C 程序从文件中读取一定范围的字节并将其打印到控制台
给定一个文件F ,任务是编写 C 程序来打印给定文件中任意范围的字节并将其打印到控制台。
使用的功能:
- fopen() :创建新文件。文件以“a”或“a+”或“w”或“w++”的属性打开。
- fgetc ():从文件中读取字符。
- fclose():对于 c丢失文件。
方法:
- 初始化一个文件指针,比如File *fptr1 。
- 初始化一个数组来存储将从文件中读取的字节。
- 使用函数fopen()作为fptr1 = fopen(argv[1], “r”)打开文件。
- 迭代一个循环,直到给定的文件被读取和存储,字符在变量中被扫描,比如使用fgetc()函数的C。
- 将上述步骤中提取的每个字符C存储到一个新字符串S 中,并使用printf()函数打印该字符串。
- 完成上述步骤后,使用fclose()函数关闭文件。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C
// C program to read particular bytes
// from the existing file
#include
#include
// Maximum range of bytes
#define MAX 1000
// Filename given as the command
// line argument
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
// Pointer to the file to be
// read from
FILE* fptr1;
char c;
// Stores the bytes to read
char str[MAX];
int i = 0, j, from, to;
// If the file exists and has
// read permission
fptr1 = fopen(argv[1], "r");
if (fptr1 == NULL) {
return 1;
}
// Input from the user range of
// bytes inclusive of from and to
printf("Read bytes from: ");
scanf("%d", &from);
printf("Read bytes upto: ");
scanf("%d", &to);
// Loop to read required byte
// of file
for (i = 0, j = 0; i <= to
&& c != EOF;
i++) {
// Skip the bytes not required
if (i >= from) {
str[j] = c;
j++;
}
// Get the characters
c = fgetc(fptr1);
}
// Print the bytes as string
printf("%s", str);
// Close the file
fclose(fptr1);
return 0;
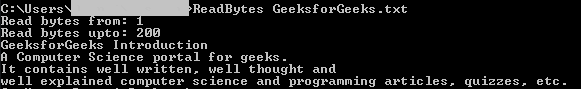
} 输出:
想要从精选的视频和练习题中学习,请查看C 基础到高级C 基础课程。