Java中的HashMap与示例
HashMap
HashMap类似于 HashTable,但它是不同步的。它也允许存储空键,但应该只有一个空键对象,并且可以有任意数量的空值。此类不保证地图的顺序。要使用该类及其方法,您需要导入Java.util.HashMap包或其超类。
Java
// Java program to illustrate HashMap class of java.util
// package
// Importing HashMap class
import java.util.HashMap;
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Create an empty hash map by declaring object
// of string and integer type
HashMap map = new HashMap<>();
// Adding elements to the Map
// using standard put() method
map.put("vishal", 10);
map.put("sachin", 30);
map.put("vaibhav", 20);
// Print size and content of the Map
System.out.println("Size of map is:- "
+ map.size());
// Printing elements in object of Map
System.out.println(map);
// Checking if a key is present and if
// present, print value by passing
// random element
if (map.containsKey("vishal")) {
// Mapping
Integer a = map.get("vishal");
// Printing value fr the corresponding key
System.out.println("value for key"
+ " \"vishal\" is:- " + a);
}
}
} Java
// Java program to Demonstrate the HashMap() constructor
// Importing basic required classes
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// Main class
// To add elements to HashMap
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// No need to mention the
// Generic type twice
HashMap hm1 = new HashMap<>();
// Initialization of a HashMap using Generics
HashMap hm2
= new HashMap();
// Adding elements using put method
// Custom input elements
hm1.put(1, "one");
hm1.put(2, "two");
hm1.put(3, "three");
hm2.put(4, "four");
hm2.put(5, "five");
hm2.put(6, "six");
// Print and display mapping of HashMap 1
System.out.println("Mappings of HashMap hm1 are : "
+ hm1);
// Print and display mapping of HashMap 2
System.out.println("Mapping of HashMap hm2 are : "
+ hm2);
}
} Java
// Java program to Demonstrate
// HashMap(int initialCapacity) Constructor
// Importing basic classes
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// Main class
// To add elements to HashMap
class AddElementsToHashMap {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// No need to mention the
// Generic type twice
HashMap hm1 = new HashMap<>(10);
// Initialization of a HashMap using Generics
HashMap hm2
= new HashMap(2);
// Adding elements to object of HashMap
// using put method
// HashMap 1
hm1.put(1, "one");
hm1.put(2, "two");
hm1.put(3, "three");
// HashMap 2
hm2.put(4, "four");
hm2.put(5, "five");
hm2.put(6, "six");
// Printing elements of HashMap 1
System.out.println("Mappings of HashMap hm1 are : "
+ hm1);
// Printing elements of HashMap 2
System.out.println("Mapping of HashMap hm2 are : "
+ hm2);
}
} Java
// Java program to Demonstrate
// HashMap(int initialCapacity,float loadFactor) Constructor
// Importing basic classes
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// Main class
// To add elements to HashMap
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// No need to mention the generic type twice
HashMap hm1
= new HashMap<>(5, 0.75f);
// Initialization of a HashMap using Generics
