根据 CLRS 算法使用向量和队列的 BFS
使用 CLRS 书中给出的算法对图进行广度优先搜索遍历。
BFS 是遍历图的方法之一。之所以如此命名,是因为它在边界的宽度上均匀地扩展了已发现和未发现顶点之间的边界。这意味着该算法首先发现与“u”相距 k 的所有顶点,然后再发现距离 u 为 k+1 的顶点。 CLRS 中给出的算法使用“颜色”的概念来检查顶点是完全发现还是部分发现或未发现。它还跟踪顶点 u 与源 s 的距离。
BFS(G,s)
1 for each vertex u in G.V - {s}
2 u.color = white
3 u.d = INF
4 u.p = NIL
5 s.color = green
6 s.d = 0
7 s.p = NIL
8 Q = NULL
9 ENQUEUE(Q,s)
10 while Q != NULL
11 u = DEQUEUE(Q)
12 for each v in G.Adj[u]
13 if v.color == white
14 v.color = green
15 v.d = u.d + 1
16 v.p = u
17 ENQUEUE(Q,v)
18 u.color = dark_green它产生一个“广度优先树”,其根 s 包含所有可到达的顶点。我们来看一个简单的有向图,看看 BFS 是如何遍历它的。
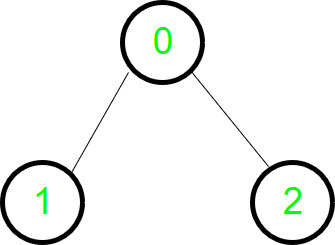
图表
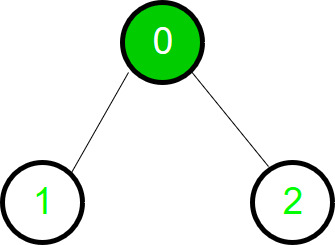
开始遍历
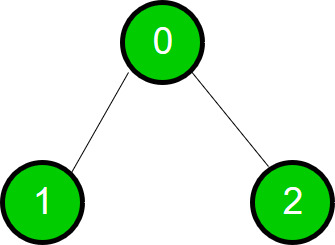
第一次遍历
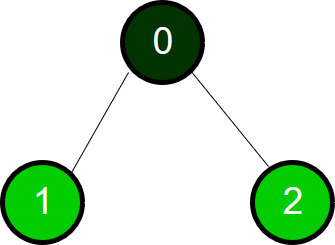
第一次遍历完成
C++
// CPP program to implement BFS as per CLRS
// algorithm.
#include
using namespace std;
// Declaring the vectors to store color, distance
// and parent
vector colour;
vector d;
vector p;
/* This function adds an edge to the graph.
It is an undirected graph. So edges are
added for both the nodes. */
void addEdge(vector g[], int u, int v)
{
g[u].push_back(v);
g[v].push_back(u);
}
/* This function does the Breadth First Search*/
void BFSSingleSource(vector g[], int s)
{
// The Queue used for the BFS operation
queue q;
// Pushing the root node inside the queue
q.push(s);
/* Distance of root node is 0 & colour
is gray as it is visited partially now */
d[s] = 0;
colour[s] = "green";
/* Loop to traverse the graph. Traversal
will happen traverse until the queue is
not empty.*/
while (!q.empty())
{
/* Extracting the front element(node)
and poping it out of queue. */
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
cout << u << " ";
/* This loop traverses all the child nodes of u */
for (auto i = g[u].begin(); i != g[u].end(); i++)
{
/* If the colour is white then the said node
is not traversed. */
if (colour[*i] == "white")
{
colour[*i] = "green";
d[*i] = d[u] + 1;
p[*i] = u;
/* Pushing the node inside queue
to traverse its children. */
q.push(*i);
}
}
/* Now the node u is completely traversed
and colour is changed to black. */
colour[u] = "dark_green";
}
}
void BFSFull(vector g[], int n)
{
/* Initially all nodes are not traversed.
Therefore, the colour is white. */
colour.assign(n, "white");
d.assign(n, 0);
p.assign(n, -1);
// Calling BFSSingleSource() for all white
// vertices.
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (colour[i] == "white")
BFSSingleSource(g, i);
}
// Driver Function
int main()
{
// Graph with 7 nodes and 6 edges.
int n = 7;
// The Graph vector
vector g[n];
addEdge(g, 0, 1);
addEdge(g, 0, 2);
addEdge(g, 1, 3);
addEdge(g, 1, 4);
addEdge(g, 2, 5);
addEdge(g, 2, 6);
BFSFull(g, n);
return 0;
} Python3
# Python3 program to implement BFS as
# per CLRS algorithm.
import queue
# This function adds an edge to the graph.
# It is an undirected graph. So edges
# are added for both the nodes.
def addEdge(g, u, v):
g[u].append(v)
g[v].append(u)
# This function does the Breadth
# First Search
def BFSSingleSource(g, s):
# The Queue used for the BFS operation
q = queue.Queue()
# Pushing the root node inside
# the queue
q.put(s)
# Distance of root node is 0 & colour is
# gray as it is visited partially now
d[s] = 0
colour[s] = "green"
# Loop to traverse the graph. Traversal
# will happen traverse until the queue
# is not empty.
while (not q.empty()):
# Extracting the front element(node)
# and poping it out of queue.
u = q.get()
print(u, end = " ")
# This loop traverses all the child
# nodes of u
i = 0
while i < len(g[u]):
# If the colour is white then
# the said node is not traversed.
if (colour[g[u][i]] == "white"):
colour[g[u][i]] = "green"
d[g[u][i]] = d[u] + 1
p[g[u][i]] = u
# Pushing the node inside queue
# to traverse its children.
q.put(g[u][i])
i += 1
# Now the node u is completely traversed
# and colour is changed to black.
colour[u] = "dark_green"
def BFSFull(g, n):
# Initially all nodes are not traversed.
# Therefore, the colour is white.
colour = ["white"] * n
d = [0] * n
p = [-1] * n
# Calling BFSSingleSource() for all
# white vertices
for i in range(n):
if (colour[i] == "white"):
BFSSingleSource(g, i)
# Driver Code
# Graph with 7 nodes and 6 edges.
n = 7
# Declaring the vectors to store color,
# distance and parent
colour = [None] * n
d = [None] * n
p = [None] * n
# The Graph vector
g = [[] for i in range(n)]
addEdge(g, 0, 1)
addEdge(g, 0, 2)
addEdge(g, 1, 3)
addEdge(g, 1, 4)
addEdge(g, 2, 5)
addEdge(g, 2, 6)
BFSFull(g, n)
# This code is contributed by PranchalkJavascript
输出:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6