Java中的优先队列
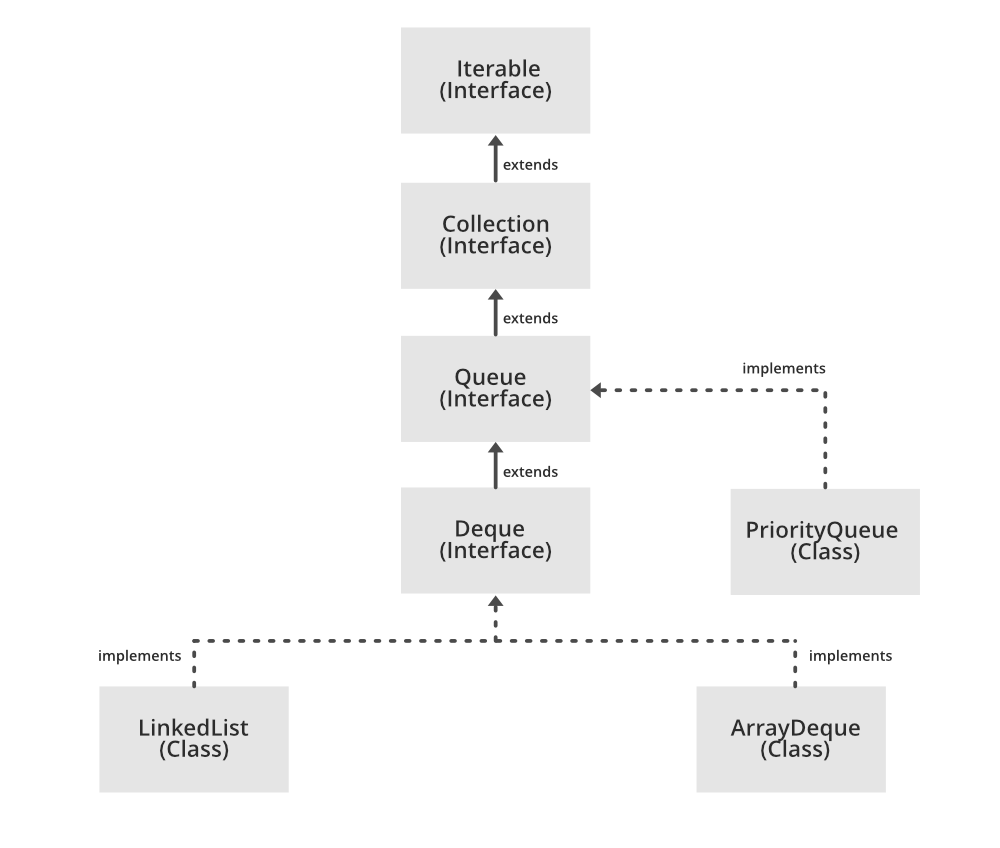
当对象应该基于优先级进行处理时,使用 PriorityQueue。众所周知,Queue 遵循先进先出的算法,但有时需要根据优先级对队列中的元素进行处理,这时 PriorityQueue 就派上用场了。 PriorityQueue 基于优先级堆。优先级队列的元素按照自然顺序排序,或者由队列构造时提供的 Comparator 排序,具体取决于使用的构造函数。
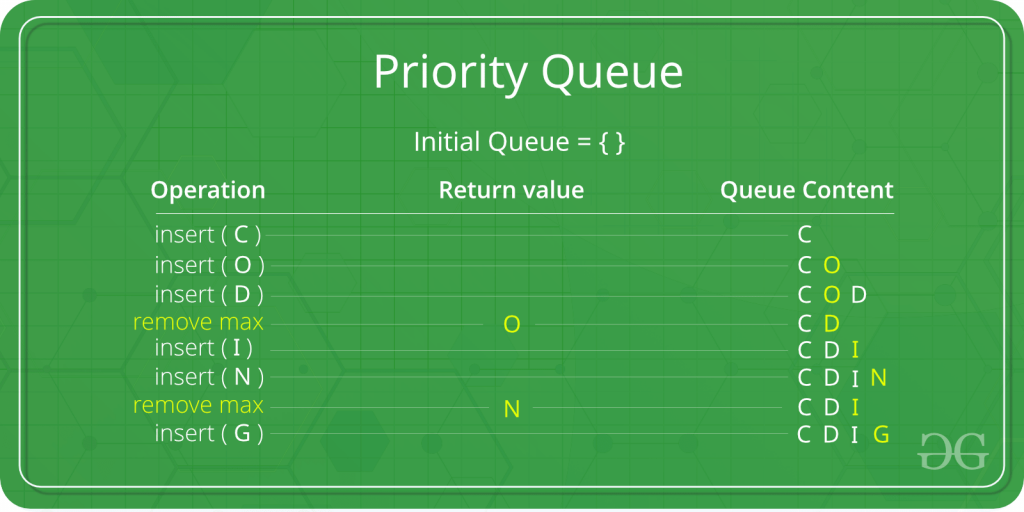
在下面的优先级队列中,具有最大 ASCII 值的元素将具有最高优先级。
宣言:
public class PriorityQueue extends AbstractQueue implements Serializable
where E is the type of elements held in this queue
该类实现了Serializable 、 Iterable
优先队列的几个要点如下:
- PriorityQueue 不允许为空。
- 我们无法创建不可比较对象的 PriorityQueue
- PriorityQueue 是未绑定的队列。
- 此队列的头部是相对于指定排序的最小元素。如果多个元素以最低价值绑定,则头部是这些元素之一——绑定被任意打破。
- 由于 PriorityQueue 不是线程安全的,所以Java提供了实现 BlockingQueue 接口的 PriorityBlockingQueue 类用于Java多线程环境。
- 队列检索操作 poll、remove、peek 和 element 访问队列头部的元素。
- 它为 add 和 poll 方法提供 O(log(n)) 时间。
- 它继承了AbstractQueue 、 AbstractCollection 、 Collection和Object类的方法。
构造函数:
1. PriorityQueue():创建一个具有默认初始容量 (11) 的 PriorityQueue,它根据元素的自然顺序对其元素进行排序。
PriorityQueue
2. PriorityQueue(Collection
PriorityQueue
3. PriorityQueue(int initialCapacity) :创建一个具有指定初始容量的PriorityQueue,它根据元素的自然顺序对其元素进行排序。
PriorityQueue
4. PriorityQueue(int initialCapacity, Comparator
PriorityQueue
5. PriorityQueue(PriorityQueue
PriorityQueue
6. PriorityQueue(SortedSet
PriorityQueue
例子:
下面的例子解释了优先队列的以下基本操作。
- boolean add(E element):此方法将指定元素插入此优先级队列。
- public peek():此方法检索但不删除此队列的头部,如果此队列为空,则返回 null。
- public poll():此方法检索并移除此队列的头部,如果此队列为空,则返回 null。
Java
// Java program to demonstrate the
// working of PriorityQueue
import java.util.*;
class PriorityQueueDemo {
// Main Method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Creating empty priority queue
PriorityQueue pQueue = new PriorityQueue();
// Adding items to the pQueue using add()
pQueue.add(10);
pQueue.add(20);
pQueue.add(15);
// Printing the top element of PriorityQueue
System.out.println(pQueue.peek());
// Printing the top element and removing it
// from the PriorityQueue container
System.out.println(pQueue.poll());
// Printing the top element again
System.out.println(pQueue.peek());
}
} Java
// Java program to add elements
// to a PriorityQueue
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class PriorityQueueDemo {
public static void main(String args[])
{
PriorityQueue pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
pq.add("Geeks");
pq.add("For");
pq.add("Geeks");
System.out.println(pq);
}
} Java
// Java program to remove elements
// from a PriorityQueue
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class PriorityQueueDemo {
public static void main(String args[])
{
PriorityQueue pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
pq.add("Geeks");
pq.add("For");
pq.add("Geeks");
System.out.println("Initial PriorityQueue " + pq);
// using the method
pq.remove("Geeks");
System.out.println("After Remove - " + pq);
System.out.println("Poll Method - " + pq.poll());
System.out.println("Final PriorityQueue - " + pq);
}
} Java
// Java program to access elements
// from a PriorityQueue
import java.util.*;
class PriorityQueueDemo {
// Main Method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating a priority queue
PriorityQueue pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
pq.add("Geeks");
pq.add("For");
pq.add("Geeks");
System.out.println("PriorityQueue: " + pq);
