给定一个无向非加权图 G 。对于给定的节点开始返回最短路径,即从开始到 G 的补充图中所有节点的边数。
Complement Graph is a graph such that it contains only those edges which are not present in the original graph.
例子:
Input: Undirected Edges = (1, 2), (1, 3), (3, 4), (3, 5), Start = 1
Output: 0 2 3 1 1
Explanation:
Original Graph:
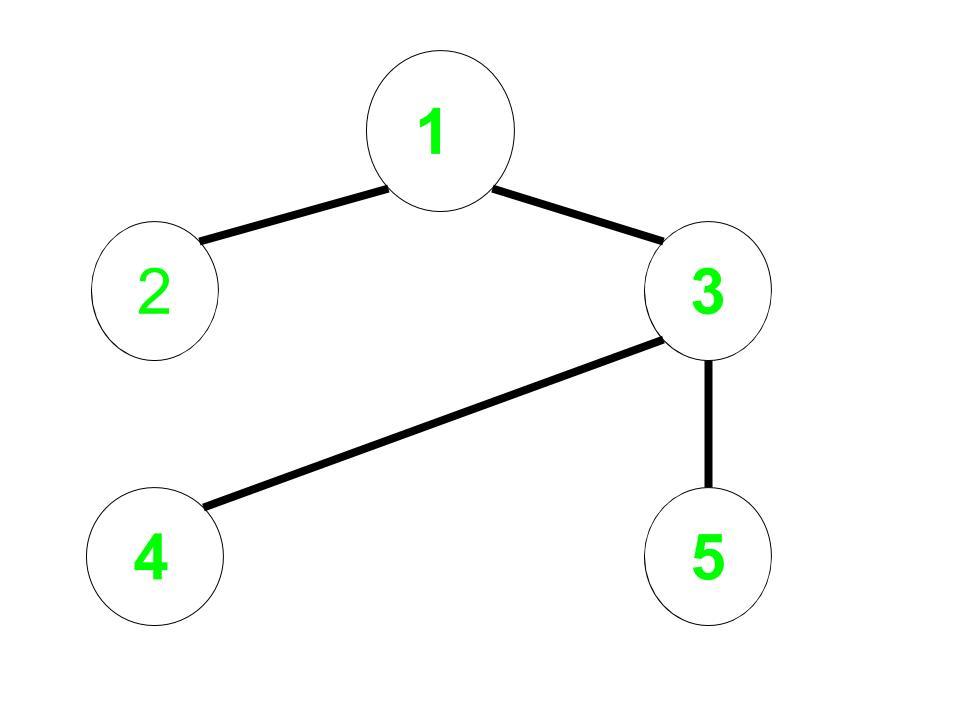
Complement Graph:
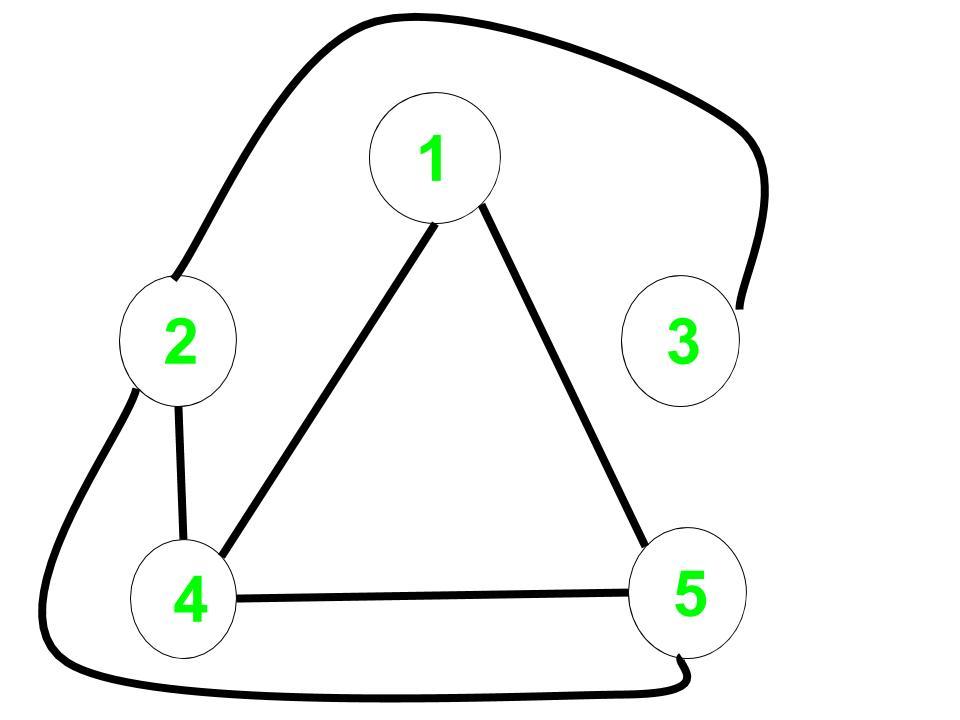
The distance from 1 to every node in the complement graph are:
1 to 1 = 0,
1 to 2 = 2,
1 to 3 = 3,
1 to 4 = 1,
1 to 5 = 1
朴素的方法:一个简单的解决方案是创建补充图并在该图上使用广度优先搜索来查找到所有节点的距离。
时间复杂度: O(n 2 ) 用于创建补图,O(n + m) 用于广度优先搜索。
Efficient Approach:思想是使用Modified Breadth-First Search来计算答案,然后就不需要构造补图了。
- 对于每个顶点或节点,减少与当前顶点互补且尚未被发现的顶点的距离。
- 对于这个问题,我们必须观察到,如果 Graph 是稀疏的,那么未发现的节点将被非常快地访问。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ implementation to find the
// shortest path in a complement graph
#include
using namespace std;
const int inf = 100000;
void bfs(int start, int n, int m,
map, int> edges)
{
int i;
// List of undiscovered vertices
// initially it will contain all
// the vertices of the graph
set undiscovered;
// Distance will store the distance
// of all vertices from start in the
// complement graph
vector distance_node(10000);
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
// All vertices are undiscovered
undiscovered.insert(i);
// Let initial distance be infinity
distance_node[i] = inf;
}
undiscovered.erase(start);
distance_node[start] = 0;
queue q;
q.push(start);
// Check if queue is not empty and the
// size of undiscovered vertices
// is greater than 0
while (undiscovered.size() && !q.empty()) {
int cur = q.front();
q.pop();
// Vector to store all the complement
// vertex to the current vertex
// which has not been
// discovered or visited yet.
