/* Class to print the left view */
public class BinaryTree {
public Node root;
public static int max_level = 0;
// recursive function to print left view
public virtual void leftViewUtil(Node node, int level)
{
// Base Case
if (node == null) {
return;
}
// If this is the first node of its level
if (max_level < level) {
Console.Write(" " + node.data);
max_level = level;
}
// Recur for left and right subtrees
leftViewUtil(node.left, level + 1);
leftViewUtil(node.right, level + 1);
}
// A wrapper over leftViewUtil()
public virtual void leftView()
{
leftViewUtil(root, 1);
}
/* testing for example nodes */
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
/* creating a binary tree and entering the nodes */
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(10);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(7);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(8);
tree.root.right.right = new Node(15);
tree.root.right.left = new Node(12);
tree.root.right.right.left = new Node(14);
tree.leftView();
}
}
// This code is contributed by Shrikant13Javascript
C++
// C++ program to print left view of
// Binary Tree
#include
using namespace std;
// A Binary Tree Node
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *left, *right;
};
// Utility function to create a new tree node
Node* newNode(int data)
{
Node *temp = new Node;
temp->data = data;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
// function to print left view of
// binary tree
void printLeftView(Node* root)
{
if (!root)
return;
queue q;
q.push(root);
while (!q.empty())
{
// number of nodes at current level
int n = q.size();
// Traverse all nodes of current level
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
Node* temp = q.front();
q.pop();
// Print the left most element
// at the level
if (i == 1)
cout<data<<" ";
// Add left node to queue
if (temp->left != NULL)
q.push(temp->left);
// Add right node to queue
if (temp->right != NULL)
q.push(temp->right);
}
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// Let's construct the tree as
// shown in example
Node* root = newNode(10);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(7);
root->left->right = newNode(8);
root->right->right = newNode(15);
root->right->left = newNode(12);
root->right->right->left = newNode(14);
printLeftView(root);
}
// This code is contributed by
// Manne SreeCharan Java
// Java program to print left view of Binary
// Tree
import java.util.*;
public class PrintRightView {
// Binary tree node
private static class Node {
int data;
Node left, right;
public Node(int data)
{
this.data = data;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
// function to print left view of binary tree
private static void printLeftView(Node root)
{
if (root == null)
return;
Queue queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
// number of nodes at current level
int n = queue.size();
// Traverse all nodes of current level
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
Node temp = queue.poll();
// Print the left most element at
// the level
if (i == 1)
System.out.print(temp.data + " ");
// Add left node to queue
if (temp.left != null)
queue.add(temp.left);
// Add right node to queue
if (temp.right != null)
queue.add(temp.right);
}
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// construct binary tree as shown in
// above diagram
Node root = new Node(10);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(7);
root.left.right = new Node(8);
root.right.right = new Node(15);
root.right.left = new Node(12);
root.right.right.left = new Node(14);
printLeftView(root);
}
}
// This code is contributed by
// Manne SreeCharan Python
# Python3 program to print left view of
# Binary Tree
# Binary Tree Node
""" utility that allocates a newNode
with the given key """
class newNode:
# Construct to create a newNode
def __init__(self, key):
self.data = key
self.left = None
self.right = None
self.hd = 0
# function to print left view of
# binary tree
def printLeftView(root):
if (not root):
return
q = []
q.append(root)
while (len(q)):
# number of nodes at current level
n = len(q)
# Traverse all nodes of current level
for i in range(1, n + 1):
temp = q[0]
q.pop(0)
# Print the left most element
# at the level
if (i == 1):
print(temp.data, end=" ")
# Add left node to queue
if (temp.left != None):
q.append(temp.left)
# Add right node to queue
if (temp.right != None):
q.append(temp.right)
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
root = newNode(10)
root.left = newNode(2)
root.right = newNode(3)
