创建临时文件的Java程序
File 是一个抽象的路径,它没有物理存在。只有在“使用”该文件时,才会命中底层物理存储。当文件被间接创建时,抽象路径被创建。该文件是一种方式,其中数据将根据需要存储。
Type of File
- .txt
- .tmp (Default File Type)
主要,为了创建一个临时文件,使用了内置文件和函数,这些文件和函数肯定会在这里抛出异常,以确保安全。所以为了处理它,我们将使用异常处理技术。在这里,我们将使用其中一种已知的 as-try-catch 块技术。
其次,额外的工作只是我们将导入我们将为其导入文件类的文件类。
语法:导入文件库或类
import java.util.File ;
语法:创建一个新文件
File object_name = new File(Directory)
语法:指定目录在不同的操作系统中是不同的(假设Java文件在桌面上创建的名为'Folder'的文件夹中)
在 Linux 和 Mac 中
/Users/mayanksolanki/Desttop/Folder/
在 Windows 中:使用 '\\' 代替 '/' 来转义 '\'字符。所以访问相同的目录
\\Users\\mayanksolanki\\Desktop\\Folder\\
一个临时文件,这本身意味着应该被创建,只是不太可能创建一个新文件,稍后应该在调用删除文件的命令时擦除。
方法:在Java中创建临时文件的标准方法是使用,例如,创建,写入,比较两个路径名,检查特定文件是否存在等等。要理解这个话题,首先考虑一个简单的代码作为例子。所以这里的任务分为两部分。首先,应该在指定的目录中创建一个新文件,并在创建它的同一目录中删除相同的文件。 Java提供了许多处理文件的方法。
创建临时文件有两种标准方法
- File.createTempFile
- file.getAbsolutePath
方法一:File.createTempFile(String prefix, String suffix, File directory)
它是一个内置的标准方法,负责创建一个临时文件。它在本地个人计算机上指定的目录中创建一个临时文件,只要有访问权限即可。它需要 3 个参数,即前缀、后缀和应该创建临时文件的目录
该方法中的参数为:
- 前缀:前缀字符串是文件的名称。
- 后缀:后缀字符串是必须创建的文件类型的扩展名(例如:.txt)。但是,如果没有给出参数,.tmp 将是默认文件类型。
- 文件目录是将存储临时文件的目录。必须指定“NULL”才能使用默认目录。
示例:目录访问与操作系统不同。因此,为了实现 mac 生态系统,需要考虑访问目录的语法。
基本终端命令
- Terminal Command used to compile any java code on the machine
- Terminal Command used to Run any java code on the machine
- javac class_name.java // For Compilation
- java class_name // For Execution
Terminal of Mac operating system will be used for implementation and providing an output of accessing the directory
Directory Used : /Users/mayanksolanki/Desktop/Folder/
举个例子来说明Java程序中临时文件的创建
Java
/// Java program to illustrate a temporary file creation
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
public class GFG {
// Main Method
public static void main(String[] args)
throws IOException
{
// Creating a string for the prefix
String prefix = "exampleFile";
// Creating a string for the suffix
String suffix = ".txt";
// Creating a File object for the directory path
File directoryPath = new File(
"/Users/mayanksolanki/Desktop/Folder/");
// Creating the temporary file
File tempFile = File.createTempFile(prefix, suffix,
directoryPath);
// Deleting the File after while exiting the
// program(optional)
tempFile.delete();
}
}Java
// Importing Classes/Files
import java.io.File;
public class GFG {
// Main Driver Method
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
// Creating the temporary file
File file = File.createTempFile(
"temp", ".txt",
new File(
" /Users/mayanksolanki/Desktop/Folder/"));
// Printing the path of the directory where the file
// is created
System.out.println(file.getAbsolutePath());
Sysytem.out.print(/Users/mayanksolanki/Desktop/Folder/);
// Deleting the file while exiting the program
file.deleteOnExit();
}
}输出:

