给定一个大小为N的数组arr[] 。任务是寻找是否有可能用给定的元素数组制作二叉搜索树,使得由公共边连接的任何两个顶点的最大公约数> 1 。如果可能,则打印Yes否则打印No 。
例子:
Input: arr[] = {3, 6, 9, 18, 36, 108}
Output: Yes
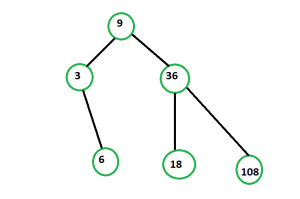
This is one of the possible Binary Search Tree with given array.
Input: arr[] = {2, 17}
Output: No
方法:让DP(l, r, root)是一个决定是否可以从子段 [l..r] 组装以根为根的树的 DP。
很容易看出,计算它需要提取[l..root – 1]留下了这样的根和根直接从[根+ 1..right]这样的:
- gcd(a root , a rootleft ) > 1
- gcd(a root , a rootright ) > 1
- DP(l, root-1, root left ) = 1
- DP(root+1, r, root right ) = 1
这可以在 O(r – l) 中完成,前提是我们为 [l..r] 的所有子段提供了所有 DP(x, y, z) 值。考虑到总共 O(n 3 ) 个 DP 状态,最终的复杂度是 O(n 4 ),这太多了。
让我们把我们的 DP 变成 DPnew(l, r, state) ,其中状态可以是 0 或 1。 立即证明 DP(l, r, root) 继承自 DPnew(l, root-1, 1) 和DPnew(root+1, r, 0)。现在我们有 O(n 2 ) 个状态,但同时,所有转换都是在线性时间内执行的。因此最终的复杂度是 O(n 3 ),足以通过。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Maximum number of vertices
#define N 705
// To store is it possible at
// particular pace or not
int dp[N][N][2];
// Return 1 if from l to r, it is possible with
// the given state
int possibleWithState(int l, int r, int state, int a[])
{
// Base condition
if (l > r)
return 1;
// If it is already calculated
if (dp[l][r][state] != -1)
return dp[l][r][state];
// Choose the root
int root;
if (state == 1)
root = a[r + 1];
else
root = a[l - 1];
// Traverse in range l to r
for (int i = l; i <= r; i++) {
// If gcd is greater than one
// check for both sides
if (__gcd(a[i], root) > 1) {
int x = possibleWithState(l, i - 1, 1, a);
if (x != 1)
continue;
int y = possibleWithState(i + 1, r, 0, a);
if (x == 1 && y == 1)
return dp[l][r][state] = 1;
}
}
// If not possible
return dp[l][r][state] = 0;
}
// Function that return true if it is possible
// to make Binary Search Tree
bool isPossible(int a[], int n)
{
memset(dp, -1, sizeof dp);
// Sort the given array
sort(a, a + n);
// Check it is possible rooted at i
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
// Check at both sides
if (possibleWithState(0, i - 1, 1, a)
&& possibleWithState(i + 1, n - 1, 0, a)) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int a[] = { 3, 6, 9, 18, 36, 108 };
int n = sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]);
if (isPossible(a, n))
cout << "Yes";
else
cout << "No";
return 0;
} Java
// Java implementation of the approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static int __gcd(int a, int b)
{
// Everything divides 0
if (a == 0)
return b;
if (b == 0)
return a;
// base case
if (a == b)
return a;
// a is greater
if (a > b)
return __gcd(a - b, b);
return __gcd(a, b-a);
}
// Maximum number of vertices
static final int N = 705;
// To store is it possible at
// particular pace or not
static int dp[][][] = new int[N][N][2];
// Return 1 if from l to r, it is
// possible with the given state
static int possibleWithState(int l, int r,
int state, int a[])
{
// Base condition
if (l > r)
return 1;
// If it is already calculated
if (dp[l][r][state] != -1)
return dp[l][r][state];
// Choose the root
int root;
if (state == 1)
root = a[r + 1];
else
root = a[l - 1];
// Traverse in range l to r
for (int i = l; i <= r; i++)
{
// If gcd is greater than one
// check for both sides
if (__gcd(a[i], root) > 1)
{
int x = possibleWithState(l, i - 1, 1, a);
if (x != 1)
continue;
int y = possibleWithState(i + 1, r, 0, a);
if (x == 1 && y == 1)
return dp[l][r][state] = 1;
}
}
// If not possible
return dp[l][r][state] = 0;
}
// Function that return true if it is possible
// to make Binary Search Tree
static boolean isPossible(int a[], int n)
{
for(int i = 0; i < dp.length; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < dp[i].length; j++)
for(int k = 0; k < dp[i][j].length; k++)
dp[i][j][k]=-1;
// Sort the given array
