给定一棵二叉树,打印所有从根到叶的路径
For the below example tree, all root-to-leaf paths are:
10 –> 8 –> 3
10 –> 8 –> 5
10 –> 2 –> 2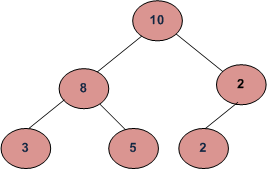
算法:
使用路径数组 path[] 将当前根存储到叶路径。以自上而下的方式从根遍历到所有叶子。遍历时,将当前路径中所有节点的数据存储在数组path[]中。当我们到达叶节点时,打印路径数组。
C++
#include
using namespace std;
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
and a pointer to right child */
class node
{
public:
int data;
node* left;
node* right;
};
/* Prototypes for functions needed in printPaths() */
void printPathsRecur(node* node, int path[], int pathLen);
void printArray(int ints[], int len);
/*Given a binary tree, print out all of its root-to-leaf
paths, one per line. Uses a recursive helper to do the work.*/
void printPaths(node* node)
{
int path[1000];
printPathsRecur(node, path, 0);
}
/* Recursive helper function -- given a node,
and an array containing the path from the root
node up to but not including this node,
print out all the root-leaf paths.*/
void printPathsRecur(node* node, int path[], int pathLen)
{
if (node == NULL)
return;
/* append this node to the path array */
path[pathLen] = node->data;
pathLen++;
/* it's a leaf, so print the path that lead to here */
if (node->left == NULL && node->right == NULL)
{
printArray(path, pathLen);
}
else
{
/* otherwise try both subtrees */
printPathsRecur(node->left, path, pathLen);
printPathsRecur(node->right, path, pathLen);
}
}
/* UTILITY FUNCTIONS */
/* Utility that prints out an array on a line. */
void printArray(int ints[], int len)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
cout << ints[i] << " ";
}
cout<data = data;
Node->left = NULL;
Node->right = NULL;
return(Node);
}
/* Driver code*/
int main()
{
/* Constructed binary tree is
10
/ \
8 2
/ \ /
3 5 2
*/
node *root = newnode(10);
root->left = newnode(8);
root->right = newnode(2);
root->left->left = newnode(3);
root->left->right = newnode(5);
root->right->left = newnode(2);
printPaths(root);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by rathbhupendra C
#include
#include
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
and a pointer to right child */
struct node
{
int data;
struct node* left;
struct node* right;
};
/* Prototypes for functions needed in printPaths() */
void printPathsRecur(struct node* node, int path[], int pathLen);
void printArray(int ints[], int len);
/*Given a binary tree, print out all of its root-to-leaf
paths, one per line. Uses a recursive helper to do the work.*/
void printPaths(struct node* node)
{
int path[1000];
printPathsRecur(node, path, 0);
}
/* Recursive helper function -- given a node, and an array containing
the path from the root node up to but not including this node,
print out all the root-leaf paths.*/
void printPathsRecur(struct node* node, int path[], int pathLen)
{
if (node==NULL)
return;
/* append this node to the path array */
path[pathLen] = node->data;
pathLen++;
/* it's a leaf, so print the path that lead to here */
if (node->left==NULL && node->right==NULL)
{
printArray(path, pathLen);
}
else
{
/* otherwise try both subtrees */
printPathsRecur(node->left, path, pathLen);
printPathsRecur(node->right, path, pathLen);
}
}
/* UTILITY FUNCTIONS */
/* Utility that prints out an array on a line. */
void printArray(int ints[], int len)
{
int i;
for (i=0; idata = data;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return(node);
}
/* Driver program to test above functions*/
int main()
{
/* Constructed binary tree is
10
/ \
8 2
/ \ /
3 5 2
*/
struct node *root = newnode(10);
root->left = newnode(8);
root->right = newnode(2);
root->left->left = newnode(3);
root->left->right = newnode(5);
root->right->left = newnode(2);
printPaths(root);
getchar();
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to print all the node to leaf path
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
and a pointer to right child */
class Node
{
int data;
Node left, right;
Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
class BinaryTree
{
Node root;
/*Given a binary tree, print out all of its root-to-leaf
paths, one per line. Uses a recursive helper to do
the work.*/
void printPaths(Node node)
{
int path[] = new int[1000];
printPathsRecur(node, path, 0);
}
/* Recursive helper function -- given a node, and an array
containing the path from the root node up to but not
including this node, print out all the root-leaf paths.*/
void printPathsRecur(Node node, int path[], int pathLen)
{
if (node == null)
return;
/* append this node to the path array */
path[pathLen] = node.data;
pathLen++;
/* it's a leaf, so print the path that lead to here */
