给定由N 个节点组成的二叉树,任务是找到从根到任何节点 X 的路径数,使得该路径中的所有节点值至多为 X 。
例子:
Input: Below is the given Tree:

Output: 4
Explanation:
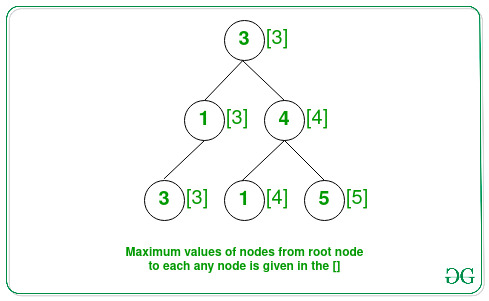
The paths from the root to any node X that have value at most values of node X are:
- Node 3(root node): It always follows the given property.
- Node 4: The path starting from the root to node with value 4 has order (3 → 4), with the maximum value of a node being 4.
- Node 5: The path starting from the root to node with value 5 has order (3 → 4 → 5), with the maximum value of a node being 5.
- Node 3: The path starting from the root to node with value 3 has order (3 → 1 → 3), with the maximum value of a node being 3.
Therefore, the count of required paths is 4.
Input: Below is the given Tree:
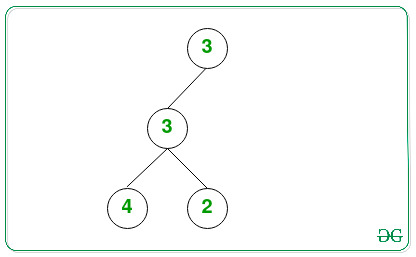
Output: 3
方法——使用 DFS:想法是使用深度优先搜索遍历树,同时检查从根到任何节点X的最大值是否等于X。
请按照以下步骤解决问题:
- 初始化一个变量,比如count为0以存储从根到任何节点 X 的路径计数,该路径中的所有节点值最多为 X 。
- 使用深度优先搜索递归遍历树并执行以下步骤:
- 每次递归调用 DFS Traversal,除了父节点,都会传递到目前为止在该路径中获得的节点的最大值。
- 检查当前节点值是否大于或等于到目前为止得到的最大值,然后将count的值加1 ,并将最大值更新为当前节点值。
- 完成以上步骤后,打印count的值作为结果。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Node structure of the binary tree
struct Node {
int val;
Node *left, *right;
};
// Function for creating new node
struct Node* newNode(int data)
{
// Allocate memory for new node
struct Node* temp = new Node();
// Assigning data value
temp->val = data;
temp->left = NULL;
temp->right = NULL;
// Return the Node
return temp;
}
// Function to perform the DFS Traversal
// to find the number of paths having
// root to node X has value at most X
int countNodes(Node* root, int max)
{
// If the root node is NULL
if (!root)
return 0;
// Check if the current value is
// greater than the maximum value
// in path from root to current node
if (root->val >= max)
return 1 + countNodes(root->left,
root->val)
+ countNodes(root->right, root->val);
// Otherwise
return countNodes(root->left,
max)
+ countNodes(root->right,
max);
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Given Binary Tree
Node* root = NULL;
root = newNode(3);
root->left = newNode(1);
root->right = newNode(4);
root->left->left = newNode(3);
root->right->left = newNode(1);
root->right->right = newNode(5);
cout << countNodes(root, INT_MIN);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for the above approach
import java.util.*;
// Class containing left and
// right child of current
// node and key value
class Node {
int data;
Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
class GFG {
// Root of the Binary Tree
Node root;
public GFG()
{
root = null;
}
// Function to perform the DFS Traversal
// to find the number of paths having
// root to node X has value at most X
static int countNodes(Node root, int max)
{
// If the root node is NULL
if (root == null)
return 0;
// Check if the current value is
// greater than the maximum value
// in path from root to current node
if (root.data >= max)
return 1 + countNodes(root.left,
root.data)
+ countNodes(root.right, root.data);
// Otherwise
return countNodes(root.left,
max)
+ countNodes(root.right,
max);
}
// Driver code
public static void main (String[] args)
{
GFG tree = new GFG();
tree.root = new Node(3);
tree.root.left = new Node(1);
tree.root.right = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(3);
tree.root.right.left = new Node(1);
tree.root.right.right = new Node(5);
System.out.println(countNodes(tree.root, Integer.MIN_VALUE));
}
}
// This code is contributed by offbeatPython3
# Python3 program for the above approach
# Node structure of the binary tree
class Node:
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
# Function to perform the DFS Traversal
# to find the number of paths having
# root to node X has value at most X
def countNodes(root, max):
# If the root node is NULL
if (not root):
return 0
# Check if the current value is
# greater than the maximum value
#in path from root to current node
if (root.val >= max):
return 1 + countNodes(root.left,root.val) + countNodes(root.right, root.val)
# Otherwise
return countNodes(root.left, max) + countNodes(root.right, max)
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Given Binary Tree
root = Node(3)
root.left = Node(1)
root.right = Node(4)
root.left.left = Node(3)
root.right.left = Node(1)
root.right.right = Node(5)
print(countNodes(root, -10**19))
# This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29.C#
// C# program to count frequencies of array items
using System;
// Class containing left and
// right child of current
// node and key value
class Node {
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