HashMap hm2
= new HashMap(3, 0.5f);
// Add Elements using put() method
// Custom input elements
hm1.put(1, "one");
hm1.put(2, "two");
hm1.put(3, "three");
hm2.put(4, "four");
hm2.put(5, "five");
hm2.put(6, "six");
// Print and display elements in object of hashMap 1
System.out.println("Mappings of HashMap hm1 are : "
+ hm1);
// Print and display elements in object of hashMap 2
System.out.println("Mapping of HashMap hm2 are : "
+ hm2);
}
} Java
// Java program to demonstrate the
// HashMap(Map map) Constructor
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class AddElementsToHashMap {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// No need to mention the
// Generic type twice
Map hm1 = new HashMap<>();
// Add Elements using put method
hm1.put(1, "one");
hm1.put(2, "two");
hm1.put(3, "three");
// Initialization of a HashMap
// using Generics
HashMap hm2
= new HashMap(hm1);
System.out.println("Mappings of HashMap hm1 are : "
+ hm1);
System.out.println("Mapping of HashMap hm2 are : "
+ hm2);
}
} Java
// Java program to add elements
// to the HashMap
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class AddElementsToHashMap {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// No need to mention the
// Generic type twice
HashMap hm1 = new HashMap<>();
// Initialization of a HashMap
// using Generics
HashMap hm2
= new HashMap();
// Add Elements using put method
hm1.put(1, "Geeks");
hm1.put(2, "For");
hm1.put(3, "Geeks");
hm2.put(1, "Geeks");
hm2.put(2, "For");
hm2.put(3, "Geeks");
System.out.println("Mappings of HashMap hm1 are : "
+ hm1);
System.out.println("Mapping of HashMap hm2 are : "
+ hm2);
}
} Java
// Java program to change
// elements of HashMap
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class ChangeElementsOfHashMap {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Initialization of a HashMap
HashMap hm
= new HashMap();
// Change Value using put method
hm.put(1, "Geeks");
hm.put(2, "Geeks");
hm.put(3, "Geeks");
System.out.println("Initial Map " + hm);
hm.put(2, "For");
System.out.println("Updated Map " + hm);
}
} Java
// Java program to remove
// elements from HashMap
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class RemoveElementsOfHashMap{
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Initialization of a HashMap
Map hm
= new HashMap();
// Add elements using put method
hm.put(1, "Geeks");
hm.put(2, "For");
hm.put(3, "Geeks");
hm.put(4, "For");
// Initial HashMap
System.out.println("Mappings of HashMap are : "
+ hm);
// remove element with a key
// using remove method
hm.remove(4);
// Final HashMap
System.out.println("Mappings after removal are : "
+ hm);
}
} Java
// Java program to traversal a
// Java.util.HashMap
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class TraversalTheHashMap {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// initialize a HashMap
HashMap map = new HashMap<>();
// Add elements using put method
map.put("vishal", 10);
map.put("sachin", 30);
