C中的嵌套结构与示例
先决条件:C 中的结构
C 中的嵌套结构是结构中的结构。一个结构可以在另一个结构中声明,就像在一个结构中声明结构成员一样。
句法:
struct name_1
{
member1;
member2;
.
.
membern;
struct name_2
{
member_1;
member_2;
.
.
member_n;
}, var1
} var2;
可以使用以下语法访问嵌套结构的成员:
Variable name of Outer_Structure.Variable name of Nested_Structure.data member to access
例子:
- 考虑有两个结构Employee (依赖结构)和另一个结构称为Organisation(Outer structure) 。
- 结构组织具有组织名称、组织编号等数据成员。
- Employee结构嵌套在结构Organization中,它具有employee_id、name、salary等数据成员。
为了访问组织和员工的成员,将使用以下语法:
org.emp.employee_id;
org.emp.name;
org.emp.salary;
org.organisation_name;
org.organisation_number;
Here, org is the structure variable of the outer structure Organisation and emp is the structure variable of the inner structure Employee.
嵌套结构的不同方式
该结构可以通过以下不同方式嵌套:
- 通过单独的嵌套结构
- 通过嵌入式嵌套结构。
1.通过单独的嵌套结构:在这种方法中,创建了两个结构,但是依赖结构(Employee)应该在主结构(Organisation)内部作为成员使用。下面是实现该方法的 C 程序:
C
// C program to implement
// the above approach
#include
#include
// Declaration of the
// dependent structure
struct Employee
{
int employee_id;
char name[20];
int salary;
};
// Declaration of the
// Outer structure
struct Organisation
{
char organisation_name[20];
char org_number[20];
// Dependent structure is used
// as a member inside the main
// structure for implementing
// nested structure
struct Employee emp;
};
// Driver code
int main()
{
// Structure variable
struct Organisation org;
// Print the size of organisation
// structure
printf("The size of structure organisation : %ld\n",
sizeof(org));
org.emp.employee_id = 101;
strcpy(org.emp.name, "Robert");
org.emp.salary = 400000;
strcpy(org.organisation_name,
"GeeksforGeeks");
strcpy(org.org_number, "GFG123768");
// Printing the details
printf("Organisation Name : %s\n",
org.organisation_name);
printf("Organisation Number : %s\n",
org.org_number);
printf("Employee id : %d\n",
org.emp.employee_id);
printf("Employee name : %s\n",
org.emp.name);
printf("Employee Salary : %d\n",
org.emp.salary);
} C
// C program to implement
// the above approach
#include
// Declaration of the outer
// structure
struct Organisation
{
char organisation_name[20];
char org_number[20];
// Declaration of the employee
// structure
struct Employee
{
int employee_id;
char name[20];
int salary;
// This line will cause error because
// datatype struct Employee is present ,
// but Structure variable is missing.
};
};
// Driver code
int main()
{
// Structure variable of organisation
struct Organisation org;
printf("%ld", sizeof(org));
} C
// C program to implement
// the above approach
#include
#include
// Declaration of the main
// structure
struct Organisation
{
char organisation_name[20];
char org_number[20];
// Declaration of the dependent
// structure
struct Employee
{
int employee_id;
char name[20];
int salary;
// variable is created which acts
// as member to Organisation structure.
