Python中的循环冗余检查
先决条件:了解循环冗余、套接字编程
什么是 CRC?
CRC 或循环冗余校验是一种检测通信通道中意外更改/错误的方法。
CRC 使用在发送方和接收方都可用的生成多项式。一个示例生成多项式的形式为 x^3 + 1。该生成多项式表示密钥 1001。另一个示例是 x^2 + x。表示键 110。
例子:
让数据发送为“EVN”
我们将字符串转换为二进制字符串数据。
Python
input_string = "EVN"
# CONVERT string data to binary string data
data = (''.join(format(ord(x), 'b') for x in input_string))
print (data)Python3
# Import socket module
import socket
def xor(a, b):
# initialize result
result = []
# Traverse all bits, if bits are
# same, then XOR is 0, else 1
for i in range(1, len(b)):
if a[i] == b[i]:
result.append('0')
else:
result.append('1')
return ''.join(result)
# Performs Modulo-2 division
def mod2div(divident, divisor):
# Number of bits to be XORed at a time.
pick = len(divisor)
# Slicing the divident to appropriate
# length for particular step
tmp = divident[0 : pick]
while pick < len(divident):
if tmp[0] == '1':
# replace the divident by the result
# of XOR and pull 1 bit down
tmp = xor(divisor, tmp) + divident[pick]
else: # If leftmost bit is '0'
# If the leftmost bit of the dividend (or the
# part used in each step) is 0, the step cannot
# use the regular divisor; we need to use an
# all-0s divisor.
tmp = xor('0'*pick, tmp) + divident[pick]
# increment pick to move further
pick += 1
# For the last n bits, we have to carry it out
# normally as increased value of pick will cause
# Index Out of Bounds.
if tmp[0] == '1':
tmp = xor(divisor, tmp)
else:
tmp = xor('0'*pick, tmp)
checkword = tmp
return checkword
# Function used at the sender side to encode
# data by appending remainder of modular division
# at the end of data.
def encodeData(data, key):
l_key = len(key)
# Appends n-1 zeroes at end of data
appended_data = data + '0'*(l_key-1)
remainder = mod2div(appended_data, key)
# Append remainder in the original data
codeword = data + remainder
return codeword
# Create a socket object
s = socket.socket()
# Define the port on which you want to connect
port = 12345
# connect to the server on local computer
s.connect(('127.0.0.1', port))
# Send data to server 'Hello world'
## s.sendall('Hello World')
input_string = input("Enter data you want to send->")
#s.sendall(input_string)
data =(''.join(format(ord(x), 'b') for x in input_string))
print("Entered data in binary format :",data)
key = "1001"
ans = encodeData(data,key)
print("Encoded data to be sent to server in binary format :",ans)
s.sendto(ans.encode(),('127.0.0.1', 12345))
# receive data from the server
print("Received feedback from server :",s.recv(1024).decode())
# close the connection
s.close()Python3
# First of all import the socket library
import socket
def xor(a, b):
# initialize result
result = []
# Traverse all bits, if bits are
# same, then XOR is 0, else 1
for i in range(1, len(b)):
if a[i] == b[i]:
result.append('0')
else:
result.append('1')
return ''.join(result)
# Performs Modulo-2 division
def mod2div(divident, divisor):
# Number of bits to be XORed at a time.
pick = len(divisor)
# Slicing the divident to appropriate
# length for particular step
tmp = divident[0: pick]
while pick < len(divident):
if tmp[0] == '1':
# replace the divident by the result
# of XOR and pull 1 bit down
tmp = xor(divisor, tmp) + divident[pick]
else: # If leftmost bit is '0'
# If the leftmost bit of the dividend (or the
# part used in each step) is 0, the step cannot
# use the regular divisor; we need to use an
# all-0s divisor.
tmp = xor('0'*pick, tmp) + divident[pick]