map.put("vaibhav", 20);
// Iterate the map using
// for-each loop
for (Map.Entry e : map.entrySet())
System.out.println("Key: " + e.getKey()
+ " Value: " + e.getValue());
}
} Size of map is:- 3
{vaibhav=20, vishal=10, sachin=30}
value for key "vishal" is:- 10HashMap的层次结构如下:
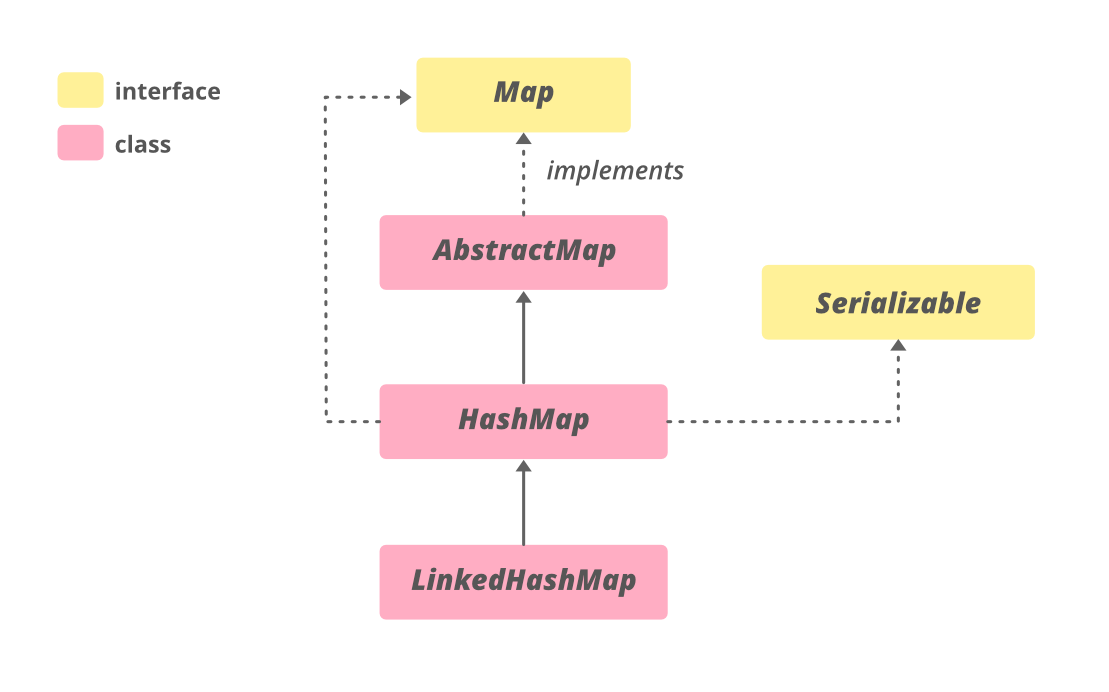
语法:声明
public class HashMap extends AbstractMap
implements Map, Cloneable, Serializable 参数:它有两个参数,分别如下:
- 此映射维护的键的类型
- 映射值的类型
HashMap 实现了 Serializable 、 Cloneable 、 Map
HashMap 中的构造函数如下:
HashMap 提供了 4 个构造函数,每个构造函数的访问修饰符都是 public,列举如下:
- 哈希映射()
- HashMap(int initialCapacity)
- HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor)
- HashMap(地图地图)
现在一一讨论上述构造函数,并在干净的Java程序的帮助下实现相同的构造函数。
构造函数 1: HashMap()
它是默认构造函数,它创建一个初始容量为 16 且负载因子为 0.75 的 HashMap 实例。
句法:
HashMap hm = new HashMap(); 例子
Java
// Java program to Demonstrate the HashMap() constructor
// Importing basic required classes
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// Main class
// To add elements to HashMap
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// No need to mention the
// Generic type twice
HashMap hm1 = new HashMap<>();
// Initialization of a HashMap using Generics
HashMap hm2
= new HashMap();
// Adding elements using put method
// Custom input elements
hm1.put(1, "one");
hm1.put(2, "two");
hm1.put(3, "three");
hm2.put(4, "four");
hm2.put(5, "five");
hm2.put(6, "six");
// Print and display mapping of HashMap 1
System.out.println("Mappings of HashMap hm1 are : "
+ hm1);
// Print and display mapping of HashMap 2
System.out.println("Mapping of HashMap hm2 are : "
+ hm2);
}
}
Mappings of HashMap hm1 are : {1=one, 2=two, 3=three}
Mapping of HashMap hm2 are : {4=four, 5=five, 6=six}构造函数 2: HashMap(int initialCapacity)
它创建一个 HashMap 实例,其中包含 指定的初始容量和负载系数 0.75。
句法:
HashMap hm = new HashMap(int initialCapacity); 例子
Java
// Java program to Demonstrate
// HashMap(int initialCapacity) Constructor
// Importing basic classes
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// Main class
// To add elements to HashMap
class AddElementsToHashMap {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// No need to mention the
// Generic type twice
HashMap hm1 = new HashMap<>(10);
// Initialization of a HashMap using Generics
HashMap hm2
= new HashMap(2);
// Adding elements to object of HashMap
// using put method
// HashMap 1
hm1.put(1, "one");
hm1.put(2, "two");
hm1.put(3, "three");
// HashMap 2
hm2.put(4, "four");
hm2.put(5, "five");
hm2.put(6, "six");
// Printing elements of HashMap 1
System.out.println("Mappings of HashMap hm1 are : "
+ hm1);
// Printing elements of HashMap 2
System.out.println("Mapping of HashMap hm2 are : "
+ hm2);
}
}
Mappings of HashMap hm1 are : {1=one, 2=two, 3=three}
Mapping of HashMap hm2 are : {4=four, 5=five, 6=six}构造函数 3: HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor)
它创建一个具有指定初始容量和指定负载因子的 HashMap 实例。
句法:
HashMap hm = new HashMap(int initialCapacity, int loadFactor); 例子
Java
// Java program to Demonstrate
