在给定的直方图中找到最大的矩形区域,其中最大的矩形可以由许多连续的条形组成。为简单起见,假定所有条形都具有相同的宽度,并且宽度为1个单位。
例如,考虑以下7个高度为{6,2,5,4,4,5,1,6}的直方图。可能的最大矩形是12(请参见下图,最大面积的矩形以红色突出显示)
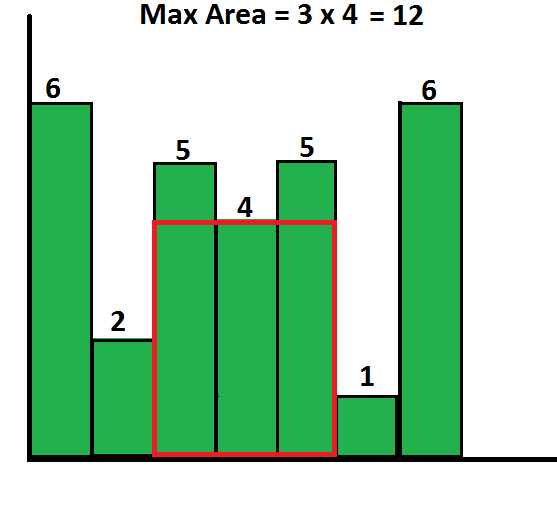
一个简单的解决方案是一个接一个地将所有条形图作为起点,并计算从每个条形图开始的所有矩形的面积。最后返回所有可能区域的最大值。该解决方案的时间复杂度为O(n ^ 2)。
我们可以使用分而治之在O(nLogn)时间内解决此问题。这个想法是在给定的数组中找到最小值。一旦我们有了最小值的索引,则最大面积就是以下三个值中的最大值。
a)最小值左侧的最大面积(不包括最小值)
b)最小值右侧的最大面积(不包括最小值)
c)条数乘以最小值。
最小值栏左右的区域可以递归计算。如果我们使用线性搜索来找到最小值,那么该算法在最坏情况下的时间复杂度将变为O(n ^ 2)。在最坏的情况下,我们总是在一侧有(n-1)个元素,在另一侧总是有0个元素,并且如果发现最小值花费O(n)的时间,则得到的重复率类似于快速排序的最坏情况。
如何有效地找到最小值?为此,可以使用使用段树的范围最小查询。我们构建给定直方图高度的细分树。一旦构建了细分树,所有范围的最小查询都将花费O(Logn)时间。因此,整个算法变得非常复杂。
总时间=建立细分树的时间+递归找到最大面积的时间
建立段树的时间为O(n)。令递归找到最大面积的时间为T(n)。可以这样写。
T(n)= O(登录)+ T(n-1)
上述重复的解决方案是O(nLogn)。因此,总时间为O(n)+ O(nLogn),即O(nLogn)。
以下是上述算法的C++实现。
C++
// A Divide and Conquer Program to find maximum rectangular area in a histogram
#include
using namespace std;
// A utility function to find minimum of three integers
int max(int x, int y, int z)
{ return max(max(x, y), z); }
// A utility function to get minimum of two numbers in hist[]
int minVal(int *hist, int i, int j)
{
if (i == -1) return j;
if (j == -1) return i;
return (hist[i] < hist[j])? i : j;
}
// A utility function to get the middle index from corner indexes.
int getMid(int s, int e)
{ return s + (e -s)/2; }
/* A recursive function to get the index of minimum value in a given range of
indexes. The following are parameters for this function.
hist --> Input array for which segment tree is built
st --> Pointer to segment tree
index --> Index of current node in the segment tree. Initially 0 is
passed as root is always at index 0
ss & se --> Starting and ending indexes of the segment represented by
current node, i.e., st[index]
qs & qe --> Starting and ending indexes of query range */
int RMQUtil(int *hist, int *st, int ss, int se, int qs, int qe, int index)
{
// If segment of this node is a part of given range, then return the
// min of the segment
if (qs <= ss && qe >= se)
return st[index];
// If segment of this node is outside the given range
if (se < qs || ss > qe)
return -1;
// If a part of this segment overlaps with the given range
int mid = getMid(ss, se);
return minVal(hist, RMQUtil(hist, st, ss, mid, qs, qe, 2*index+1),
RMQUtil(hist, st, mid+1, se, qs, qe, 2*index+2));
}
// Return index of minimum element in range from index qs (quey start) to
// qe (query end). It mainly uses RMQUtil()
int RMQ(int *hist, int *st, int n, int qs, int qe)
{
// Check for erroneous input values
if (qs < 0 || qe > n-1 || qs > qe)
{
cout << "Invalid Input";
return -1;
}
return RMQUtil(hist, st, 0, n-1, qs, qe, 0);
}
// A recursive function that constructs Segment Tree for hist[ss..se].
// si is index of current node in segment tree st
int constructSTUtil(int hist[], int ss, int se, int *st, int si)
{
// If there is one element in array, store it in current node of
// segment tree and return
if (ss == se)
return (st[si] = ss);
// If there are more than one elements, then recur for left and
// right subtrees and store the minimum of two values in this node
int mid = getMid(ss, se);
st[si] = minVal(hist, constructSTUtil(hist, ss, mid, st, si*2+1),
constructSTUtil(hist, mid+1, se, st, si*2+2));
return st[si];
}
/* Function to construct segment tree from given array. This function
allocates memory for segment tree and calls constructSTUtil() to
fill the allocated memory */
int *constructST(int hist[], int n)
{
// Allocate memory for segment tree
int x = (int)(ceil(log2(n))); //Height of segment tree
int max_size = 2*(int)pow(2, x) - 1; //Maximum size of segment tree
int *st = new int[max_size];
// Fill the allocated memory st
constructSTUtil(hist, 0, n-1, st, 0);
// Return the constructed segment tree
return st;
}
// A recursive function to find the maximum rectangular area.
