打印所有没有兄弟节点的节点
给定二叉树,打印所有没有兄弟节点的节点(兄弟节点是具有相同父节点的节点。在二叉树中,最多可以有一个兄弟节点)。不应打印根,因为根不能有兄弟。
例如,以下树的输出应为“4 5 6”。
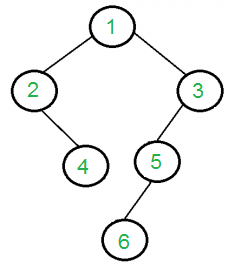
这是一个典型的树遍历问题。我们从根开始检查该节点是否有一个孩子,如果是,则打印该节点的唯一孩子。如果节点有两个孩子,则为两个孩子重复。
以下是上述方法的实现:
C++
/* Program to find singles in a given binary tree */
#include
using namespace std;
// A Binary Tree Node
struct node
{
struct node *left, *right;
int key;
};
// Utility function to create a new tree node
node* newNode(int key)
{
node *temp = new node;
temp->key = key;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
// Function to print all non-root nodes
// that don't have a sibling
void printSingles(struct node *root)
{
// Base case
if (root == NULL)
return;
// If this is an internal node, recur for left
// and right subtrees
if (root->left != NULL && root->right != NULL)
{
printSingles(root->left);
printSingles(root->right);
}
// If left child is NULL and right is not,
// print right child
// and recur for right child
else if (root->right != NULL)
{
cout << root->right->key << " ";
printSingles(root->right);
}
// If right child is NULL and left is
// not, print left child
// and recur for left child
else if (root->left != NULL)
{
cout << root->left->key << " ";
printSingles(root->left);
}
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
// Let us create binary tree
// given in the above example
node *root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->right = newNode(4);
root->right->left = newNode(5);
root->right->left->left = newNode(6);
printSingles(root);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to print all nodes
// that don't have sibling
// A binary tree node
class Node
{
int data;
Node left, right;
Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
class BinaryTree
{
Node root;
// Function to print all non-root nodes
// that don't have a sibling
void printSingles(Node node)
{
// Base case
if (node == null)
return;
// If this is an internal node, recur for left
// and right subtrees
if (node.left != null && node.right != null)
{
printSingles(node.left);
printSingles(node.right);
}
// If left child is NULL and right
// is not, print right child
// and recur for right child
else if (node.right != null)
{
System.out.print(node.right.data + " ");
printSingles(node.right);
}
// If right child is NULL and left
// is not, print left child
// and recur for left child
else if (node.left != null)
{
System.out.print( node.left.data + " ");
printSingles(node.left);
}
}
// Driver program to test the above functions
public static void main(String args[])
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
/* Let us construct the tree
shown in above diagram */
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(4);
tree.root.right.left = new Node(5);
tree.root.right.left.right = new Node(6);
tree.printSingles(tree.root);
}
}
// This code has been contributed by Mayank JaiswalPython3
# Python3 program to find singles in a given binary tree
# A Binary Tree Node
class Node:
# A constructor to create new tree node
def __init__(self, key):
self.key = key
self.left = None
self.right = None
# Function to print all non-root nodes that don't have
# a sibling
def printSingles(root):
# Base Case
if root is None:
return
# If this is an internal node , recur for left
# and right subtrees
if root.left is not None and root.right is not None:
printSingles(root.left)
printSingles(root.right)
# If left child is NULL, and right is not, print
# right child and recur for right child
elif root.right is not None:
print (root.right.key,end=" ")
printSingles(root.right)
# If right child is NULL and left is not, print
# left child and recur for left child
elif root.left is not None:
print (root.left.key,end=" ")
printSingles(root.left)
# Driver program to test above function
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.left.right = Node(4)
root.right.left = Node(5)
root.right.left.left = Node(6)
printSingles(root)
# This code is contributed by Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007)C#
using System;
// C# program to print all nodes that don't have sibling
// A binary tree node
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
public class BinaryTree
{
public Node root;
// Function to print all non-root nodes that don't have a sibling
public virtual void printSingles(Node node)
{
// Base case
if (node == null)
{
return;
}
// If this is an internal node, recur for left
// and right subtrees
if (node.left != null && node.right != null)
{
printSingles(node.left);
printSingles(node.right);
}
// If left child is NULL and right is not, print right child