if (node.left == null && node.right == null)
printArray(path, pathLen);
else
{
/* otherwise try both subtrees */
printPathsRecur(node.left, path, pathLen);
printPathsRecur(node.right, path, pathLen);
}
}
/* Utility function that prints out an array on a line. */
void printArray(int ints[], int len)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
System.out.print(ints[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println("");
}
// driver program to test above functions
public static void main(String args[])
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(10);
tree.root.left = new Node(8);
tree.root.right = new Node(2);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
tree.root.right.left = new Node(2);
/* Let us test the built tree by printing Inorder traversal */
tree.printPaths(tree.root);
}
}
// This code has been contributed by Mayank JaiswalPython3
"""
Python program to print all path from root to
leaf in a binary tree
"""
# binary tree node contains data field ,
# left and right pointer
class Node:
# constructor to create tree node
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.left = None
self.right = None
# function to print all path from root
# to leaf in binary tree
def printPaths(root):
# list to store path
path = []
printPathsRec(root, path, 0)
# Helper function to print path from root
# to leaf in binary tree
def printPathsRec(root, path, pathLen):
# Base condition - if binary tree is
# empty return
if root is None:
return
# add current root's data into
# path_ar list
# if length of list is gre
if(len(path) > pathLen):
path[pathLen] = root.data
else:
path.append(root.data)
# increment pathLen by 1
pathLen = pathLen + 1
if root.left is None and root.right is None:
# leaf node then print the list
printArray(path, pathLen)
else:
# try for left and right subtree
printPathsRec(root.left, path, pathLen)
printPathsRec(root.right, path, pathLen)
# Helper function to print list in which
# root-to-leaf path is stored
def printArray(ints, len):
for i in ints[0 : len]:
print(i," ",end="")
print()
# Driver program to test above function
"""
Constructed binary tree is
10
/ \
8 2
/ \ /
3 5 2
"""
root = Node(10)
root.left = Node(8)
root.right = Node(2)
root.left.left = Node(3)
root.left.right = Node(5)
root.right.left = Node(2)
printPaths(root)
# This code has been contributed by Shweta Singh.C#
using System;
// C# program to print all the node to leaf path
/* A binary tree node has data, pointer to left child
and a pointer to right child */
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
public class BinaryTree
{
public Node root;
/*Given a binary tree, print out all of its root-to-leaf
paths, one per line. Uses a recursive helper to do
the work.*/
public virtual void printPaths(Node node)
{
int[] path = new int[1000];
printPathsRecur(node, path, 0);
}
/* Recursive helper function -- given a node, and an array
containing the path from the root node up to but not
including this node, print out all the root-leaf paths.*/
public virtual void printPathsRecur(Node node, int[] path, int pathLen)
{
if (node == null)
{
return;
}
/* append this node to the path array */
path[pathLen] = node.data;
pathLen++;
/* it's a leaf, so print the path that lead to here */
if (node.left == null && node.right == null)
{
printArray(path, pathLen);
}
else
{
/* otherwise try both subtrees */
printPathsRecur(node.left, path, pathLen);
printPathsRecur(node.right, path, pathLen);
}
}
/* Utility function that prints out an array on a line. */
public virtual void printArray(int[] ints, int len)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
Console.Write(ints[i] + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine("");
}
// driver program to test above functions
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(10);
tree.root.left = new Node(8);
tree.root.right = new Node(2);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
tree.root.right.left = new Node(2);
/* Let us test the built tree by printing Inorder traversal */
tree.printPaths(tree.root);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Shrikant13Javascript
C++
#include
using namespace std;
/*Binary Tree representation using structure where data is in integer and 2 pointer
struct Node* left and struct Node* right represents left and right pointers of a node
in a tree respectively*/
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node* left;
struct Node* right;
Node(int x){
data = x;
left = right = NULL;
}
};
/*Recursive helper function which will recursively update our ans vector.