// It uses segment tree 'st' to find the minimum value in hist[l..r]
int getMaxAreaRec(int *hist, int *st, int n, int l, int r)
{
// Base cases
if (l > r) return INT_MIN;
if (l == r) return hist[l];
// Find index of the minimum value in given range
// This takes O(Logn)time
int m = RMQ(hist, st, n, l, r);
/* Return maximum of following three possible cases
a) Maximum area in Left of min value (not including the min)
a) Maximum area in right of min value (not including the min)
c) Maximum area including min */
return max(getMaxAreaRec(hist, st, n, l, m-1),
getMaxAreaRec(hist, st, n, m+1, r),
(r-l+1)*(hist[m]) );
}
// The main function to find max area
int getMaxArea(int hist[], int n)
{
// Build segment tree from given array. This takes
// O(n) time
int *st = constructST(hist, n);
// Use recursive utility function to find the
// maximum area
return getMaxAreaRec(hist, st, n, 0, n-1);
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
int hist[] = {6, 1, 5, 4, 5, 2, 6};
int n = sizeof(hist)/sizeof(hist[0]);
cout << "Maximum area is " << getMaxArea(hist, n);
return 0;
} Python3
# Python3 program for range minimum
# query using segment tree
# modified to return index of minimum instead of minimum itself
# for further reference link
# https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/segment-tree-set-1-range-minimum-query/
#-------------------------------------------------------------------------
from math import ceil,log2;
# A utility function to get
# minimum of two numbers
def minVal(hist,x, y) :
if x==-1:
return y
if y==-1:
return x
return x if (hist[x] < hist[y]) else y;
# A utility function to get the
# middle index from corner indexes.
def getMid(s, e) :
return s + (e - s) // 2;
""" A recursive function to get the
minimum value in a given range
of array indexes. The following
are parameters for this function.
st --> Pointer to segment tree
index --> Index of current node in the
segment tree. Initially 0 is
passed as root is always at index 0
ss & se --> Starting and ending indexes
of the segment represented
by current node, i.e., st[index]
qs & qe --> Starting and ending indexes of query range """
def RMQUtil( hist,st, ss, se, qs, qe, index) :
# If segment of this node is a part
# of given range, then return
# the min of the segment
if (qs <= ss and qe >= se) :
return st[index];
# If segment of this node
# is outside the given range
if (se < qs or ss > qe) :
return -1;
# If a part of this segment
# overlaps with the given range
mid = getMid(ss, se);
return minVal(hist,RMQUtil(hist,st, ss, mid, qs,
qe, 2 * index + 1),
RMQUtil(hist,st, mid + 1, se,
qs, qe, 2 * index + 2));
# Return minimum of elements in range
# from index qs (query start) to
# qe (query end). It mainly uses RMQUtil()
def RMQ( hist,st, n, qs, qe) :
# Check for erroneous input values
if (qs < 0 or qe > n - 1 or qs > qe) :
print("Invalid Input");
return -1;
return RMQUtil(hist,st, 0, n - 1, qs, qe, 0);
# A recursive function that constructs
# Segment Tree for array[ss..se].
# si is index of current node in segment tree st
def constructSTUtil(hist, ss, se, st, si) :
# If there is one element in array,
# store it in current node of
# segment tree and return
if (ss == se) :
st[si] = ss;
return st[si];
# If there are more than one elements,
# then recur for left and right subtrees
# and store the minimum of two values in this node
mid = getMid(ss, se);
st[si] = minVal(hist,constructSTUtil(hist, ss, mid,
st, si * 2 + 1),
constructSTUtil(hist, mid + 1, se,
st, si * 2 + 2));
return st[si];
"""Function to construct segment tree
from given array. This function allocates
memory for segment tree and calls constructSTUtil()
to fill the allocated memory """
def constructST( hist, n) :
# Allocate memory for segment tree
# Height of segment tree
x = (int)(ceil(log2(n)));
# Maximum size of segment tree
max_size = 2 * (int)(2**x) - 1;
st = [0] * (max_size);
# Fill the allocated memory st
constructSTUtil(hist, 0, n - 1, st, 0);
# Return the constructed segment tree
return st;
#----------------------------------------------------------------
# main program
# Python3 program using Divide and Conquer
# to find maximum rectangular area under a histogram
def max_area_histogram(hist):
area=0
#initialize area
st = constructST(hist, len(hist))
# contruct the segment tree
try:
# try except block is generally used in this way
# to suppress all type of exceptions raised.
def fun(left,right):
# this function "fun" calculates area
# recursively between indices left and right
nonlocal area
# global area won't work here as
# variable area is defined inside function
# not in main().
if left==right:
return
# the recursion has reached end
index = RMQ(hist,st, len(hist), left, right-1)
# RMQ function returns index
# of minimum value
# in the range of [left,right-1]
# can also be found by using min() but
# results in O(n) instead of O(log n) for traversing
area=max(area,hist[index]*(right-left))
# calculate area with minimum above
fun(index+1,right)
fun(left,index)
# initiate further recursion
return
fun(0,len(hist))
# initializes the recursion
return(area)
# return the max area to calling function
# in this case "print"
except:
pass
# Driver Code
hist = [6, 2, 5, 4, 5, 1, 6]
print("Maximum area is",
max_area_histogram(hist))
# This code is contributed
# by Vishnudev C.输出:
Maximum area is 12这个问题可以在线性时间内解决。有关线性时间解,请参见下面的第2组。
直方图中最大矩形区域的线性时间解