// and recur for right child
else if (node.right != null)
{
Console.Write(node.right.data + " ");
printSingles(node.right);
}
// If right child is NULL and left is not, print left child
// and recur for left child
else if (node.left != null)
{
Console.Write(node.left.data + " ");
printSingles(node.left);
}
}
// Driver program to test the above functions
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
/* Let us construct the tree shown in above diagram */
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(4);
tree.root.right.left = new Node(5);
tree.root.right.left.right = new Node(6);
tree.printSingles(tree.root);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Shrikant13Javascript
C++14
// CPP program for above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// A Binary Tree Node
struct node
{
struct node *left, *right;
int data;
};
// Utility function to
// create a new tree node
node* newNode(int key)
{
node *temp = new node;
temp->data= key;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
// Function to print all
// non-root nodes that
// don't have a sibling
void printSingles(struct node *root)
{
// Base case
if (root == NULL)
return;
queue q1;
q1.push(root);
int flag=0;
vector v;
// While q1 is not empty
while(q1.empty() == false)
{
struct node * temp=q1.front();
q1.pop();
// Check if temp->left is not
// NULL and temp->right is NULL
if(temp->left != NULL &&
temp->right == NULL)
{
flag=1;
v.push_back(temp->left->data);
}
// Check if temp->left is equal
// NULL and temp->right is not NULL
if(temp->left == NULL &&
temp->right != NULL)
{
flag=1;
v.push_back(temp->right->data);
}
// Check if temp->left is not
// NULL
if(temp->left != NULL)
{
q1.push(temp->left);
}
// Check if temp->right is not
// NULL
if(temp->right != NULL)
{
q1.push(temp->right);
}
}
// Sort v in increasing order
sort(v.begin(), v.end());
// Iterate i from 0 to v.size() - 1
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++)
{
cout<< v[i] << " ";
}
// Check is v is empty
if (v.size() == 0)
{
cout<<"-1";
}
}
// Driver program to test
// above functions
int main()
{
// Let us create binary tree
// given in the above example
node *root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->right = newNode(4);
root->right->left = newNode(5);
root->right->left->left = newNode(6);
// Function Call
printSingles(root);
return 0;
} Java
// JAVA program for above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
// A Binary Tree Node
static class node
{
node left, right;
int data;
};
// Utility function to
// create a new tree node
static node newNode(int key)
{
node temp = new node();
temp.data = key;
temp.left = temp.right = null;
return temp;
}
// Function to print all
// non-root nodes that
// don't have a sibling
static void printSingles(node root)
{
// Base case
if (root == null)
return;
Queue q1 = new LinkedList<>();
q1.add(root);
int flag = 0;
Vector v = new Vector<>();
// While q1 is not empty
while(q1.isEmpty() == false)
{
node temp = q1.peek();
q1.remove();
// Check if temp.left is not
// null and temp.right is null
if(temp.left != null &&
temp.right == null)
{
flag = 1;
v.add(temp.left.data);
}
// Check if temp.left is equal
// null and temp.right is not null
if(temp.left == null &&
temp.right != null)
{
flag = 1;
v.add(temp.right.data);
}
// Check if temp.left is not
// null
if(temp.left != null)
{
q1.add(temp.left);
}
// Check if temp.right is not
// null
if(temp.right != null)
{
q1.add(temp.right);
}
}
// Sort v in increasing order
Collections.sort(v);
// Iterate i from 0 to v.size() - 1
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++)
{
System.out.print( v.get(i) + " ");
}
// Check is v is empty
if (v.size() == 0)
{
System.out.print("-1");
}
}
// Driver program to test
// above functions
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Let us create binary tree
// given in the above example
node root = newNode(1);
root.left = newNode(2);
root.right = newNode(3);
root.left.right = newNode(4);
root.right.left = newNode(5);
root.right.left.left = newNode(6);
// Function Call
printSingles(root);
}
}
// This code is contributed by aashish1995 Python3
# Python3 program for above approach
from queue import Queue
# A Binary Tree Node
class Node:
# A constructor to create new tree node
def __init__(self, key):
self.key = key
self.left = None
self.right = None
# Function to print all non-root nodes
# that don't have a sibling
def printSingles(root):
# Base Case
if root is None:
return
q1 = Queue(maxsize = 100)
q1.put(root)
flag = 0
v = []