Ambiguity lies in the delete operation- tempFile.delete() // Refer to line number 27 in above code
The rate at which above java command executes is too faster that no file is seen in the directory window. Actually the file is created in the directory and deleted at the same time. Other proof can be if after file creation the programmer insert print statement “Temp file created ” than it will be displayed as the output but again no temporary file icon will be visible in the directory.
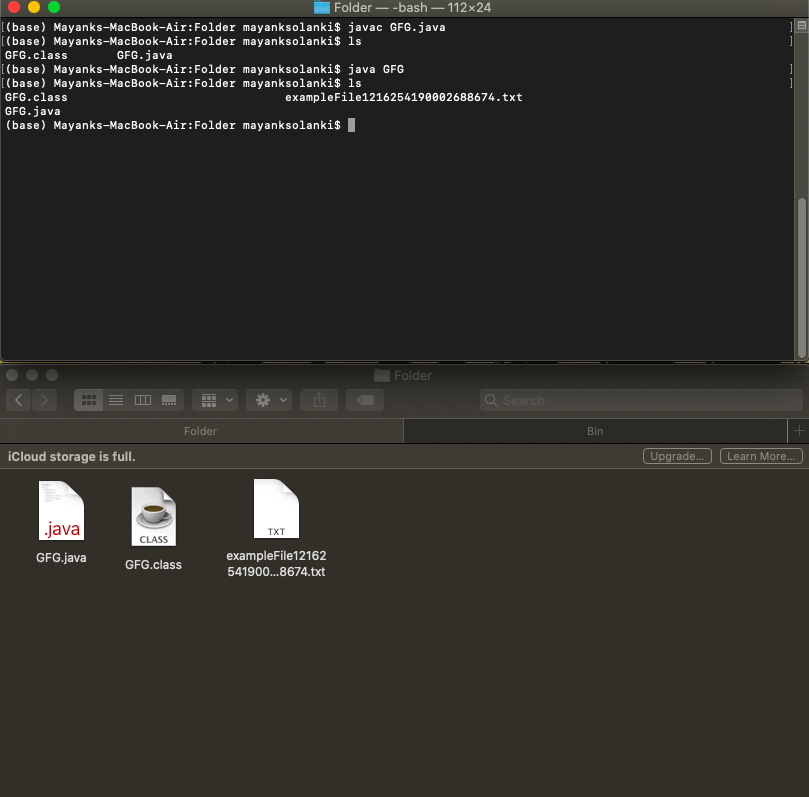
通过实例可视化输出,以达到更高水平的理解。在目录中,当代码被执行时:
Image1:代码成功编译时的快照,直到现在代码没有在终端中执行

Image2:代表在系统上创建任何临时文件之前的实例的快照
ls // The terminal command used here to check files inside the current folder

Image3:它应该是通过眼球看到的实际输出,但事实并非如此。用户将无法看到在指定目录(此处为文件夹)中创建的任何临时文件,但它已创建。整个概念围绕着最后需要的删除操作的速度来终止代码以制作应该临时创建的文件。
方法二:
让我们再举一个对上述方法略有改进的例子来说明Java程序中的临时文件
Java
// Importing Classes/Files
import java.io.File;
public class GFG {
// Main Driver Method
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
// Creating the temporary file
File file = File.createTempFile(
"temp", ".txt",
new File(
" /Users/mayanksolanki/Desktop/Folder/"));
// Printing the path of the directory where the file
// is created
System.out.println(file.getAbsolutePath());
Sysytem.out.print(/Users/mayanksolanki/Desktop/Folder/);
// Deleting the file while exiting the program
file.deleteOnExit();
}
}
输出:
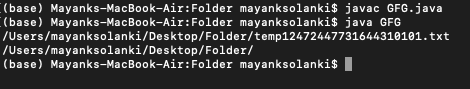
这里,程序返回在指定目录中创建的空临时文件的路径,并在退出时删除该文件。