// Using the peek() method
String element = pq.peek();
System.out.println("Accessed Element: " + element);
}
} Java
// Java program to iterate elements
// to a PriorityQueue
import java.util.*;
public class PriorityQueueDemo {
// Main Method
public static void main(String args[])
{
PriorityQueue pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
pq.add("Geeks");
pq.add("For");
pq.add("Geeks");
Iterator iterator = pq.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.print(iterator.next() + " ");
}
}
} 输出:
10
10
15
PriorityQueue 上的操作
让我们看看如何在 Priority Queue 类上执行一些常用的操作。
1. 添加元素:为了在优先级队列中添加元素,我们可以使用 add() 方法。插入顺序不会保留在 PriorityQueue 中。元素根据默认升序的优先级顺序存储。
Java
// Java program to add elements
// to a PriorityQueue
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class PriorityQueueDemo {
public static void main(String args[])
{
PriorityQueue pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
pq.add("Geeks");
pq.add("For");
pq.add("Geeks");
System.out.println(pq);
}
}
输出:
[For, Geeks, Geeks]
2. 移除元素:为了从优先级队列中移除一个元素,我们可以使用 remove() 方法。如果有多个这样的对象,则删除第一次出现的对象。除此之外,poll() 方法还用于移除头部并返回它。
Java
// Java program to remove elements
// from a PriorityQueue
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class PriorityQueueDemo {
public static void main(String args[])
{
PriorityQueue pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
pq.add("Geeks");
pq.add("For");
pq.add("Geeks");
System.out.println("Initial PriorityQueue " + pq);
// using the method
pq.remove("Geeks");
System.out.println("After Remove - " + pq);
System.out.println("Poll Method - " + pq.poll());
System.out.println("Final PriorityQueue - " + pq);
}
}
输出:
Initial PriorityQueue [For, Geeks, Geeks]
After Remove - [For, Geeks]
Poll Method - For
Final PriorityQueue - [Geeks]
3、访问元素:由于队列遵循先进先出的原则,我们只能访问队列的头部。要访问优先级队列中的元素,我们可以使用 peek() 方法。
Java
// Java program to access elements
// from a PriorityQueue
import java.util.*;
class PriorityQueueDemo {
// Main Method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating a priority queue
PriorityQueue pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
pq.add("Geeks");
pq.add("For");
pq.add("Geeks");
System.out.println("PriorityQueue: " + pq);
// Using the peek() method
String element = pq.peek();
System.out.println("Accessed Element: " + element);
}
}
输出:
PriorityQueue: [For, Geeks, Geeks]
Accessed Element: For
4. 迭代PriorityQueue:有多种方法可以迭代PriorityQueue。最著名的方法是将队列转换为数组并使用 for 循环进行遍历。但是,队列也有一个内置的迭代器,可用于遍历队列。
Java
// Java program to iterate elements
// to a PriorityQueue
import java.util.*;
public class PriorityQueueDemo {
// Main Method
public static void main(String args[])
{
PriorityQueue pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
pq.add("Geeks");
pq.add("For");
pq.add("Geeks");
Iterator iterator = pq.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.print(iterator.next() + " ");
}
}
}
输出:
For Geeks Geeks
PriorityQueue 类中的方法
| METHOD | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| add(E e) | Inserts the specified element into this priority queue. |
| clear() | Removes all of the elements from this priority queue. |
| comparator() | Returns the comparator used to order the elements in this queue, or null if this queue is sorted according to the natural ordering of its elements. |