// HashMap(int initialCapacity,float loadFactor) Constructor
// Importing basic classes
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// Main class
// To add elements to HashMap
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// No need to mention the generic type twice
HashMap hm1
= new HashMap<>(5, 0.75f);
// Initialization of a HashMap using Generics
HashMap hm2
= new HashMap(3, 0.5f);
// Add Elements using put() method
// Custom input elements
hm1.put(1, "one");
hm1.put(2, "two");
hm1.put(3, "three");
hm2.put(4, "four");
hm2.put(5, "five");
hm2.put(6, "six");
// Print and display elements in object of hashMap 1
System.out.println("Mappings of HashMap hm1 are : "
+ hm1);
// Print and display elements in object of hashMap 2
System.out.println("Mapping of HashMap hm2 are : "
+ hm2);
}
}
Mappings of HashMap hm1 are : {1=one, 2=two, 3=three}
Mapping of HashMap hm2 are : {4=four, 5=five, 6=six}4. HashMap(Map map):创建一个HashMap的实例,其映射与指定的map相同。
HashMap
Java
// Java program to demonstrate the
// HashMap(Map map) Constructor
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class AddElementsToHashMap {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// No need to mention the
// Generic type twice
Map hm1 = new HashMap<>();
// Add Elements using put method
hm1.put(1, "one");
hm1.put(2, "two");
hm1.put(3, "three");
// Initialization of a HashMap
// using Generics
HashMap hm2
= new HashMap(hm1);
System.out.println("Mappings of HashMap hm1 are : "
+ hm1);
System.out.println("Mapping of HashMap hm2 are : "
+ hm2);
}
}
Mappings of HashMap hm1 are : {1=one, 2=two, 3=three}
Mapping of HashMap hm2 are : {1=one, 2=two, 3=three}对 HashMap 执行各种操作
1. 添加元素:为了向地图添加元素,我们可以使用 put() 方法。但是,插入顺序不会保留在 Hashmap 中。在内部,对于每个元素,都会生成一个单独的散列,并根据该散列对元素进行索引,以提高效率。
Java
// Java program to add elements
// to the HashMap
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class AddElementsToHashMap {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// No need to mention the
// Generic type twice
HashMap hm1 = new HashMap<>();
// Initialization of a HashMap
// using Generics
HashMap hm2
= new HashMap();
// Add Elements using put method
hm1.put(1, "Geeks");
hm1.put(2, "For");
hm1.put(3, "Geeks");
hm2.put(1, "Geeks");
hm2.put(2, "For");
hm2.put(3, "Geeks");
System.out.println("Mappings of HashMap hm1 are : "
+ hm1);
System.out.println("Mapping of HashMap hm2 are : "
+ hm2);
}
}
Mappings of HashMap hm1 are : {1=Geeks, 2=For, 3=Geeks}
Mapping of HashMap hm2 are : {1=Geeks, 2=For, 3=Geeks}2.更改元素:添加元素后,如果我们想更改元素,可以通过 put() 方法再次添加元素来完成。由于地图中的元素是使用键索引的,因此可以通过简单地插入我们希望更改的键的更新值来更改键的值。
Java
// Java program to change
// elements of HashMap
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class ChangeElementsOfHashMap {
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Initialization of a HashMap
HashMap hm
= new HashMap();
// Change Value using put method
hm.put(1, "Geeks");
hm.put(2, "Geeks");
hm.put(3, "Geeks");
System.out.println("Initial Map " + hm);
hm.put(2, "For");
System.out.println("Updated Map " + hm);