# While q1 is not empty
while q1.empty() == False:
temp = q1.get()
# Check if temp->left is not
# NULL and temp->right is NULL
if temp.left is not None and temp.right is None:
flag = 1
v.append(temp.left.key)
# Check if temp->left is equal
# NULL and temp->right is not NULL
if temp.left is None and temp.right is not None:
flag = 1
v.append(temp.right.key)
# Check if temp->left is not
# NULL
if temp.left is not None:
q1.put(temp.left)
# Check if temp->right is not
# NULL
if temp.right is not None:
q1.put(temp.right)
# Sort v in increasing order
v.sort()
for i in v:
print(i, end = " ")
# Check is v is empty
if len(v) == 0:
print("-1")
# Driver code
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.left.right = Node(4)
root.right.left = Node(5)
root.right.left.left = Node(6)
printSingles(root)
# This code is contributed by codersatyC#
// C# program for above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
// A Binary Tree Node
public
class node
{
public
node left, right;
public
int data;
};
// Utility function to
// create a new tree node
static node newNode(int key)
{
node temp = new node();
temp.data = key;
temp.left = temp.right = null;
return temp;
}
// Function to print all
// non-root nodes that
// don't have a sibling
static void printSingles(node root)
{
// Base case
if (root == null)
return;
Queue q1 = new Queue();
q1.Enqueue(root);
int flag = 0;
List v = new List();
// While q1 is not empty
while(q1.Count != 0)
{
node temp = q1.Peek();
q1.Dequeue();
// Check if temp.left is not
// null and temp.right is null
if(temp.left != null &&
temp.right == null)
{
flag = 1;
v.Add(temp.left.data);
}
// Check if temp.left is equal
// null and temp.right is not null
if(temp.left == null &&
temp.right != null)
{
flag = 1;
v.Add(temp.right.data);
}
// Check if temp.left is not
// null
if(temp.left != null)
{
q1.Enqueue(temp.left);
}
// Check if temp.right is not
// null
if(temp.right != null)
{
q1.Enqueue(temp.right);
}
}
// Sort v in increasing order
v.Sort();
// Iterate i from 0 to v.Count - 1
for (int i = 0; i < v.Count; i++)
{
Console.Write( v[i] + " ");
}
// Check is v is empty
if (v.Count == 0)
{
Console.Write("-1");
}
}
// Driver program to test
// above functions
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Let us create binary tree
// given in the above example
node root = newNode(1);
root.left = newNode(2);
root.right = newNode(3);
root.left.right = newNode(4);
root.right.left = newNode(5);
root.right.left.left = newNode(6);
// Function Call
printSingles(root);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji. Javascript
输出:
4 5 6 时间复杂度: O(n)
迭代方法中的替代实现:
我们从根开始检查该节点是否有一个孩子,如果是,则打印该节点的唯一孩子。如果节点有两个孩子,则将两个孩子都推入队列。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++14
// CPP program for above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// A Binary Tree Node
struct node
{
struct node *left, *right;
int data;
};
// Utility function to
// create a new tree node
node* newNode(int key)
{
node *temp = new node;
temp->data= key;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
// Function to print all
// non-root nodes that
// don't have a sibling
void printSingles(struct node *root)
{
// Base case
if (root == NULL)
return;
queue q1;
q1.push(root);
int flag=0;
vector v;
// While q1 is not empty
while(q1.empty() == false)
{
struct node * temp=q1.front();
q1.pop();
// Check if temp->left is not
// NULL and temp->right is NULL
if(temp->left != NULL &&
temp->right == NULL)
{
flag=1;
v.push_back(temp->left->data);
}
// Check if temp->left is equal
// NULL and temp->right is not NULL
if(temp->left == NULL &&
temp->right != NULL)
{
flag=1;
v.push_back(temp->right->data);
}
// Check if temp->left is not
// NULL
if(temp->left != NULL)
{
q1.push(temp->left);
}
// Check if temp->right is not
// NULL
if(temp->right != NULL)
{
q1.push(temp->right);
}
}
// Sort v in increasing order
sort(v.begin(), v.end());
// Iterate i from 0 to v.size() - 1
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++)
{
cout<< v[i] << " ";
}
// Check is v is empty
if (v.size() == 0)
{
cout<<"-1";
}
}
// Driver program to test
// above functions
int main()
{
// Let us create binary tree
// given in the above example
node *root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->right = newNode(4);
root->right->left = newNode(5);
root->right->left->left = newNode(6);
// Function Call
printSingles(root);
return 0;
}
Java
// JAVA program for above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
// A Binary Tree Node
static class node
{
node left, right;
int data;
};
// Utility function to
// create a new tree node
