有向无环图的所有拓扑排序
有向循环图( DAG ) 的拓扑排序是顶点的线性排序,使得对于每个有向边 uv,顶点 u 在排序中位于 v 之前。如果图不是 DAG,则无法对图进行拓扑排序。
给定一个 DAG,打印所有拓扑类型的图。
For example, consider the below graph.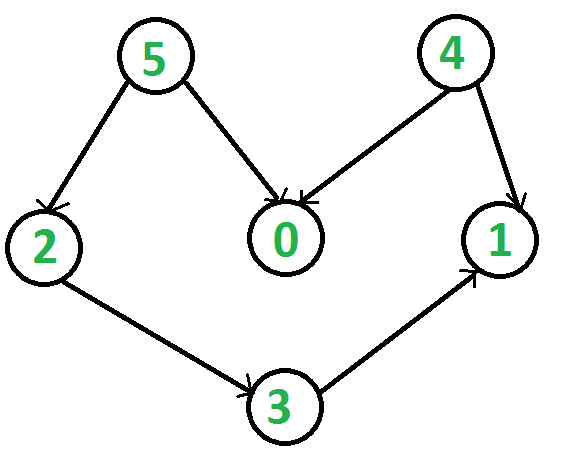
给定图的所有拓扑类型是:
4 5 0 2 3 1
4 5 2 0 3 1
4 5 2 3 0 1
4 5 2 3 1 0
5 2 3 4 0 1
5 2 3 4 1 0
5 2 4 0 3 1
5 2 4 3 0 1
5 2 4 3 1 0
5 4 0 2 3 1
5 4 2 0 3 1
5 4 2 3 0 1
5 4 2 3 1 0
在有向无环图中,很多时候我们可以有彼此不相关的顶点,因此我们可以以多种方式对它们进行排序。这些不同的拓扑排序在很多情况下都很重要,例如,如果顶点之间也有一些相对权重,这是为了最小化,那么我们需要处理相对排序以及它们的相对权重,这就需要检查所有可能的拓扑排序。
我们可以通过回溯遍历所有可能的排序,算法步骤如下:
- 将所有顶点初始化为未访问。
- 现在选择未访问且入度为零的顶点,并将所有这些顶点的入度减少 1(对应于删除边)现在将此顶点添加到结果中并再次调用递归函数并回溯。
- 从函数返回后,重置visited、result 和indegree 的值,用于枚举其他可能性。
下面是上述步骤的实现。
C++
// C++ program to print all topological sorts of a graph
#include
using namespace std;
class Graph
{
int V; // No. of vertices
// Pointer to an array containing adjacency list
list *adj;
// Vector to store indegree of vertices
vector indegree;
// A function used by alltopologicalSort
void alltopologicalSortUtil(vector& res,
bool visited[]);
public:
Graph(int V); // Constructor
// function to add an edge to graph
void addEdge(int v, int w);
// Prints all Topological Sorts
void alltopologicalSort();
};
// Constructor of graph
Graph::Graph(int V)
{
this->V = V;
adj = new list[V];
// Initialising all indegree with 0
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
indegree.push_back(0);
}
// Utility function to add edge
void Graph::addEdge(int v, int w)
{
adj[v].push_back(w); // Add w to v's list.
// increasing inner degree of w by 1
indegree[w]++;
}
// Main recursive function to print all possible
// topological sorts
void Graph::alltopologicalSortUtil(vector& res,
bool visited[])
{
// To indicate whether all topological are found
// or not
bool flag = false;
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
// If indegree is 0 and not yet visited then
// only choose that vertex
if (indegree[i] == 0 && !visited[i])
{
// reducing indegree of adjacent vertices
list:: iterator j;
for (j = adj[i].begin(); j != adj[i].end(); j++)
indegree[*j]--;
// including in result
res.push_back(i);
visited[i] = true;
alltopologicalSortUtil(res, visited);
// resetting visited, res and indegree for
// backtracking
visited[i] = false;
res.erase(res.end() - 1);
for (j = adj[i].begin(); j != adj[i].end(); j++)
indegree[*j]++;
flag = true;
}
}
// We reach here if all vertices are visited.
// So we print the solution here
if (!flag)
{
for (int i = 0; i < res.size(); i++)
cout << res[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
}
// The function does all Topological Sort.