| contains(Object o) | Returns true if this queue contains the specified element. |
| forEach(Consumer action) | Performs the given action for each element of the Iterable until all elements have been processed or the action throws an exception. |
| iterator() | Returns an iterator over the elements in this queue. |
| offer(E e) | Inserts the specified element into this priority queue. |
| remove(Object o) | Removes a single instance of the specified element from this queue, if it is present. |
| removeAll(Collection c) | Removes all of this collection’s elements that are also contained in the specified collection (optional operation). |
| removeIf(Predicate filter) | Removes all of the elements of this collection that satisfy the given predicate. |
| retainAll(Collection c) | Retains only the elements in this collection that are contained in the specified collection (optional operation). |
| spliterator() | Creates a late-binding and fail-fast Spliterator over the elements in this queue. |
| toArray() | Returns an array containing all of the elements in this queue. |
| toArray(T[] a) | Returns an array containing all of the elements in this queue; the runtime type of the returned array is that of the specified array. |
在类Java.util.AbstractQueue 中声明的方法
| METHOD | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| addAll(Collection c) | Adds all of the elements in the specified collection to this queue. |
| element() | Retrieves, but does not remove, the head of this queue. |
| remove() | Retrieves and removes the head of this queue. |
在类Java.util.AbstractCollection 中声明的方法
| METHOD | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| containsAll(Collection c) | Returns true if this collection contains all of the elements in the specified collection. |
| isEmpty() | Returns true if this collection contains no elements. |
| toString() | Returns a string representation of this collection. |
在接口Java.util.Collection 中声明的方法
| METHOD | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| containsAll(Collection c) | Returns true if this collection contains all of the elements in the specified collection. |
| equals(Object o) | Compares the specified object with this collection for equality. |
| hashCode() | Returns the hash code value for this collection. |
| isEmpty() | Returns true if this collection contains no elements. |
| parallelStream() | Returns a possibly parallel Stream with this collection as its source. |
| size() | Returns the number of elements in this collection. |
| stream() | Returns a sequential Stream with this collection as its source. |
| toArray(IntFunction | Returns an array containing all of the elements in this collection, using the provided generator function to allocate the returned array. |
接口Java.util.Queue 中声明的方法
| METHOD | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| peek() | Retrieves, but does not remove, the head of this queue, or returns null if this queue is empty. |
| poll() | Retrieves and removes the head of this queue, or returns null if this queue is empty. |
应用:
- 实现 Dijkstra 和 Prim 算法。
- 在 K 次否定后最大化数组总和
相关文章:
- Java Java类
- Java中通过Comparator实现PriorityQueue