static node newNode(int key)
{
node temp = new node();
temp.data = key;
temp.left = temp.right = null;
return temp;
}
// Function to print all
// non-root nodes that
// don't have a sibling
static void printSingles(node root)
{
// Base case
if (root == null)
return;
Queue q1 = new LinkedList<>();
q1.add(root);
int flag = 0;
Vector v = new Vector<>();
// While q1 is not empty
while(q1.isEmpty() == false)
{
node temp = q1.peek();
q1.remove();
// Check if temp.left is not
// null and temp.right is null
if(temp.left != null &&
temp.right == null)
{
flag = 1;
v.add(temp.left.data);
}
// Check if temp.left is equal
// null and temp.right is not null
if(temp.left == null &&
temp.right != null)
{
flag = 1;
v.add(temp.right.data);
}
// Check if temp.left is not
// null
if(temp.left != null)
{
q1.add(temp.left);
}
// Check if temp.right is not
// null
if(temp.right != null)
{
q1.add(temp.right);
}
}
// Sort v in increasing order
Collections.sort(v);
// Iterate i from 0 to v.size() - 1
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++)
{
System.out.print( v.get(i) + " ");
}
// Check is v is empty
if (v.size() == 0)
{
System.out.print("-1");
}
}
// Driver program to test
// above functions
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Let us create binary tree
// given in the above example
node root = newNode(1);
root.left = newNode(2);
root.right = newNode(3);
root.left.right = newNode(4);
root.right.left = newNode(5);
root.right.left.left = newNode(6);
// Function Call
printSingles(root);
}
}
// This code is contributed by aashish1995
Python3
# Python3 program for above approach
from queue import Queue
# A Binary Tree Node
class Node:
# A constructor to create new tree node
def __init__(self, key):
self.key = key
self.left = None
self.right = None
# Function to print all non-root nodes
# that don't have a sibling
def printSingles(root):
# Base Case
if root is None:
return
q1 = Queue(maxsize = 100)
q1.put(root)
flag = 0
v = []
# While q1 is not empty
while q1.empty() == False:
temp = q1.get()
# Check if temp->left is not
# NULL and temp->right is NULL
if temp.left is not None and temp.right is None:
flag = 1
v.append(temp.left.key)
# Check if temp->left is equal
# NULL and temp->right is not NULL
if temp.left is None and temp.right is not None:
flag = 1
v.append(temp.right.key)
# Check if temp->left is not
# NULL
if temp.left is not None:
q1.put(temp.left)
# Check if temp->right is not
# NULL
if temp.right is not None:
q1.put(temp.right)
# Sort v in increasing order
v.sort()
for i in v:
print(i, end = " ")
# Check is v is empty
if len(v) == 0:
print("-1")
# Driver code
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.left.right = Node(4)
root.right.left = Node(5)
root.right.left.left = Node(6)
printSingles(root)
# This code is contributed by codersaty
C#
// C# program for above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
// A Binary Tree Node
public
class node
{
public
node left, right;
public
int data;
};
// Utility function to
// create a new tree node
static node newNode(int key)
{
node temp = new node();
temp.data = key;
temp.left = temp.right = null;
return temp;
}
// Function to print all
// non-root nodes that
// don't have a sibling
static void printSingles(node root)
{
// Base case
if (root == null)
return;
Queue q1 = new Queue();
q1.Enqueue(root);
int flag = 0;
List v = new List();
// While q1 is not empty
while(q1.Count != 0)
{
node temp = q1.Peek();
q1.Dequeue();
// Check if temp.left is not
// null and temp.right is null
if(temp.left != null &&
temp.right == null)
{
flag = 1;
v.Add(temp.left.data);
}
// Check if temp.left is equal
// null and temp.right is not null
if(temp.left == null &&
temp.right != null)
{
flag = 1;
v.Add(temp.right.data);
}
// Check if temp.left is not
// null
if(temp.left != null)
{
q1.Enqueue(temp.left);
}
// Check if temp.right is not
// null
if(temp.right != null)
{
q1.Enqueue(temp.right);
}
}
// Sort v in increasing order
v.Sort();
// Iterate i from 0 to v.Count - 1
for (int i = 0; i < v.Count; i++)
{
Console.Write( v[i] + " ");
}
// Check is v is empty
if (v.Count == 0)
{
Console.Write("-1");
}
}
// Driver program to test
// above functions
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Let us create binary tree
// given in the above example
node root = newNode(1);
root.left = newNode(2);
root.right = newNode(3);
root.left.right = newNode(4);
root.right.left = newNode(5);
root.right.left.left = newNode(6);
// Function Call
printSingles(root);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji.
Javascript
输出
4 5 6