Java中的 ConcurrentSkipListSet 示例
Java中的ConcurrentSkipListSet类是Java Collection Framework 的一部分,实现了Collection 接口和AbstractSet 类。它在Java中提供了可扩展和并发的 NavigableSet 版本。 ConcurrentSkipListSet 的实现基于ConcurrentSkipListMap 。 ConcurrentSkipListSet 中的元素默认按其自然顺序或在集合创建时提供的 Comparator 排序,具体取决于使用的构造函数。
由于它实现了SortedSet
类层次结构:
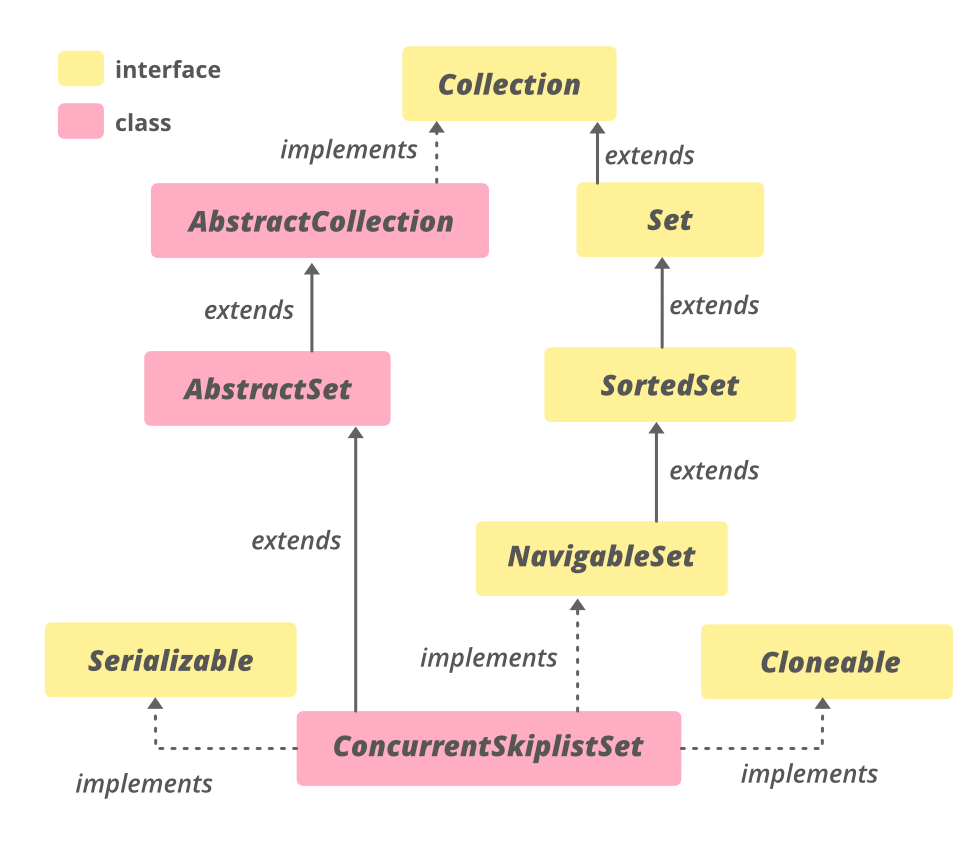
宣言:
public class ConcurrentSkipListSet
extends AbstractSet
implements NavigableSet, Cloneable, Serializable
Where E is the type of elements maintained by this collection
ConcurrentSkipListSet 的一些要点:
- 它实现了 Serializable 、 Cloneable 、 Iterable
、 Collection 、 NavigableSet 、 Set 、 SortedSet 接口。 - 它不允许空元素,因为空参数和返回值无法可靠地区分不存在元素。
- 它的实现为包含、添加和删除操作及其变体提供了平均 log(n) 时间成本。
- 它是线程安全的。
- 当需要同时修改 set 时,应该优先于实现 Set 接口。
构造函数:
1. ConcurrentSkipListSet() :该构造函数用于构造一个空集。
ConcurrentSkipListSet
2. ConcurrentSkipListSet(Collection
ConcurrentSkipListSet
3. ConcurrentSkipListSet(Comparator
ConcurrentSkipListSet
4. ConcurrentSkipListSet(SortedSet
ConcurrentSkipListSet
示例 1:
Java
// Java program to demonstrate ConcurrentSkipListSet
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentSkipListSet;
class ConcurrentSkipListSetLastExample1 {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Initializing the set using
// ConcurrentSkipListSet()
ConcurrentSkipListSet set
= new ConcurrentSkipListSet();
// Adding elements to this set
set.add(78);
set.add(64);
set.add(12);
set.add(45);
set.add(8);
// Printing the ConcurrentSkipListSet
System.out.println("ConcurrentSkipListSet: " + set);
// Initializing the set using
// ConcurrentSkipListSet(Collection)
ConcurrentSkipListSet set1
= new ConcurrentSkipListSet(set);
// Printing the ConcurrentSkipListSet1
System.out.println("ConcurrentSkipListSet1: "
+ set1);
// Initializing the set using
// ConcurrentSkipListSet()
ConcurrentSkipListSet set2
= new ConcurrentSkipListSet<>();
// Adding elements to this set
set2.add("Apple");
set2.add("Lemon");
set2.add("Banana");
set2.add("Apple");
// creating an iterator
Iterator itr = set2.iterator();
System.out.print("Fruits Set: ");
while (itr.hasNext()) {
System.out.print(itr.next() + " ");
}
}
} Java
// Java program to demonstrate ConcurrentSkipListSet
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentSkipListSet;