# increment pick to move further
pick += 1
# For the last n bits, we have to carry it out
# normally as increased value of pick will cause
# Index Out of Bounds.
if tmp[0] == '1':
tmp = xor(divisor, tmp)
else:
tmp = xor('0'*pick, tmp)
checkword = tmp
return checkword
# Function used at the receiver side to decode
# data received by sender
def decodeData(data, key):
l_key = len(key)
# Appends n-1 zeroes at end of data
appended_data = data.decode() + '0'*(l_key-1)
remainder = mod2div(appended_data, key)
return remainder
# Creating Socket
s = socket.socket()
print("Socket successfully created")
# reserve a port on your computer in our
# case it is 12345 but it can be anything
port = 12345
s.bind(('', port))
print("socket binded to %s" % (port))
# put the socket into listening mode
s.listen(5)
print("socket is listening")
while True:
# Establish connection with client.
c, addr = s.accept()
print('Got connection from', addr)
# Get data from client
data = c.recv(1024)
print("Received encoded data in binary format :", data.decode())
if not data:
break
key = "1001"
ans = decodeData(data, key)
print("Remainder after decoding is->"+ans)
# If remainder is all zeros then no error occured
temp = "0" * (len(key) - 1)
if ans == temp:
c.sendto(("THANK you Data ->"+data.decode() +
" Received No error FOUND").encode(), ('127.0.0.1', 12345))
else:
c.sendto(("Error in data").encode(), ('127.0.0.1', 12345))
c.close()100010110101101001110 CRC 密钥:1001
代码:CRC 密钥长度 -1 -> 000 附加在数据末尾。
New data: 100010110101101001110000
Key:1001现在我们在发送方和接收方的套接字编程Python中应用 CRC。
发送方
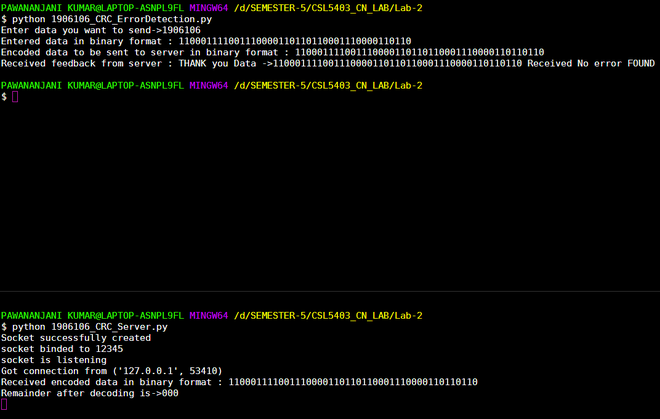
1. 任务是将字符串数据发送到服务器/接收端。
2. 发送者发送一个字符串让我们说“EVN”。
3. 首先,将该字符串转换为二进制字符串“100010110101101001110” 密钥对于发送方和接收方来说都是已知的,这里使用的密钥是 1001。
4. 该数据使用客户端/发送方的密钥使用 CRC 码进行编码。
5. 这个编码数据被发送到接收器。
6. 接收方稍后对编码的数据字符串进行解码,以验证是否有任何错误。
Python3
# Import socket module
import socket
def xor(a, b):
# initialize result
result = []
# Traverse all bits, if bits are
# same, then XOR is 0, else 1
for i in range(1, len(b)):
if a[i] == b[i]:
result.append('0')
else:
result.append('1')
return ''.join(result)
# Performs Modulo-2 division
def mod2div(divident, divisor):
# Number of bits to be XORed at a time.
pick = len(divisor)
# Slicing the divident to appropriate
# length for particular step
tmp = divident[0 : pick]
while pick < len(divident):
if tmp[0] == '1':
# replace the divident by the result
# of XOR and pull 1 bit down
tmp = xor(divisor, tmp) + divident[pick]
else: # If leftmost bit is '0'
# If the leftmost bit of the dividend (or the
# part used in each step) is 0, the step cannot
# use the regular divisor; we need to use an
# all-0s divisor.
tmp = xor('0'*pick, tmp) + divident[pick]
# increment pick to move further
pick += 1
# For the last n bits, we have to carry it out
# normally as increased value of pick will cause
# Index Out of Bounds.
if tmp[0] == '1':
tmp = xor(divisor, tmp)
else:
tmp = xor('0'*pick, tmp)