public class GFG
{
// Root of the Binary Tree
Node root;
public GFG()
{
root = null;
}
// Function to perform the DFS Traversal
// to find the number of paths having
// root to node X has value at most X
static int countNodes(Node root, int max)
{
// If the root node is NULL
if (root == null)
return 0;
// Check if the current value is
// greater than the maximum value
// in path from root to current node
if (root.data >= max)
return 1 + countNodes(root.left,
root.data)
+ countNodes(root.right, root.data);
// Otherwise
return countNodes(root.left,
max)
+ countNodes(root.right,
max);
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String []args)
{
GFG tree = new GFG();
tree.root = new Node(3);
tree.root.left = new Node(1);
tree.root.right = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(3);
tree.root.right.left = new Node(1);
tree.root.right.right = new Node(5);
Console.WriteLine(countNodes(tree.root, Int32.MinValue));
}
}
// This code is contributed by jana_sayantan.C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Node of the binary tree
struct Node {
int val;
Node *left, *right;
};
// Function for creating new node
struct Node* newNode(int data)
{
// Allocate memory for new node
struct Node* temp = new Node();
temp->val = data;
temp->left = NULL;
temp->right = NULL;
// Return the created node
return temp;
}
// Function to perform the DFS Traversal
// to find the number of paths having
// root to node X has value at most X
int countNodes(Node* root)
{
// Initialize queue
queue > q;
int m = INT_MIN;
// Push root in queue with the
// maximum value m
q.push({ root, m });
// Stores the count of good nodes
int count = 0;
// Traverse all nodes
while (!q.empty()) {
// Store the front node of
// the queue
auto temp = q.front();
q.pop();
Node* node = temp.first;
int num = temp.second;
// Check is current node is
// greater than the maximum
// value in path from root to
// the current node
if (node->val >= num)
count++;
// Update the maximum value m
m = max(node->val, num);
// If left child is not null,
// push it to queue with the
// maximum value m
if (node->left)
q.push({ node->left, m });
// If right child is not null,
// push it to queue with the
// maximum value m
if (node->right)
q.push({ node->right, m });
}
// Returns the answer
return count;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Construct a Binary Tree
Node* root = NULL;
root = newNode(3);
root->left = newNode(1);
root->right = newNode(4);
root->left->left = newNode(3);
root->right->left = newNode(1);
root->right->right = newNode(5);
cout << countNodes(root);
return 0;
} 输出:
4时间复杂度: O(N)
辅助空间: O(N)
使用 BFS 的方法:想法是使用广度优先搜索遍历树,同时检查从根到X的最大值是否等于X 。请按照以下步骤解决问题:
- 初始化一个变量,比如count为0以存储从根到任何节点 X 的路径计数,该路径中的所有节点值最多为 X和一个队列Q以执行 BFS 遍历。
- 将 INT_MIN 为最大值的根节点推送到队列中。
- 现在,直到Q非空,执行以下操作:
- 从队列中弹出前端节点。
- 如果前节点值至少是目前获得的最大值,则将count的值增加1 。
- 使用当前节点值更新到目前为止发生的最大值。
- 如果当前弹出的节点存在左右节点,则将其推入具有上述步骤中更新的最大值的队列Q。
- 完成以上步骤后,打印count的值作为结果。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Node of the binary tree
struct Node {
int val;
Node *left, *right;
};
// Function for creating new node
struct Node* newNode(int data)
{
// Allocate memory for new node
struct Node* temp = new Node();
temp->val = data;
temp->left = NULL;
temp->right = NULL;
// Return the created node
return temp;
}
// Function to perform the DFS Traversal
// to find the number of paths having
// root to node X has value at most X
int countNodes(Node* root)
{
// Initialize queue
queue > q;
int m = INT_MIN;
// Push root in queue with the
// maximum value m
q.push({ root, m });
// Stores the count of good nodes
int count = 0;
// Traverse all nodes
while (!q.empty()) {
// Store the front node of
// the queue
auto temp = q.front();
q.pop();
Node* node = temp.first;
int num = temp.second;
// Check is current node is
// greater than the maximum
// value in path from root to
// the current node
if (node->val >= num)
count++;
// Update the maximum value m
m = max(node->val, num);
// If left child is not null,
// push it to queue with the
// maximum value m
if (node->left)
q.push({ node->left, m });
// If right child is not null,
// push it to queue with the
// maximum value m
if (node->right)
q.push({ node->right, m });
}
// Returns the answer
return count;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Construct a Binary Tree
Node* root = NULL;
root = newNode(3);
root->left = newNode(1);
root->right = newNode(4);
root->left->left = newNode(3);
root->right->left = newNode(1);
root->right->right = newNode(5);
cout << countNodes(root);
return 0;
}
输出:
4时间复杂度: O(N)
辅助空间: O(N)
如果您想与行业专家一起参加直播课程,请参阅Geeks Classes Live