class ConcurrentSkipListSetLastExample1 {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Initializing the set using ConcurrentSkipListSet()
ConcurrentSkipListSet
set = new ConcurrentSkipListSet();
// Adding elements to this set
// using add() method
set.add(78);
set.add(64);
set.add(12);
set.add(45);
set.add(8);
// Printing the ConcurrentSkipListSet
System.out.println("ConcurrentSkipListSet: "
+ set);
// Printing the highest element of the set
// using last() method
System.out.println("The highest element of the set: "
+ set.last());
// Retrieving and removing first element of the set
System.out.println("The first element of the set: "
+ set.pollFirst());
// Checks if 9 is present in the set
// using contains() method
if (set.contains(9))
System.out.println("9 is present in the set.");
else
System.out.println("9 is not present in the set.");
// Printing the size of the set
// using size() method
System.out.println("Number of elements in the set = "
+ set.size());
}
} 输出:
ConcurrentSkipListSet: [8, 12, 45, 64, 78]
ConcurrentSkipListSet1: [8, 12, 45, 64, 78]
Fruits Set: Apple Banana Lemon
示例 2:
Java
// Java program to demonstrate ConcurrentSkipListSet
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentSkipListSet;
class ConcurrentSkipListSetLastExample1 {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Initializing the set using ConcurrentSkipListSet()
ConcurrentSkipListSet
set = new ConcurrentSkipListSet();
// Adding elements to this set
// using add() method
set.add(78);
set.add(64);
set.add(12);
set.add(45);
set.add(8);
// Printing the ConcurrentSkipListSet
System.out.println("ConcurrentSkipListSet: "
+ set);
// Printing the highest element of the set
// using last() method
System.out.println("The highest element of the set: "
+ set.last());
// Retrieving and removing first element of the set
System.out.println("The first element of the set: "
+ set.pollFirst());
// Checks if 9 is present in the set
// using contains() method
if (set.contains(9))
System.out.println("9 is present in the set.");
else
System.out.println("9 is not present in the set.");
// Printing the size of the set
// using size() method
System.out.println("Number of elements in the set = "
+ set.size());
}
}
输出:
ConcurrentSkipListSet: [8, 12, 45, 64, 78]
The highest element of the set: 78
The first element of the set: 8
9 is not present in the set.