} emp;
};
// Driver code
int main()
{
struct Organisation org;
// Print the size of organisation
// structure
printf("The size of structure organisation : %ld\n",
sizeof(org));
org.emp.employee_id = 101;
strcpy(org.emp.name, "Robert");
org.emp.salary = 400000;
strcpy(org.organisation_name,
"GeeksforGeeks");
strcpy(org.org_number, "GFG123768");
// Printing the details
printf("Organisation Name : %s\n",
org.organisation_name);
printf("Organisation Number : %s\n",
org.org_number);
printf("Employee id : %d\n",
org.emp.employee_id);
printf("Employee name : %s\n",
org.emp.name);
printf("Employee Salary : %d\n",
org.emp.salary);
} C
// C program to implement
// the nested structure
#include
#include
// Declaration of Outer structure
struct College
{
char college_name[20];
int ranking;
// Declaration of Inner structure
struct Student
{
int student_id;
char name[20];
int roll_no;
// Inner structure variable
} student1;
};
// Driver code
int main()
{
struct College c1 = {"GeeksforGeeks", 7,
{111, "Paul", 278}};
printf("College name : %s\n",
c1.college_name);
printf("Ranking : %d\n",
c1.ranking);
printf("Student id : %d\n",
c1.student1.student_id);
printf("Student name : %s\n",
c1.student1.name);
printf("Roll no : %d\n",
c1.student1.roll_no);
return 0;
} C
// C program to implement
// the above approach
#include
// Declaration of the inner
// structure
struct Employee
{
int employee_id;
char name[20];
int salary;
};
// Declaration of the Outer
// structure
struct Organisation
{
char organisation_name[20];
char org_number[20];
// Nested structure
struct Employee emp;
};
// Function show is expecting
// variable of outer structure
void show(struct Organisation);
// Driver code
int main()
{
struct Organisation org = {"GeeksforGeeks", "GFG111",
{278, "Paul",5000}};
// Organisation structure variable
// is passed to function show
show(org);
}
// Function shoe definition
void show(struct Organisation org )
{
// Printing the details
printf("Printing the Details :\n");
printf("Organisation Name : %s\n",
org.organisation_name);
printf("Organisation Number : %s\n",
org.org_number);
printf("Employee id : %d\n",
org.emp.employee_id);
printf("Employee name : %s\n",
org.emp.name);
printf("Employee Salary : %d\n",
org.emp.salary);
} C
// C program to implement
// the above approach
#include
// Declaration of the inner
// structure
struct Employee
{
int employee_id;
char name[20];
int salary;
};
// Declaration of the Outer
// structure
struct Organisation
{
char organisation_name[20];
char org_number[20];
// Nested structure
struct Employee emp;
};
// Function show is expecting
// members of both structures
void show(char organisation_name[],
char org_number[],
int employee_id,
char name[], int salary);
// Driver code
int main()
{
struct Organisation org = {"GeeksforGeeks", "GFG111",
{278, "Paul",5000}};
// Data members of both the structures
// are passed to the function show
show(org.organisation_name, org.org_number,
org.emp.employee_id, org.emp.name,
org.emp.salary);
}
// Function show definition
void show(char organisation_name[],
char org_number[],
int employee_id,
char name[], int salary)
{
// Printing the details
printf("Printing the Details :\n");
printf("Organisation Name : %s\n",
organisation_name);
printf("Organisation Number : %s\n",
org_number);
printf("Employee id : %d\n",
employee_id);
printf("Employee name : %s\n",
name);
printf("Employee Salary : %d\n",
salary);
} C
// C program to implement
// the above approach
#include
#include
// Declaration of inner structure
struct college_details
{
int college_id;
char college_name[50];
};
// Declaration of Outer structure
struct student_detail
{
int student_id;
char student_name[20];
float cgpa;
// Inner structure variable
struct college_details clg;
} stu;
// Driver code
int main()
{
struct student_detail stu = {12, "Kathy", 7.8,
{14567, "GeeksforGeeks"}};
// Printing the details
printf("College ID : %d \n", stu.clg.college_id);
printf("College Name : %s \n", stu.clg.college_name);
printf("Student ID : %d \n", stu.student_id);
printf("Student Name : %s \n", stu.student_name);
printf("Student CGPA : %f \n", stu.cgpa);
return 0;
} C
// C program to implement
// the above approach
#include
#include
// Declaration of inner structure
struct college_details
{
int college_id;
char college_name[50];
};
// Declaration of Outer structure
struct student_detail
{
int student_id;
char student_name[20];
float cgpa;
// Inner structure variable
struct college_details clg;
} stu, *stu_ptr;
// Driver code
int main()
{
struct student_detail stu = {12, "Kathy", 7.8,
{14567, "GeeksforGeeks"}};
stu_ptr = &stu;
// Printing the details
printf("College ID : %d \n", stu_ptr->clg.college_id);
printf("College Name : %s \n", stu_ptr->clg.college_name);
printf("Student ID : %d \n", stu_ptr->student_id);
printf("Student Name : %s \n", stu_ptr->student_name);
printf("Student CGPA : %f \n", stu_ptr->cgpa);
return 0;
} 输出:
The size of structure organisation : 68
Organisation Name : GeeksforGeeks
Organisation Number : GFG123768
Employee id : 101
Employee name : Robert
Employee Salary : 400000
2.通过嵌入式嵌套结构:使用这种方法,允许在结构中声明结构,并且需要更少的代码行。
情况 1:如果结构存在但结构变量丢失,则会发生错误。
C
// C program to implement
// the above approach
#include
// Declaration of the outer
// structure
struct Organisation
{
char organisation_name[20];
char org_number[20];
// Declaration of the employee
// structure
struct Employee
{
int employee_id;
char name[20];
int salary;
// This line will cause error because
// datatype struct Employee is present ,
// but Structure variable is missing.
