给定一棵树,有N 个节点和N-1 个边,根为 1,并给定一个N-1整数数组。任务是为树中的边分配权重,使得从每个节点到所有其他节点的距离总和最大。
例子:
Input:
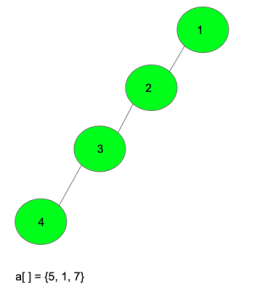
Output: 46
Assign the edge 1-2 with weight 5
Assign the edge 2-3 with weight 7
Assign the edge 3-4 with weight 1
The distance of node 1 from the nodes 2, 3, 4 is {5, 5+7, 5+7+1}
The distance of node 2 from the nodes 3, 4 is {7, 7+1}
The distance of node 3 from the node 4 is {1}
Input:
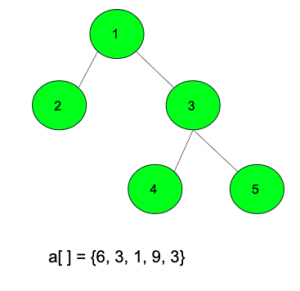
Output: 94
方法:该问题可以使用 Combinations、 DFS 、DP on tree 和 Greedy logic 解决。由于我们需要为树中的边分配权重,因此将最大权重分配给所有路径中出现次数最多的边将是获得最大和的方法。为了找到一条边在所有可能的路径中出现的次数,我们需要知道边两侧的节点数。设c1和c2为左右侧节点数的计数,则边在所有路径中出现的次数为c1 * c2 。按升序对 c1 * c2 的所有可能值进行排序。将最大权重分配给最大的 c1 * c2 值,并以相同的方式分配给其他值。我们可以按照以下步骤来获取边左侧和右侧的节点数:
- 从根开始运行dfs ,并初始化一个dp[]数组,该数组存储给定节点子树中节点的计数。
- 迭代每个可能的边,并找到边两侧的节点数。
- 要查找两侧的节点数,请找出dp[node1]或dp[node2]的较小值,其中 node1 和 node2 是边两侧的节点
- 如果一侧有min(dp[node1], dp[node2]) ,那么另一侧将有(N – min(dp[node1], dp[node2])) 。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program to implement the
// above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to add an edge to the tree
void addEdge(vector >& edges,
list* tree, int x, int y)
{
edges.push_back({ x, y });
tree[x].push_back(y);
tree[y].push_back(x);
}
// Function to run DFS and calculate the
// height of the subtree below it
void dfs(vector >& edges, list* tree,
int node, int parent, int dp[])
{
// Initially initialize with 1
dp[node] = 1;
// Traverse for all nodes connected to node
for (auto it : tree[node]) {
// If node is not parent
// then recall dfs
if (it != parent) {
dfs(edges, tree, it, node, dp);
// Add the size of the
// subtree beneath it
dp[node] += dp[it];
}
}
}
// Function to assign weights to edges
// to maximize the final sum
int maximizeSum(int a[], vector >& edges,
list* tree, int n)
{
// Initialize it which stores the
// height of the subtree beneath it
int dp[n + 1] = { 0 };
// Call the DFS function to
dfs(edges, tree, 1, 0, dp);
// Sort the given array
sort(a, a + (n - 1));
// Stores the number of times an
// edge is part of a path
vector ans;
// Iterate for all edges and find the
// number of nodes on the left and on the right
for (auto it : edges) {
// Node 1
int x = it.first;
// Node 2
int y = it.second;
// If the number of nodes below is less
// then the other will be n - dp[node]
if (dp[x] < dp[y]) {
int fi = dp[x];
int sec = n - dp[x];
ans.push_back(fi * sec);
}
// Second condition
else {
int fi = dp[y];
int sec = n - dp[y];
ans.push_back(fi * sec);
}
}
// Sort the number of times
// an edges occurs in the path
sort(ans.begin(), ans.end());
int res = 0;
// Find the summation of all those
// paths and return
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
res += ans[i] * a[i];
}
return res;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int n = 5;
vector > edges;
list* tree = new list[n + 1];
// Add an edge 1-2 in the tree
addEdge(edges, tree, 1, 2);
// Add an edge 2-3 in the tree
addEdge(edges, tree, 1, 3);
// Add an edge 3-4 in the tree
addEdge(edges, tree, 3, 4);
// Add an edge 3-5 in the tree
addEdge(edges, tree, 3, 5);
// Array which gives the edges weight
// to be assigned
int a[] = { 6, 3, 1, 9, 3 };
cout << maximizeSum(a, edges, tree, n);
} Python3
# Python3 program to implement the
# above approach
edges = [[] for i in range(100)]
tree = [[] for i in range(100)]
# Function to add an edge to the tree
def addEdge(x, y):
edges.append([x, y])
tree[x].append(y)
tree[y].append(x)
# Function to run DFS and calculate the
# height of the subtree below it
def dfs(node, parent, dp):
# Intially initialize with 1
dp[node] = 1
# Traverse for all nodes connected to node
for it in tree[node]:
# If node is not parent
# then recall dfs
if (it != parent):
dfs(it, node, dp)
# Add the size of the
# subtree beneath it
dp[node] += dp[it]
# Function to assign weights to edges
# to maximize the final sum
def maximizeSum(a, n):
# Initialize it which stores the
# height of the subtree beneath it
dp = [0 for i in range(n + 1)]
# Call the DFS function to
dfs(1, 0, dp)
# Sort the given array
a = sorted(a[:-1])
# Stores the number of times an
# edge is part of a path
ans = []
# Iterate for all edges and find the
# number of nodes on the left and on the right
for it in edges:
if len(it) > 0:
# Node 1
x = it[0]
# Node 2
y = it[1]
# If the number of nodes below is less
# then the other will be n - dp[node]
if (dp[x] < dp[y]):
fi = dp[x]
sec = n - dp[x]
ans.append(fi * sec)
# Second condition
else:
fi = dp[y]
sec = n - dp[y]
ans.append(fi * sec)
# Sort the number of times
# an edges occurs in the path
ans = sorted(ans)
res = 0
# Find the summation of all those
# paths and return
for i in range(n - 1):
res += ans[i] * a[i]
return res
# Driver code
n = 5
# Add an edge 1-2 in the tree
addEdge(1, 2)
# Add an edge 2-3 in the tree
addEdge(1, 3)
# Add an edge 3-4 in the tree
addEdge(3, 4)
# Add an edge 3-5 in the tree
addEdge(3, 5)
# Array which gives the edges weight
# to be assigned
a = [6, 3, 1, 9, 3]
print(maximizeSum(a, n))
# This code is contributed by Mohit Kumar94如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。