Number of elements in the set = 4ConcurrentSkipListSet 的方法
METHOD | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| add(E e) | Adds the specified element to this set if it is not already present. |
| ceiling(E e) | Returns the least element in this set greater than or equal to the given element, or null if there is no such element. |
| clear() | Removes all of the elements from this set. |
| clone() | Returns a shallow copy of this ConcurrentSkipListSet instance. |
| comparator() | Returns the comparator used to order the elements in this set, or null if this set uses the natural ordering of its elements. |
| contains(Object o) | Returns true if this set contains the specified element. |
| descendingIterator() | Returns an iterator over the elements in this set in descending order. |
| descendingSet() | Returns a reverse order view of the elements contained in this set. |
| equals(Object o) | Compares the specified object with this set for equality. |
| first() | Returns the first (lowest) element currently in this set. |
| floor(E e) | Returns the greatest element in this set less than or equal to the given element, or null if there is no such element. |
| headSet(E toElement) | Returns a view of the portion of this set whose elements are strictly less than toElement. |
| headSet(E toElement, boolean inclusive) | Returns a view of the portion of this set whose elements are less than (or equal to, if inclusive is true) toElement. |
| higher(E e) | Returns the least element in this set strictly greater than the given element, or null if there is no such element. |
| isEmpty() | Returns an iterator over the elements in this set in ascending order. |
| last() | Returns the last (highest) element currently in this set. |
| lower(E e) | Returns the greatest element in this set strictly less than the given element, or null if there is no such element. |
| pollFirst() | Retrieves and removes the first (lowest) element, or returns null if this set is empty. |
| pollLast() | Retrieves and removes the last (highest) element, or returns null if this set is empty. |
| remove(Object o) | Removes the specified element from this set if it is present. |
| removeAll(Collection c) | Removes from this set all of its elements that are contained in the specified collection. |
| size() | Returns the number of elements in this set. |
| spliterator() | Returns a Spliterator over the elements in this set. |
subSet(E fromElement, boolean fromInclusive, E toElement, boolean toInclusive) | Returns a view of the portion of this set whose elements range from fromElement to toElement. |
| subSet(E fromElement, E toElement) | Returns a view of the portion of this set whose elements range from fromElement, inclusive, to toElement, exclusive. |
| tailSet(E fromElement) | Returns a view of the portion of this set whose elements are greater than or equal to fromElement. |
| tailSet(E fromElement, boolean inclusive) | Returns a view of the portion of this set whose elements are greater than (or equal to, if inclusive is true) fromElement. |
从类Java.util.AbstractSet 继承的方法
METHOD | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| hashCode() | Returns the hash code value for this set. |
从类Java.util.AbstractCollection 继承的方法
METHOD | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| addAll(Collection c) | Adds all of the elements in the specified collection to this collection (optional operation). |
| containsAll(Collection c) | Returns true if this collection contains all of the elements in the specified collection. |
| retainAll(Collection c) | Retains only the elements in this collection that are contained in the specified collection (optional operation). |
| toArray() | Returns an array containing all of the elements in this collection. |
| toArray(T[] a) | Returns an array containing all of the elements in this collection; the runtime type of the returned array is that of the specified array. |
| toString() | Returns a string representation of this collection. |
从接口Java.util.Set 继承的方法
METHOD | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| addAll(Collection c) | Adds all of the elements in the specified collection to this set if they’re not already present (optional operation). |
| containsAll(Collection c) | Returns true if this set contains all of the elements of the specified collection. |
| hashCode() | Returns the hash code value for this set. |
| retainAll(Collection c) | Retains only the elements in this set that are contained in the specified collection (optional operation). |
| toArray() | Returns an array containing all of the elements in this set. |
| toArray(T[] a) | Returns an array containing all of the elements in this set; the runtime type of the returned array is that of the specified array. |
从接口Java.util.Collection 继承的方法
METHOD | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| parallelStream() | Returns a possibly parallel Stream with this collection as its source. |
| removeIf(Predicate filter) | Removes all of the elements of this collection that satisfy the given predicate. |
| stream() | Returns a sequential Stream with this collection as its source. |
从接口Java.lang.Iterable 继承的方法
METHOD | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| forEach(Consumer action) | Performs the given action for each element of the Iterable until all elements have been processed or the action throws an exception. |