// It uses recursive alltopologicalSortUtil()
void Graph::alltopologicalSort()
{
// Mark all the vertices as not visited
bool *visited = new bool[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
visited[i] = false;
vector res;
alltopologicalSortUtil(res, visited);
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
// Create a graph given in the above diagram
Graph g(6);
g.addEdge(5, 2);
g.addEdge(5, 0);
g.addEdge(4, 0);
g.addEdge(4, 1);
g.addEdge(2, 3);
g.addEdge(3, 1);
cout << "All Topological sorts\n";
g.alltopologicalSort();
return 0;
} Java
//Java program to print all topological sorts of a graph
import java.util.*;
class Graph {
int V; // No. of vertices
List adjListArray[];
public Graph(int V) {
this.V = V;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
List adjListArray[] = new LinkedList[V];
this.adjListArray = adjListArray;
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
adjListArray[i] = new LinkedList<>();
}
}
// Utility function to add edge
public void addEdge(int src, int dest) {
this.adjListArray[src].add(dest);
}
// Main recursive function to print all possible
// topological sorts
private void allTopologicalSortsUtil(boolean[] visited,
int[] indegree, ArrayList stack) {
// To indicate whether all topological are found
// or not
boolean flag = false;
for (int i = 0; i < this.V; i++) {
// If indegree is 0 and not yet visited then
// only choose that vertex
if (!visited[i] && indegree[i] == 0) {
// including in result
visited[i] = true;
stack.add(i);
for (int adjacent : this.adjListArray[i]) {
indegree[adjacent]--;
}
allTopologicalSortsUtil(visited, indegree, stack);
// resetting visited, res and indegree for
// backtracking
visited[i] = false;
stack.remove(stack.size() - 1);
for (int adjacent : this.adjListArray[i]) {
indegree[adjacent]++;
}
flag = true;
}
}
// We reach here if all vertices are visited.
// So we print the solution here
if (!flag) {
stack.forEach(i -> System.out.print(i + " "));
System.out.println();
}
}
// The function does all Topological Sort.
// It uses recursive alltopologicalSortUtil()
public void allTopologicalSorts() {
// Mark all the vertices as not visited
boolean[] visited = new boolean[this.V];
int[] indegree = new int[this.V];
for (int i = 0; i < this.V; i++) {
for (int var : this.adjListArray[i]) {
indegree[var]++;
}
}
ArrayList stack = new ArrayList<>();
allTopologicalSortsUtil(visited, indegree, stack);
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a graph given in the above diagram
Graph graph = new Graph(6);
graph.addEdge(5, 2);
graph.addEdge(5, 0);
graph.addEdge(4, 0);
graph.addEdge(4, 1);
graph.addEdge(2, 3);
graph.addEdge(3, 1);
System.out.println("All Topological sorts");
graph.allTopologicalSorts();
}
} Python3
# class to represent a graph object
class Graph:
# Constructor
def __init__(self, edges, N):
# A List of Lists to represent an adjacency list
self.adjList = [[] for _ in range(N)]
# stores in-degree of a vertex
# initialize in-degree of each vertex by 0
self.indegree = [0] * N
# add edges to the undirected graph
for (src, dest) in edges:
# add an edge from source to destination
self.adjList[src].append(dest)
# increment in-degree of destination vertex by 1
self.indegree[dest] = self.indegree[dest] + 1
# Recursive function to find
# all topological orderings of a given DAG
def findAllTopologicalOrders(graph, path, discovered, N):
# do for every vertex
for v in range(N):
# proceed only if in-degree of current node is 0 and
# current node is not processed yet
if graph.indegree[v] == 0 and not discovered[v]:
# for every adjacent vertex u of v,
# reduce in-degree of u by 1
for u in graph.adjList[v]:
graph.indegree[u] = graph.indegree[u] - 1
# include current node in the path
# and mark it as discovered
path.append(v)
discovered[v] = True
# recur
findAllTopologicalOrders(graph, path, discovered, N)
# backtrack: reset in-degree
# information for the current node
for u in graph.adjList[v]:
graph.indegree[u] = graph.indegree[u] + 1
# backtrack: remove current node from the path and
# mark it as undiscovered
path.pop()
discovered[v] = False
# print the topological order if
# all vertices are included in the path
if len(path) == N:
print(path)
# Print all topological orderings of a given DAG
def printAllTopologicalOrders(graph):
# get number of nodes in the graph
N = len(graph.adjList)
# create an auxiliary space to keep track of whether vertex is discovered
discovered = [False] * N
# list to store the topological order
path = []
# find all topological ordering and print them
findAllTopologicalOrders(graph, path, discovered, N)
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
# List of graph edges as per above diagram
edges = [(5, 2), (5, 0), (4, 0), (4, 1), (2, 3), (3, 1)]
print("All Topological sorts")
# Number of nodes in the graph
N = 6
# create a graph from edges
graph = Graph(edges, N)
# print all topological ordering of the graph
printAllTopologicalOrders(graph)
# This code is contributed by Priyadarshini Kumari输出 :
All Topological sorts
4 5 0 2 3 1
4 5 2 0 3 1
4 5 2 3 0 1
4 5 2 3 1 0
5 2 3 4 0 1
5 2 3 4 1 0
5 2 4 0 3 1
5 2 4 3 0 1
5 2 4 3 1 0
5 4 0 2 3 1
5 4 2 0 3 1
5 4 2 3 0 1
5 4 2 3 1 0