}
}
Initial Map {1=Geeks, 2=Geeks, 3=Geeks}
Updated Map {1=Geeks, 2=For, 3=Geeks}3. 移除元素:为了从 Map 中移除元素,我们可以使用 remove() 方法。此方法获取键值并从该映射中删除该键的映射(如果它存在于映射中)。
Java
// Java program to remove
// elements from HashMap
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class RemoveElementsOfHashMap{
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Initialization of a HashMap
Map hm
= new HashMap();
// Add elements using put method
hm.put(1, "Geeks");
hm.put(2, "For");
hm.put(3, "Geeks");
hm.put(4, "For");
// Initial HashMap
System.out.println("Mappings of HashMap are : "
+ hm);
// remove element with a key
// using remove method
hm.remove(4);
// Final HashMap
System.out.println("Mappings after removal are : "
+ hm);
}
}
Mappings of HashMap are : {1=Geeks, 2=For, 3=Geeks, 4=For}
Mappings after removal are : {1=Geeks, 2=For, 3=Geeks}4、HashMap的遍历
我们可以使用 Iterator 接口来遍历 Collection Framework 的任何结构。由于迭代器使用一种类型的数据,我们使用 Entry< ? , ? > 将两种不同的类型解析为兼容的格式。然后使用 next() 方法我们打印 HashMap 的条目。
Java
// Java program to traversal a
// Java.util.HashMap
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class TraversalTheHashMap {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// initialize a HashMap
HashMap map = new HashMap<>();
// Add elements using put method
map.put("vishal", 10);
map.put("sachin", 30);
map.put("vaibhav", 20);
// Iterate the map using
// for-each loop
for (Map.Entry e : map.entrySet())
System.out.println("Key: " + e.getKey()
+ " Value: " + e.getValue());
}
}
Key: vaibhav Value: 20
Key: vishal Value: 10
Key: sachin Value: 30HashMap 的重要特性
要访问一个值,必须知道它的键。 HashMap 之所以称为 HashMap,是因为它使用了一种称为 Hashing 的技术。散列是一种将大字符串转换为代表相同字符串的小字符串的技术。较短的值有助于索引和更快的搜索。 HashSet 在内部也使用 HashMap。
HashMap 的几个重要特性是:
- HashMap 是Java.util 包的一部分。
- HashMap 扩展了一个抽象类 AbstractMap,它也提供了 Map 接口的不完整实现。
- 它还实现了 Cloneable 和 Serializable 接口。上述定义中的K和V分别代表Key和Value。
- HashMap 不允许重复键,但允许重复值。这意味着单个键不能包含超过 1 个值,但超过 1 个键可以包含单个值。
- HashMap 也允许空键,但只允许一次和多个空值。
- 此类不保证地图的顺序;特别是,它不保证订单会随着时间的推移保持不变。它与 HashTable 大致相似,但不同步。
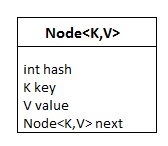
HashMap的内部结构
HashMap 内部包含一个 Node 数组,一个节点表示为一个包含 4 个字段的类:
- 整数哈希
- K键
- V值
- 下一个节点
可以看出该节点包含对其自身对象的引用。所以它是一个链表。
哈希映射:
节点:
HashMap 的性能
HashMap 的性能取决于 2 个参数,命名如下:
- 初始容量
- 负载系数
1. Initial Capacity——是HashMap在创建时的容量(就是HashMap实例化时HashMap可以容纳的桶数)。在Java中,它最初是 2^4=16,这意味着它可以容纳 16 个键值对。
2. Load Factor – Hashmap 容量增加后的容量百分比(Rehashing 发生后存储桶的百分比填充)。在Java中,默认为 0.75f,这意味着在填充 75% 的容量后进行重新散列。
3. 阈值——它是负载系数和初始容量的乘积。在Java中,默认情况下为 (16 * 0.75 = 12)。也就是说,在将 12 个键值对插入 HashMap 之后进行重新散列。
4. Rehashing ——HashMap达到Threshold后容量翻倍的过程。在Java中,HashMap 继续按以下顺序重新散列(默认情况下)——2^4、2^5、2^6、2^7、...。很快。
如果初始容量保持较高,则永远不会进行重新散列。但是通过保持较高的值会增加迭代的时间复杂度。所以应该非常巧妙地选择它来提高性能。设置初始容量时应考虑预期的值数量。最普遍优选的负载因子值是 0.75,它提供了时间和空间成本之间的良好交易。负载因子的值在 0 和 1 之间变化。
Note: From Java 8 onward, Java has started using Self Balancing BST instead of a linked list for chaining. The advantage of self-balancing bst is, we get the worst case (when every key maps to the same slot) search time is O(Log n).