vector complement_vertex;
for (int x : undiscovered) {
if (edges.count({ cur, x }) == 0 &&
edges.count({ x, cur })==0)
complement_vertex.push_back(x);
}
for (int x : complement_vertex) {
// Check if optimal change
// the distance of this
// complement vertex
if (distance_node[x]
> distance_node[cur] + 1) {
distance_node[x]
= distance_node[cur] + 1;
q.push(x);
}
// Finally this vertex has been
// discovered so erase it from
// undiscovered vertices list
undiscovered.erase(x);
}
}
// Print the result
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
cout << distance_node[i] << " ";
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// n is the number of vertex
// m is the number of edges
// start - starting vertex is 1
int n = 5, m = 4;
// Using edge hashing makes the
// algorithm faster and we can
// avoid the use of adjacency
// list representation
map, int> edges;
// Initial edges for
// the original graph
edges[{ 1, 3 }] = 1,
edges[{ 3, 1 }] = 1;
edges[{ 1, 2 }] = 1,
edges[{ 2, 1 }] = 1;
edges[{ 3, 4 }] = 1,
edges[{ 4, 3 }] = 1;
edges[{ 3, 5 }] = 1,
edges[{ 5, 3 }] = 1;
bfs(1, n, m, edges);
return 0;
} Java
// Java implementation to find the
// shortest path in a complement graph
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
// Pair class is made so as to
// store the edges between nodes
static class Pair
{
int left;
int right;
public Pair(int left, int right)
{
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
// We need to override hashCode so that
// we can use Set's properties like contains()
@Override
public int hashCode()
{
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + left;
result = prime * result + right;
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean equals( Object other )
{
if (this == other){return true;}
if (other instanceof Pair)
{
Pair m = (Pair)other;
return this.left == m.left &&
this.right == m.right;
}
return false;
}
}
public static void bfs(int start, int n, int m,
Set edges)
{
int i;
// List of undiscovered vertices
// initially it will contain all
// the vertices of the graph
Set undiscovered = new HashSet<>();
// Distance will store the distance
// of all vertices from start in the
// complement graph
int[] distance_node = new int[1000];
for(i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
// All vertices are undiscovered initially
undiscovered.add(i);
// Let initial distance be maximum value
distance_node[i] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
// Start is discovered
undiscovered.remove(start);
// Distance of the node to itself is 0
distance_node[start] = 0;
// Queue used for BFS
Queue q = new LinkedList<>();
q.add(start);
// Check if queue is not empty and the
// size of undiscovered vertices
// is greater than 0
while (undiscovered.size() > 0 && !q.isEmpty())
{
// Current node
int cur = q.peek();
q.remove();
// Vector to store all the complement
// vertex to the current vertex
// which has not been
// discovered or visited yet.
Listcomplement_vertex = new ArrayList<>();
for(int x : undiscovered)
{
Pair temp1 = new Pair(cur, x);
Pair temp2 = new Pair(x, cur);
// Add the edge if not already present
if (!edges.contains(temp1) &&
!edges.contains(temp2))
{
complement_vertex.add(x);
}
}
for(int x : complement_vertex)
{
// Check if optimal change
// the distance of this
// complement vertex
if (distance_node[x] >
distance_node[cur] + 1)
{
distance_node[x] =
distance_node[cur] + 1;
q.add(x);
}
// Finally this vertex has been
// discovered so erase it from
// undiscovered vertices list
undiscovered.remove(x);
}
}
// Print the result
for(i = 1; i <= n; i++)
System.out.print(distance_node[i] + " ");
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// n is the number of vertex
// m is the number of edges
// start - starting vertex is 1
int n = 5, m = 4;
// Using edge hashing makes the
// algorithm faster and we can
// avoid the use of adjacency
// list representation
Set edges = new HashSet<>();
// Initial edges for
// the original graph
edges.add(new Pair(1, 3));
edges.add(new Pair(3, 1));
edges.add(new Pair(1, 2));
edges.add(new Pair(2, 1));
edges.add(new Pair(3, 4));
edges.add(new Pair(4, 3));
edges.add(new Pair(3, 5)) ;
edges.add(new Pair(5, 3));
Pair t = new Pair(1, 3);
bfs(1, n, m, edges);
}
}
// This code is contributed by kunalsg18elec 输出:
0 2 3 1 1时间复杂度: O(V+E)
辅助空间: O(V)
如果您想与行业专家一起参加直播课程,请参阅Geeks Classes Live