checkword = tmp
return checkword
# Function used at the sender side to encode
# data by appending remainder of modular division
# at the end of data.
def encodeData(data, key):
l_key = len(key)
# Appends n-1 zeroes at end of data
appended_data = data + '0'*(l_key-1)
remainder = mod2div(appended_data, key)
# Append remainder in the original data
codeword = data + remainder
return codeword
# Create a socket object
s = socket.socket()
# Define the port on which you want to connect
port = 12345
# connect to the server on local computer
s.connect(('127.0.0.1', port))
# Send data to server 'Hello world'
## s.sendall('Hello World')
input_string = input("Enter data you want to send->")
#s.sendall(input_string)
data =(''.join(format(ord(x), 'b') for x in input_string))
print("Entered data in binary format :",data)
key = "1001"
ans = encodeData(data,key)
print("Encoded data to be sent to server in binary format :",ans)
s.sendto(ans.encode(),('127.0.0.1', 12345))
# receive data from the server
print("Received feedback from server :",s.recv(1024).decode())
# close the connection
s.close()

接收端
1. 接收方接收来自发送方的编码数据字符串。
2. 接收器借助密钥对数据进行解码并找出余数。
3. 如果余数为零,则表示发送方发送给接收方的数据没有错误。
4. 如果余数不为零,则表示有错误,向发送者发送否定确认。然后发送方重新发送数据,直到接收方接收到正确的数据。
Python3
# First of all import the socket library
import socket
def xor(a, b):
# initialize result
result = []
# Traverse all bits, if bits are
# same, then XOR is 0, else 1
for i in range(1, len(b)):
if a[i] == b[i]:
result.append('0')
else:
result.append('1')
return ''.join(result)
# Performs Modulo-2 division
def mod2div(divident, divisor):
# Number of bits to be XORed at a time.
pick = len(divisor)
# Slicing the divident to appropriate
# length for particular step
tmp = divident[0: pick]
while pick < len(divident):
if tmp[0] == '1':
# replace the divident by the result
# of XOR and pull 1 bit down
tmp = xor(divisor, tmp) + divident[pick]
else: # If leftmost bit is '0'
# If the leftmost bit of the dividend (or the
# part used in each step) is 0, the step cannot
# use the regular divisor; we need to use an
# all-0s divisor.
tmp = xor('0'*pick, tmp) + divident[pick]
# increment pick to move further
pick += 1
# For the last n bits, we have to carry it out
# normally as increased value of pick will cause
# Index Out of Bounds.
if tmp[0] == '1':
tmp = xor(divisor, tmp)
else:
tmp = xor('0'*pick, tmp)
checkword = tmp
return checkword
# Function used at the receiver side to decode
# data received by sender
def decodeData(data, key):
l_key = len(key)
# Appends n-1 zeroes at end of data
appended_data = data.decode() + '0'*(l_key-1)
remainder = mod2div(appended_data, key)
return remainder
# Creating Socket
s = socket.socket()
print("Socket successfully created")
# reserve a port on your computer in our
# case it is 12345 but it can be anything
port = 12345
s.bind(('', port))
print("socket binded to %s" % (port))
# put the socket into listening mode
s.listen(5)
print("socket is listening")
while True:
# Establish connection with client.
c, addr = s.accept()
print('Got connection from', addr)
# Get data from client
data = c.recv(1024)
print("Received encoded data in binary format :", data.decode())
if not data:
break
key = "1001"
ans = decodeData(data, key)
print("Remainder after decoding is->"+ans)
# If remainder is all zeros then no error occured
temp = "0" * (len(key) - 1)
if ans == temp:
c.sendto(("THANK you Data ->"+data.decode() +
" Received No error FOUND").encode(), ('127.0.0.1', 12345))
else:
c.sendto(("Error in data").encode(), ('127.0.0.1', 12345))
c.close()
笔记:
如何运行程序:
1.你应该有一个socket编程库。
2.首先运行服务器程序,然后运行客户端程序。
3.复制粘贴代码时可能会出现缩进错误,所以复制时要小心。
4. 您将在拆分终端中看到以下输出。