实现如何在Java中将文件加载为InputStream
问题陈述:已经存在一个文件,需要使用 InputStream 方法在其中加载相同的文件。
概念:在访问文件时,文件正在被读取或写入。这里有两个流,分别是 fileInputStream 和 fileOutputStream
Java Stream 是从源到目的地的数据流。 OutputStream 和 InputStream 是对低级数据访问的抽象。 InputStream 是读取数据的源。流可以有多种来源,例如磁盘文件、设备、其他程序和内存阵列。下面讨论了在Java中使用 InputStream 读取文件内容的几种方法。
假设文本文件存储在路径“ /Users/mayanksolanki/Desktop/Folder/test.txt ”中,内容如下:
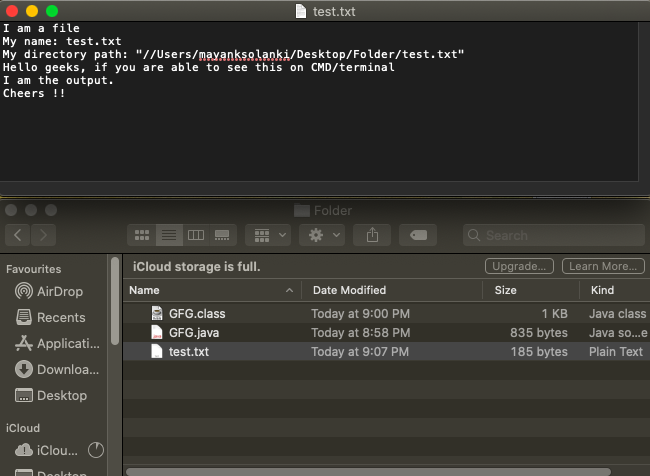
方法:
- 使用Apache命令 IO 库
- 使用 BufferedReaderClass 的readline()方法
- 使用 InputStreamClass 的read()方法
下面我们通过实例一一描述和实现这些方法:
方法一:使用Apache Common IO库
来自 Apache Commons IO 库的 IOUtils 类包含一个 toString() 方法,该方法接受 InputStream 并将其内容呈现为字符串,如下所示:
Java
// Importing generic Classes/Files
import java.util.*;
// importing Apache specific Class/es
import org.apache.commons.io.IOUtils;
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating file object and specify file path
File file = new file(
"/Users/mayanksolanki/Desktop/Folder/test.txt");
// create a stream to read contents of that file
// Try block to check exception
try {
FileInputStream input
= new FileInputStream(file);
// Representing input object in form of string
String contents = IOUtils.toString(input);
// Print contents of that file
System.out.println(contents);
}
// Catch block to handle exceptions
catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}Java
// Importing generic Classes/Files
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Create file object and specify file path
File file = new File(
"/Users/mayanksolanki/Desktop/Folder/test.txt");
try (FileInputStream input
= new FileInputStream(file)) {
// create an empty string builder to store
// string
StringBuilder content = new StringBuilder();
// create an object of bufferedReader to read
// lines from file
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(input));
String line;
// store each line one by one until reach end of
// file
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
// append string builder with line and with
// '/n' or '/r' or EOF
content.append(line
+ System.lineSeparator());
}
// print string builder object i.e content
System.out.println(content.toString());
}
// Catch block to handle exceptions
catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}Java
// Importing generic Classes/Files
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
// Main driver function
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating file object and specifying path
File file = new File(
"/Users/mayanksolanki/Desktop/Folder/test.txt");
try (FileInputStream input
= new FileInputStream(file)) {
int character;
// read character by character
// by default read() function return int between
// 0 and 255.
while ((character = input.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char)character);
}
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}Java
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// create file object and specify path
// specicified directory is random
File file = new File(
"/Users/mayanksolanki/Desktop/Folder/test.txt");
// Try block to catch exception/s if any
try {
(FileInputStream input
= new FileInputStream(file))
// create a byte array of size equal to
// length of file
byte bytes[]
= new byte[(int)file.length()];
// read bytes from file
input.read(bytes);
// decode into string format
String content
= new String(bytes, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
// print contents of that file
System.out.println(content);
}
catch (Exception e) {
//
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
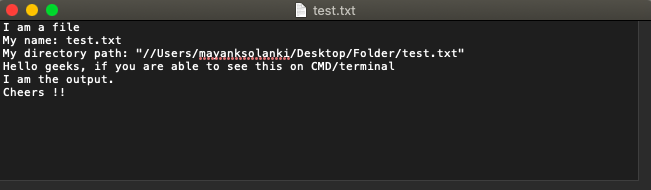
输出:
方法二:BufferedReader的readLine()方法
使用的概念:使用内置的 readLine()函数: Java中 BufferedReader 类的 readLine() 方法用于一次读取一行文本。行的结尾由 '\r' 或 '\n' 或 EOF 来理解。
下面是readLine ()方法的实现:
Java
// Importing generic Classes/Files
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Create file object and specify file path
File file = new File(
"/Users/mayanksolanki/Desktop/Folder/test.txt");
try (FileInputStream input
= new FileInputStream(file)) {
// create an empty string builder to store
// string
StringBuilder content = new StringBuilder();
// create an object of bufferedReader to read
// lines from file
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(input));
String line;
// store each line one by one until reach end of
// file
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
// append string builder with line and with
// '/n' or '/r' or EOF
content.append(line
+ System.lineSeparator());
}
// print string builder object i.e content
System.out.println(content.toString());
}
// Catch block to handle exceptions
catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
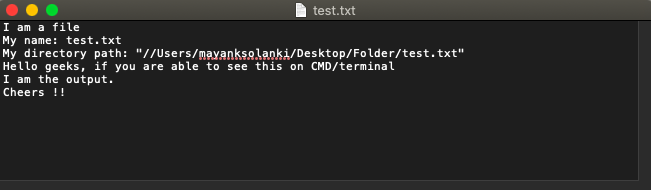
输出:
方法三:InputStream的read()方法
InputStream 类的 read() 方法从输入流中读取一个字节的数据。返回数据的下一个字节,如果到达文件末尾,则返回 -1,如果发生 I/O 错误,则抛出异常。请参阅程序。
Java
// Importing generic Classes/Files
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
// Main driver function
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating file object and specifying path
File file = new File(
"/Users/mayanksolanki/Desktop/Folder/test.txt");
try (FileInputStream input
= new FileInputStream(file)) {
int character;
// read character by character
// by default read() function return int between
// 0 and 255.
while ((character = input.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char)character);
}
}
catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
There is another overloaded version of read() method that reads the specified length of bytes from the input stream into an array of bytes. The corresponding bytes can then be decoded into characters. Refer to the below example.
Java
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// create file object and specify path
// specicified directory is random
File file = new File(
"/Users/mayanksolanki/Desktop/Folder/test.txt");
// Try block to catch exception/s if any
try {
(FileInputStream input
= new FileInputStream(file))
// create a byte array of size equal to
// length of file
byte bytes[]
= new byte[(int)file.length()];
// read bytes from file
input.read(bytes);
// decode into string format
String content
= new String(bytes, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
// print contents of that file
System.out.println(content);
}
catch (Exception e) {
//
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
输出
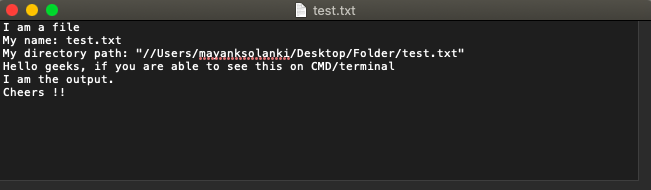
以上所有程序的输出都是一样的。