};
};
// Driver code
int main()
{
// Structure variable of organisation
struct Organisation org;
printf("%ld", sizeof(org));
}
输出:
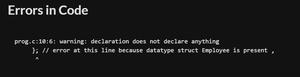
笔记:
每当创建嵌入式嵌套结构时,必须在内部结构的末尾声明变量,该内部结构充当外部结构的成员。结构变量必须在内部结构的末尾创建。
情况2:当内部结构的结构变量在内部结构的末尾声明时。下面是实现这种方法的 C 程序:
C
// C program to implement
// the above approach
#include
#include
// Declaration of the main
// structure
struct Organisation
{
char organisation_name[20];
char org_number[20];
// Declaration of the dependent
// structure
struct Employee
{
int employee_id;
char name[20];
int salary;
// variable is created which acts
// as member to Organisation structure.
} emp;
};
// Driver code
int main()
{
struct Organisation org;
// Print the size of organisation
// structure
printf("The size of structure organisation : %ld\n",
sizeof(org));
org.emp.employee_id = 101;
strcpy(org.emp.name, "Robert");
org.emp.salary = 400000;
strcpy(org.organisation_name,
"GeeksforGeeks");
strcpy(org.org_number, "GFG123768");
// Printing the details
printf("Organisation Name : %s\n",
org.organisation_name);
printf("Organisation Number : %s\n",
org.org_number);
printf("Employee id : %d\n",
org.emp.employee_id);
printf("Employee name : %s\n",
org.emp.name);
printf("Employee Salary : %d\n",
org.emp.salary);
}
输出:
The size of structure organisation : 68
Organisation Name : GeeksforGeeks
Organisation Number : GFG123768
Employee id : 101
Employee name : Robert
Employee Salary : 400000
嵌套结构的缺点
嵌套结构的缺点是:
- 不可能独立存在:重要的是要注意结构 Employee 本身并不存在。不能在程序的其他任何地方声明 struct Employee 类型的结构变量。
- 不能在多个数据结构中使用:由于在主结构中声明结构变量的限制,嵌套结构不能在多个结构中使用。所以,最推荐的方式是使用单独的结构,它可以在多个数据结构中使用
C 嵌套结构示例
下面是 C 嵌套结构的另一个示例。
C
// C program to implement
// the nested structure
#include
#include
// Declaration of Outer structure
struct College
{
char college_name[20];
int ranking;
// Declaration of Inner structure
struct Student
{
int student_id;
char name[20];
int roll_no;
// Inner structure variable
} student1;
};
// Driver code
int main()
{
struct College c1 = {"GeeksforGeeks", 7,
{111, "Paul", 278}};
printf("College name : %s\n",
c1.college_name);
printf("Ranking : %d\n",
c1.ranking);
printf("Student id : %d\n",
c1.student1.student_id);
printf("Student name : %s\n",
c1.student1.name);
printf("Roll no : %d\n",
c1.student1.roll_no);
return 0;
}
输出:
College name : GeeksforGeeks
Ranking : 7
Student id : 111
Student name : Paul
Roll no : 278
笔记:
不允许在其内部嵌套结构。
例子:
struct student
{
char name[50];
char address[100];
int roll_no;
struct student geek; // Invalid
}
将嵌套结构传递给函数
嵌套结构可以通过两种方式传递给函数:
- 一次传递嵌套结构变量。
- 将嵌套结构成员作为参数传递给函数。
让我们详细讨论这些方式。
1.一次传递嵌套结构变量:就像其他变量一样,嵌套结构变量也可以传递给函数。下面是实现这个概念的 C 程序:
C
// C program to implement
// the above approach
#include
// Declaration of the inner
// structure
struct Employee
{
int employee_id;
char name[20];
int salary;
};
// Declaration of the Outer
// structure
struct Organisation
{
char organisation_name[20];
char org_number[20];
// Nested structure
struct Employee emp;
};
// Function show is expecting
// variable of outer structure
void show(struct Organisation);
// Driver code
int main()
{
struct Organisation org = {"GeeksforGeeks", "GFG111",
{278, "Paul",5000}};
// Organisation structure variable
// is passed to function show
show(org);
}
// Function shoe definition
void show(struct Organisation org )
{
// Printing the details
printf("Printing the Details :\n");
printf("Organisation Name : %s\n",
org.organisation_name);
printf("Organisation Number : %s\n",
org.org_number);
printf("Employee id : %d\n",
org.emp.employee_id);
printf("Employee name : %s\n",
org.emp.name);