Arrays.sort(a);
// Check it is possible rooted at i
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
// Check at both sides
if (possibleWithState(0, i - 1, 1, a) != 0 &&
possibleWithState(i + 1, n - 1, 0, a) != 0)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
int a[] = { 3, 6, 9, 18, 36, 108 };
int n = a.length;
if (isPossible(a, n))
System.out.println("Yes");
else
System.out.println("No");
}
}
// This code is contributed by
// Arnab KunduPython3
# Python3 implementation of the approach
import math
# Maximum number of vertices
N = 705
# To store is it possible at
# particular pace or not
dp = [[[-1 for z in range(2)]
for x in range(N)]
for y in range(N)]
# Return 1 if from l to r, it is
# possible with the given state
def possibleWithState(l, r, state, a):
# Base condition
if (l > r):
return 1
# If it is already calculated
if (dp[l][r][state] != -1):
return dp[l][r][state]
# Choose the root
root = 0
if (state == 1) :
root = a[r + 1]
else:
root = a[l - 1]
# Traverse in range l to r
for i in range(l, r + 1):
# If gcd is greater than one
# check for both sides
if (math.gcd(a[i], root) > 1):
x = possibleWithState(l, i - 1, 1, a)
if (x != 1):
continue
y = possibleWithState(i + 1, r, 0, a)
if (x == 1 and y == 1) :
return 1
# If not possible
return 0
# Function that return true if it is
# possible to make Binary Search Tree
def isPossible(a, n):
# Sort the given array
a.sort()
# Check it is possible rooted at i
for i in range(n):
# Check at both sides
if (possibleWithState(0, i - 1, 1, a) and
possibleWithState(i + 1, n - 1, 0, a)):
return True
return False
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
a = [3, 6, 9, 18, 36, 108]
n = len(a)
if (isPossible(a, n)):
print("Yes")
else:
print("No")
# This code is contributed by
# Shubham Singh(SHUBHAMSINGH10)C#
// C# implementation of the approach
using System;
class GFG
{
static int __gcd(int a, int b)
{
// Everything divides 0
if (a == 0)
return b;
if (b == 0)
return a;
// base case
if (a == b)
return a;
// a is greater
if (a > b)
return __gcd(a - b, b);
return __gcd(a, b-a);
}
// Maximum number of vertices
static int N = 705;
// To store is it possible at
// particular pace or not
static int [,,]dp = new int[N, N, 2];
// Return 1 if from l to r, it is
// possible with the given state
static int possibleWithState(int l, int r,
int state, int []a)
{
// Base condition
if (l > r)
return 1;
// If it is already calculated
if (dp[l, r, state] != -1)
return dp[l, r, state];
// Choose the root
int root;
if (state == 1)
root = a[r + 1];
else
root = a[l - 1];
// Traverse in range l to r
for (int i = l; i <= r; i++)
{
// If gcd is greater than one
// check for both sides
if (__gcd(a[i], root) > 1)
{
int x = possibleWithState(l, i - 1, 1, a);
if (x != 1)
continue;
int y = possibleWithState(i + 1, r, 0, a);
if (x == 1 && y == 1)
return dp[l,r,state] = 1;
}
}
// If not possible
return dp[l,r,state] = 0;
}
// Function that return true
// if it is possible to make
// Binary Search Tree
static bool isPossible(int []a, int n)
{
for(int i = 0; i < dp.GetLength(0); i++)
for(int j = 0; j < dp.GetLength(1); j++)
for(int k = 0; k < dp.GetLength(2); k++)
dp[i, j, k]=-1;
// Sort the given array
Array.Sort(a);
// Check it is possible rooted at i
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
// Check at both sides
if (possibleWithState(0, i - 1, 1, a) != 0 &&
possibleWithState(i + 1, n - 1, 0, a) != 0)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String []args)
{
int []a = { 3, 6, 9, 18, 36, 108 };
int n = a.Length;
if (isPossible(a, n))
Console.WriteLine("Yes");
else
Console.WriteLine("No");
}
}
// This code is contributed by 29AjayKumarJavascript
输出:
Yes