root.left.left = newNode(7)
root.left.right = newNode(8)
root.right.right = newNode(15)
root.right.left = newNode(12)
root.right.right.left = newNode(14)
printLeftView(root)
# This code is contributed by
# Manne SreeCharanC#
// C# program to print left view
// of Binary Tree
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class PrintRightView {
// Binary tree node
private class Node {
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int data)
{
this.data = data;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
// function to print left view of binary tree
private static void printRightView(Node root)
{
if (root == null)
return;
Queue queue = new Queue();
queue.Enqueue(root);
while (queue.Count != 0) {
// number of nodes at current level
int n = queue.Count;
// Traverse all nodes of current level
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
Node temp = queue.Dequeue();
// Print the left most element at
// the level
if (i == n)
Console.Write(temp.data + " ");
// Add left node to queue
if (temp.left != null)
queue.Enqueue(temp.left);
// Add right node to queue
if (temp.right != null)
queue.Enqueue(temp.right);
}
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// construct binary tree as shown in
// above diagram
Node root = new Node(10);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(7);
root.left.right = new Node(8);
root.right.right = new Node(15);
root.right.left = new Node(12);
root.right.right.left = new Node(14);
printRightView(root);
}
}
// This code is contributed Manne SreeCharan C++
#include
using namespace std;
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *left, *right;
};
// A utility function to
// create a new Binary Tree Node
struct Node *newNode(int item)
{
struct Node *temp = (struct Node *)malloc(
sizeof(struct Node));
temp->data = item;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
vector leftView(Node *root)
{
// Your code here
vectorans;
if(!root)
{
return ans;
}
queueq;
q.push(root);
q.push(NULL);
bool ok=true;
while(!q.empty())
{
auto it=q.front();
q.pop();
if(it==NULL)
{
if(ok==false)
{
ok=true;
}
if(q.size()==0)
{
break;
}
else
{
q.push(NULL);
}
}
else
{
if(ok)
{
ans.push_back(it->data);
ok=false;
}
if(it->left)
{
q.push(it->left);
}
if(it->right)
{
q.push(it->right);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
int main()
{
Node* root = newNode(10);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(7);
root->left->right = newNode(8);
root->right->right = newNode(15);
root->right->left = newNode(12);
root->right->right->left = newNode(14);
vector vec = leftView(root);
for(int x : vec)
cout< 输出
10 2 7 14 时间复杂度:该函数对树进行简单的遍历,因此复杂度为 O(n)。
辅助空间: O(n),由于递归调用期间的堆栈空间。
方法2 (使用队列):
在该方法中,讨论了基于级别顺序遍历的解决方案。如果我们仔细观察,我们会发现我们的主要任务是打印每个级别的最左边的节点。因此,我们将对树进行级别顺序遍历,并在每个级别打印最左边的节点。以下是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program to print left view of
// Binary Tree
#include
using namespace std;
// A Binary Tree Node
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *left, *right;
};
// Utility function to create a new tree node
Node* newNode(int data)
{
Node *temp = new Node;
temp->data = data;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
// function to print left view of
// binary tree
void printLeftView(Node* root)
{
if (!root)
return;
queue q;
q.push(root);
while (!q.empty())
{
// number of nodes at current level
int n = q.size();
// Traverse all nodes of current level
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
Node* temp = q.front();
q.pop();
// Print the left most element
// at the level
if (i == 1)
cout<data<<" ";
// Add left node to queue
if (temp->left != NULL)
q.push(temp->left);
// Add right node to queue
if (temp->right != NULL)
q.push(temp->right);
}
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// Let's construct the tree as
// shown in example
Node* root = newNode(10);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(7);
root->left->right = newNode(8);
root->right->right = newNode(15);
root->right->left = newNode(12);
root->right->right->left = newNode(14);
printLeftView(root);
}
// This code is contributed by
// Manne SreeCharan
Java
// Java program to print left view of Binary
// Tree
import java.util.*;
public class PrintRightView {
// Binary tree node
private static class Node {
int data;
Node left, right;
public Node(int data)
{
this.data = data;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
// function to print left view of binary tree
private static void printLeftView(Node root)
{
if (root == null)
return;