it takes root of our tree ,arr vector and ans vector as an argument*/
void helper(Node* root,vector arr,vector> &ans)
{
if(!root)
return;
arr.push_back(root->data);
if(root->left==NULL && root->right==NULL)
{
/*This will be only true when the node is leaf node
and hence we will update our ans vector by inserting
vector arr which have one unique path from root to leaf*/
ans.push_back(arr);
//after that we will return since we don't want to check after leaf node
return;
}
/*recursively going left and right until we find the leaf and updating the arr
and ans vector simultaneously*/
helper(root->left,arr,ans);
helper(root->right,arr,ans);
}
vector> Paths(Node* root)
{
/*creating 2-d vector in which each element is a 1-d vector
having one unique path from root to leaf*/
vector> ans;
/*if root is null than there is no further action require so return*/
if(!root)
return ans;
vector arr;
/*arr is a vector which will have one unique path from root to leaf
at a time.arr will be updated recursively*/
helper(root,arr,ans);
/*after helper function call our ans vector updated with paths so we will return ans vector*/
return ans;
}
int main()
{
/*defining root and our tree*/
Node *root = new Node(10);
root->left = new Node(8);
root->right = new Node(2);
root->left->left = new Node(3);
root->left->right = new Node(5);
root->right->left = new Node(2);
/*The answer returned will be stored in final 2-d vector*/
vector> final=Paths(root);
/*printing paths from root to leaf*/
for(int i=0;i 输出
10 8 3
10 8 5
10 2 2 时间复杂度: O(n),其中 n 是节点数。
参考资料:http://cslibrary.stanford.edu/110/BinaryTrees.html
另一种方法
C++
#include
using namespace std;
/*Binary Tree representation using structure where data is in integer and 2 pointer
struct Node* left and struct Node* right represents left and right pointers of a node
in a tree respectively*/
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node* left;
struct Node* right;
Node(int x){
data = x;
left = right = NULL;
}
};
/*Recursive helper function which will recursively update our ans vector.
it takes root of our tree ,arr vector and ans vector as an argument*/
void helper(Node* root,vector arr,vector> &ans)
{
if(!root)
return;
arr.push_back(root->data);
if(root->left==NULL && root->right==NULL)
{
/*This will be only true when the node is leaf node
and hence we will update our ans vector by inserting
vector arr which have one unique path from root to leaf*/
ans.push_back(arr);
//after that we will return since we don't want to check after leaf node
return;
}
/*recursively going left and right until we find the leaf and updating the arr
and ans vector simultaneously*/
helper(root->left,arr,ans);
helper(root->right,arr,ans);
}
vector> Paths(Node* root)
{
/*creating 2-d vector in which each element is a 1-d vector
having one unique path from root to leaf*/
vector> ans;
/*if root is null than there is no further action require so return*/
if(!root)
return ans;
vector arr;
/*arr is a vector which will have one unique path from root to leaf
at a time.arr will be updated recursively*/
helper(root,arr,ans);
/*after helper function call our ans vector updated with paths so we will return ans vector*/
return ans;
}
int main()
{
/*defining root and our tree*/
Node *root = new Node(10);
root->left = new Node(8);
root->right = new Node(2);
root->left->left = new Node(3);
root->left->right = new Node(5);
root->right->left = new Node(2);
/*The answer returned will be stored in final 2-d vector*/
vector> final=Paths(root);
/*printing paths from root to leaf*/
for(int i=0;i 输出
10 8 3
10 8 5
10 2 2