给定两个凸多边形,我们需要找到这些多边形的上下切线。
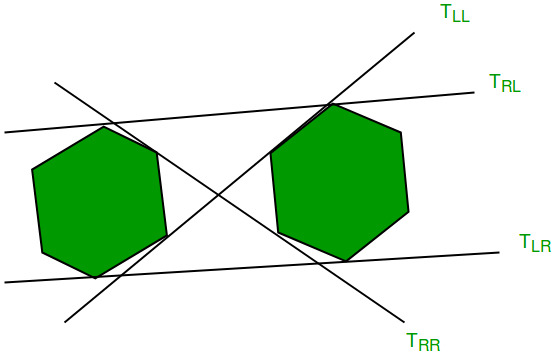
如下图所示, ![]() 和
和![]() 分别显示上切线和下切线。
分别显示上切线和下切线。
例子:
Input : First Polygon : {(2, 2), (3, 3), (5, 2), (4, 0), (3, 1)}
Second Polygon : {(-1, 0), (0, 1), (1, 0), (0, -2)}.
Output : Upper Tangent - line joining (0,1) and (3,3)
Lower Tangent - line joining (0,-2) and (4,0)
概述:
如图所示,我们有两个凸多边形, 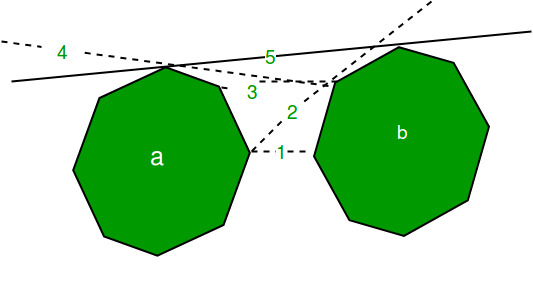
为了找到上切线,我们从两点开始。 a的最右点和b的最左点。连接它们的线标记为1。这条线穿过多边形b(不在多边形b上方),因此我们沿b的逆时针下一个点进行标记,该线标记为2。现在,该线在多边形b上方, 美好的!但是该线与多边形a相交,因此我们移至顺时针的下一个点,在图片中标记为3。它再次与多边形a相交,因此我们移至线4。这条线与b相交,因此我们移至线5。因此,这是给定多边形的上切线。
为了找到较低的切线,我们需要反向移动多边形,即,如果线与多边形b相交,则移动到下一个顺时针方向,如果线与多边形a相交,则移动到下一个逆时针方向。
上切线算法:
L Algorithm for lower tangent:
L // C++ program to find upper tangent of two polygons.#includeusing namespace std; // stores the center of polygon (It is made// global becuase it is used in compare function)pair mid; // determines the quadrant of a point// (used in compare())int quad(pair p){ if (p.first >= 0 && p.second >= 0) return 1; if (p.first <= 0 && p.second >= 0) return 2; if (p.first <= 0 && p.second <= 0) return 3; return 4;} // Checks whether the line is crossing the polygonint orientation(pair a, pair b, pair c){ int res = (b.second-a.second)*(c.first-b.first) - (c.second-b.second)*(b.first-a.first); if (res == 0) return 0; if (res > 0) return 1; return -1;} // compare function for sortingbool compare(pair p1, pair q1){ pair p = make_pair(p1.first - mid.first, p1.second - mid.second); pair q = make_pair(q1.first - mid.first, q1.second - mid.second); int one = quad(p); int two = quad(q); if (one != two) return (one < two); return (p.second*q.first < q.second*p.first);} // Finds upper tangent of two polygons 'a' and 'b'// represented as two vectors.void findUpperTangent(vector > a, vector > b){ // n1 -> number of points in polygon a // n2 -> number of points in polygon b int n1 = a.size(), n2 = b.size(); // To find a point inside the convex polygon(centroid), // we sum up all the coordinates and then divide by // n(number of points). But this would be a floating-point // value. So to get rid of this we multiply points // initially with n1 and then find the centre and // then divided it by n1 again. // Similarly we do divide and multiply for n2 (i.e., // elements of b) // maxa and minb are used to check if polygon a // is left of b. int maxa = INT_MIN; for (int i=0; i rightmost point of a int ia = 0, ib = 0; for (int i=1; i a[ia].first) ia = i; // ib -> leftmost point of b for (int i=1; i 0) inda = (inda + 1) % n1; while (orientation(a[inda], b[indb], b[(n2+indb-1)%n2]) < 0) { indb = (n2+indb-1)%n2; done = 0; } } cout << "upper tangent (" << a[inda].first << "," << a[inda].second << ") (" << b[indb].first << "," << b[indb].second << ")\n";} // Driver codeint main(){ vector > a; a.push_back({2, 2}); a.push_back({3, 1}); a.push_back({3, 3}); a.push_back({5, 2}); a.push_back({4, 0}); vector > b; b.push_back({0, 1}); b.push_back({1, 0}); b.push_back({0, -2}); b.push_back({-1, 0}); findUpperTangent(a, b); return 0;}Output:
Upper tangent (0,1) (3,3)
Note that the above code only finds upper tangent. We can similarly find lower tangent.