printf("Employee Salary : %d\n",
org.emp.salary);
}
输出:
Printing the Details :
Organisation Name : GeeksforGeeks
Organisation Number : GFG111
Employee id : 278
Employee name : Paul
Employee Salary : 5000
2. 将嵌套结构成员作为参数传递给函数:考虑以下示例,将员工的结构成员传递给用于显示员工详细信息的函数display()。
C
// C program to implement
// the above approach
#include
// Declaration of the inner
// structure
struct Employee
{
int employee_id;
char name[20];
int salary;
};
// Declaration of the Outer
// structure
struct Organisation
{
char organisation_name[20];
char org_number[20];
// Nested structure
struct Employee emp;
};
// Function show is expecting
// members of both structures
void show(char organisation_name[],
char org_number[],
int employee_id,
char name[], int salary);
// Driver code
int main()
{
struct Organisation org = {"GeeksforGeeks", "GFG111",
{278, "Paul",5000}};
// Data members of both the structures
// are passed to the function show
show(org.organisation_name, org.org_number,
org.emp.employee_id, org.emp.name,
org.emp.salary);
}
// Function show definition
void show(char organisation_name[],
char org_number[],
int employee_id,
char name[], int salary)
{
// Printing the details
printf("Printing the Details :\n");
printf("Organisation Name : %s\n",
organisation_name);
printf("Organisation Number : %s\n",
org_number);
printf("Employee id : %d\n",
employee_id);
printf("Employee name : %s\n",
name);
printf("Employee Salary : %d\n",
salary);
}
输出:
Printing the Details :
Organisation Name : GeeksforGeeks
Organisation Number : GFG111
Employee id : 278
Employee name : Paul
Employee Salary : 5000
访问嵌套结构
可以通过两种方式访问嵌套结构:
- 使用普通变量。
- 使用指针变量。
让我们详细讨论这些方法。
1. 使用普通变量:外部和内部结构变量声明为普通变量,外部结构的数据成员使用单个点(.)访问,内部结构的数据成员使用两个点访问。下面是实现这个概念的 C 程序:
C
// C program to implement
// the above approach
#include
#include
// Declaration of inner structure
struct college_details
{
int college_id;
char college_name[50];
};
// Declaration of Outer structure
struct student_detail
{
int student_id;
char student_name[20];
float cgpa;
// Inner structure variable
struct college_details clg;
} stu;
// Driver code
int main()
{
struct student_detail stu = {12, "Kathy", 7.8,
{14567, "GeeksforGeeks"}};
// Printing the details
printf("College ID : %d \n", stu.clg.college_id);
printf("College Name : %s \n", stu.clg.college_name);
printf("Student ID : %d \n", stu.student_id);
printf("Student Name : %s \n", stu.student_name);
printf("Student CGPA : %f \n", stu.cgpa);
return 0;
}
输出:
College ID : 14567
College Name : GeeksforGeeks
Student ID : 12
Student Name : Kathy
Student CGPA : 7.800000
2、使用指针变量:声明结构体的1个普通变量和1个指针变量,说明两者的区别。在指针变量的情况下,点(.)和箭头(->)的组合将用于访问数据成员。下面是实现上述方法的 C 程序:
C
// C program to implement
// the above approach
#include
#include
// Declaration of inner structure
struct college_details
{
int college_id;
char college_name[50];
};
// Declaration of Outer structure
struct student_detail
{
int student_id;
char student_name[20];
float cgpa;
// Inner structure variable
struct college_details clg;
} stu, *stu_ptr;
// Driver code
int main()
{
struct student_detail stu = {12, "Kathy", 7.8,
{14567, "GeeksforGeeks"}};
stu_ptr = &stu;
// Printing the details
printf("College ID : %d \n", stu_ptr->clg.college_id);
printf("College Name : %s \n", stu_ptr->clg.college_name);
printf("Student ID : %d \n", stu_ptr->student_id);
printf("Student Name : %s \n", stu_ptr->student_name);
printf("Student CGPA : %f \n", stu_ptr->cgpa);
return 0;
}
输出:
College ID : 14567
College Name : GeeksforGeeks
Student ID : 12
Student Name : Kathy
Student CGPA : 7.800000
嵌套结构将允许根据程序的要求创建复杂的数据类型。