Queue queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
// number of nodes at current level
int n = queue.size();
// Traverse all nodes of current level
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
Node temp = queue.poll();
// Print the left most element at
// the level
if (i == 1)
System.out.print(temp.data + " ");
// Add left node to queue
if (temp.left != null)
queue.add(temp.left);
// Add right node to queue
if (temp.right != null)
queue.add(temp.right);
}
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// construct binary tree as shown in
// above diagram
Node root = new Node(10);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(7);
root.left.right = new Node(8);
root.right.right = new Node(15);
root.right.left = new Node(12);
root.right.right.left = new Node(14);
printLeftView(root);
}
}
// This code is contributed by
// Manne SreeCharan
Python
# Python3 program to print left view of
# Binary Tree
# Binary Tree Node
""" utility that allocates a newNode
with the given key """
class newNode:
# Construct to create a newNode
def __init__(self, key):
self.data = key
self.left = None
self.right = None
self.hd = 0
# function to print left view of
# binary tree
def printLeftView(root):
if (not root):
return
q = []
q.append(root)
while (len(q)):
# number of nodes at current level
n = len(q)
# Traverse all nodes of current level
for i in range(1, n + 1):
temp = q[0]
q.pop(0)
# Print the left most element
# at the level
if (i == 1):
print(temp.data, end=" ")
# Add left node to queue
if (temp.left != None):
q.append(temp.left)
# Add right node to queue
if (temp.right != None):
q.append(temp.right)
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
root = newNode(10)
root.left = newNode(2)
root.right = newNode(3)
root.left.left = newNode(7)
root.left.right = newNode(8)
root.right.right = newNode(15)
root.right.left = newNode(12)
root.right.right.left = newNode(14)
printLeftView(root)
# This code is contributed by
# Manne SreeCharan
C#
// C# program to print left view
// of Binary Tree
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class PrintRightView {
// Binary tree node
private class Node {
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int data)
{
this.data = data;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
// function to print left view of binary tree
private static void printRightView(Node root)
{
if (root == null)
return;
Queue queue = new Queue();
queue.Enqueue(root);
while (queue.Count != 0) {
// number of nodes at current level
int n = queue.Count;
// Traverse all nodes of current level
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
Node temp = queue.Dequeue();
// Print the left most element at
// the level
if (i == n)
Console.Write(temp.data + " ");
// Add left node to queue
if (temp.left != null)
queue.Enqueue(temp.left);
// Add right node to queue
if (temp.right != null)
queue.Enqueue(temp.right);
}
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// construct binary tree as shown in
// above diagram
Node root = new Node(10);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(7);
root.left.right = new Node(8);
root.right.right = new Node(15);
root.right.left = new Node(12);
root.right.right.left = new Node(14);
printRightView(root);
}
}
// This code is contributed Manne SreeCharan
输出
10 2 7 14 时间复杂度: O(n),其中 n 是二叉树中的节点数。
方法三:
使用队列和空指针标记每一层的第一个元素
我们在第一个插入一个空指针,当到达那个空指针时,我们将 bool 标记为真,并将下一个元素作为我们的左视图元素
C++
#include
using namespace std;
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *left, *right;
};
// A utility function to
// create a new Binary Tree Node
struct Node *newNode(int item)
{
struct Node *temp = (struct Node *)malloc(
sizeof(struct Node));
temp->data = item;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
vector leftView(Node *root)
{
// Your code here
vectorans;
if(!root)
{
return ans;
}
queueq;
q.push(root);
q.push(NULL);
bool ok=true;
while(!q.empty())
{
auto it=q.front();
q.pop();
if(it==NULL)
{
if(ok==false)
{
ok=true;
}
if(q.size()==0)
{
break;
}
else
{
q.push(NULL);
}
}
else
{
if(ok)
{
ans.push_back(it->data);
ok=false;
}
if(it->left)
{
q.push(it->left);
}
if(it->right)
{
q.push(it->right);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
int main()
{
Node* root = newNode(10);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(7);
root->left->right = newNode(8);
root->right->right = newNode(15);
root->right->left = newNode(12);
root->right->right->left = newNode(14);
vector vec = leftView(root);
for(int x : vec)
cout< 时间复杂度:O(N) 其中 N 是节点总数