同步HashMap
据说 HashMap 是不同步的,即多个线程可以同时访问它。如果多个线程同时访问该类并且至少有一个线程在结构上对其进行操作,则有必要使其在外部同步。它是通过同步一些封装地图的对象来完成的。如果不存在这样的对象,则可以将其包裹在 Collections.synchronizedMap() 周围以使 HashMap 同步并避免意外的不同步访问。如下例所示:
Map m = Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap(...));现在 Map m 已同步。如果在创建迭代器之后以任何方式修改了任何结构,则此类的迭代器是快速失败的,除了通过迭代器的 remove 方法。在迭代器失败时,它会抛出 ConcurrentModificationException。 HashMap 的时间复杂度: HashMap 为基本操作提供了恒定的时间复杂度,如果哈希函数写得正确,则 get 和 put 并且它可以将元素正确地分散在桶中。 HashMap 的迭代取决于 HashMap 的容量和键值对的数量。基本上,它与容量+大小成正比。容量是 HashMap 中的桶数。因此,最初在 HashMap 中保留大量存储桶并不是一个好主意。 HashMap的应用: HashMap主要是散列的实现。当我们需要高效执行搜索、插入和删除操作时,它很有用。详情请参考散列的应用。
HashMap 中的方法
- K - 映射中键的类型。
- V – 映射中映射的值的类型。
METHOD | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| clear() | Removes all of the mappings from this map. |
| clone() | Returns a shallow copy of this HashMap instance: the keys and values themselves are not cloned. |
| compute(K key, BiFunction remappingFunction) | Attempts to compute a mapping for the specified key and its current mapped value (or null if there is no current mapping). |
| computeIfAbsent(K key, Function mappingFunction) | If the specified key is not already associated with a value (or is mapped to null), attempts to compute its value using the given mapping function and enters it into this map unless null. |
| computeIfPresent(K key, BiFunction remappingFunction) | If the value for the specified key is present and non-null, attempts to compute a new mapping given the key and its current mapped value. |
| containsKey(Object key) | Returns true if this map contains a mapping for the specified key. |
| containsValue(Object value) | Returns true if this map maps one or more keys to the specified value. |
| entrySet() | Returns a Set view of the mappings contained in this map. |
| get(Object key) | Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped, or null if this map contains no mapping for the key. |
| isEmpty() | Returns true if this map contains no key-value mappings. |
| keySet() | Returns a Set view of the keys contained in this map. |
| merge(K key, V value, BiFunction remappingFunction) | If the specified key is not already associated with a value or is associated with null, associates it with the given non-null value. |
| put(K key, V value) | Associates the specified value with the specified key in this map. |
| putAll(Map m) | Copies all of the mappings from the specified map to this map. |
| remove(Object key) | Removes the mapping for the specified key from this map if present. |
| size() | Returns the number of key-value mappings in this map. |
| values() | Returns a Collection view of the values contained in this map. |
从类Java.util.AbstractMap 继承的方法
METHOD | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| equals() | Compares the specified object with this map for equality. |
| hashCode() | Returns the hash code value for this map. |
| toString() | Returns a string representation of this map. |
从接口Java.util.Map 继承的方法
METHOD | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| equals() | Compares the specified object with this map for equality. |
forEach(BiConsumer ? super V> action) | Performs the given action for each entry in this map until all entries have been processed or the action throws an exception. |
| getOrDefault(Object key, V defaultValue) | Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped, or defaultValue if this map contains no mapping for the key. |
| hashCode() | Returns the hash code value for this map. |
| putIfAbsent(K key, V value) | If the specified key is not already associated with a value (or is mapped to null) associates it with the given value and returns null, else returns the current value. |
| remove(Object key, Object value) | Removes the entry for the specified key only if it is currently mapped to the specified value. |
| replace(K key, V value) | Replaces the entry for the specified key only if it is currently mapped to some value. |
| replace(K key, V oldValue, V newValue) | Replaces the entry for the specified key only if currently mapped to the specified value. |
replaceAll(BiFunction ? super V,? extends V> function) | Replaces each entry’s value with the result of invoking the given function on that entry until all entries have been processed or the function throws an exception. |
必读:
- 哈希图与树图
- 哈希图与哈希表
- 最近关于Java HashMap 的文章!