两个排序的双向循环链表的排序合并
给定两个排序的双向循环链表,分别包含n1和n2 个节点。问题是合并两个列表,使结果列表也按排序顺序。
例子:
清单 1:
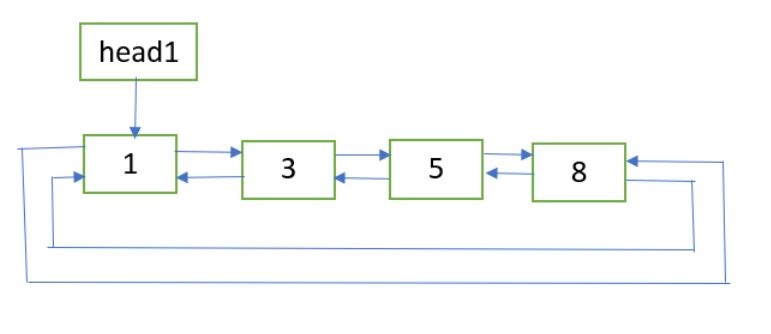
清单 2:
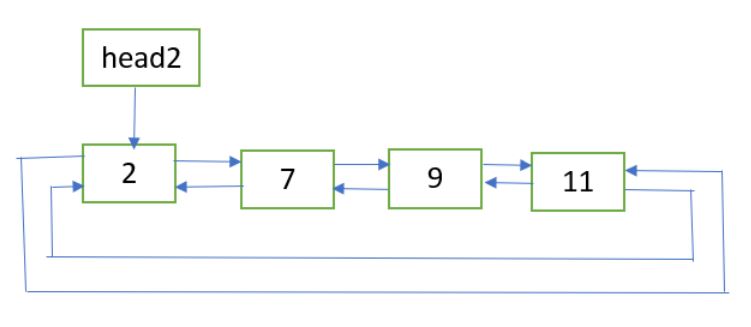
最终名单:

方法:以下是步骤:
- 如果 head1 == NULL,则返回 head2。
- 如果 head2 == NULL,则返回 head1。
- 让last1和last2分别是两个列表的最后一个节点。它们可以在第一个节点的先前链接的帮助下获得。
- 获取指向将成为最终列表的最后一个节点的节点的指针。如果last1.data < last2.data,则last_node = last2,否则last_node = last1。
- 更新 last1.next = last2.next = NULL。
- 现在合并两个列表,因为两个排序的双向链表正在合并。参考这篇文章的合并程序。让最终列表的第一个节点为finalHead 。
- 更新 finalHead.prev = last_node 和 last_node.next = finalHead。
- 返回finalHead 。
C++
// C++ implementation for Sorted merge of two
// sorted doubly circular linked list
#include
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int data;
Node *next, *prev;
};
// A utility function to insert a new node at the
// beginning of doubly circular linked list
void insert(Node** head_ref, int data)
{
// allocate space
Node* new_node = new Node;
// put in the data
new_node->data = data;
// if list is empty
if (*head_ref == NULL) {
new_node->next = new_node;
new_node->prev = new_node;
}
else {
// pointer points to last Node
Node* last = (*head_ref)->prev;
// setting up previous and next of new node
new_node->next = *head_ref;
new_node->prev = last;
// update next and previous pointers of head_ref
// and last.
last->next = (*head_ref)->prev = new_node;
}
// update head_ref pointer
*head_ref = new_node;
}
// function for Sorted merge of two
// sorted doubly linked list
Node* merge(Node* first, Node* second)
{
// If first list is empty
if (!first)
return second;
// If second list is empty
if (!second)
return first;
// Pick the smaller value and adjust
// the links
if (first->data < second->data) {
first->next = merge(first->next, second);
first->next->prev = first;
first->prev = NULL;
return first;
}
else {
second->next = merge(first, second->next);
second->next->prev = second;
second->prev = NULL;
return second;
}
}
// function for Sorted merge of two sorted
// doubly circular linked list
Node* mergeUtil(Node* head1, Node* head2)
{
// if 1st list is empty
if (!head1)
return head2;
// if 2nd list is empty
if (!head2)
return head1;
// get pointer to the node which will be the
// last node of the final list
Node* last_node;
if (head1->prev->data < head2->prev->data)
last_node = head2->prev;
else
last_node = head1->prev;
// store NULL to the 'next' link of the last nodes
// of the two lists
head1->prev->next = head2->prev->next = NULL;
// sorted merge of head1 and head2
Node* finalHead = merge(head1, head2);
// 'prev' of 1st node pointing the last node
// 'next' of last node pointing to 1st node
finalHead->prev = last_node;
last_node->next = finalHead;
return finalHead;
}
// function to print the list
void printList(Node* head)
{
Node* temp = head;
while (temp->next != head) {
cout << temp->data << " ";
temp = temp->next;
}
cout << temp->data << " ";
}
// Driver program to test above
int main()
{
Node *head1 = NULL, *head2 = NULL;
// list 1:
insert(&head1, 8);
insert(&head1, 5);
insert(&head1, 3);
insert(&head1, 1);
// list 2:
insert(&head2, 11);
insert(&head2, 9);
insert(&head2, 7);
insert(&head2, 2);
Node* newHead = mergeUtil(head1, head2);
cout << "Final Sorted List: ";
printList(newHead);
return 0;
} Java
// Java implementation for Sorted merge of two
// sorted doubly circular linked list
class GFG
{
static class Node
{
int data;
Node next, prev;
};
// A utility function to insert a new node at the
// beginning of doubly circular linked list
static Node insert(Node head_ref, int data)
{
// allocate space
Node new_node = new Node();
// put in the data
new_node.data = data;
// if list is empty
if (head_ref == null)
{
new_node.next = new_node;
new_node.prev = new_node;
}
else
{
// pointer points to last Node
Node last = (head_ref).prev;
// setting up previous and next of new node
new_node.next = head_ref;
new_node.prev = last;
// update next and previous pointers of head_ref
// and last.
last.next = (head_ref).prev = new_node;
}
// update head_ref pointer
head_ref = new_node;
return head_ref;
}
// function for Sorted merge of two
// sorted doubly linked list
static Node merge(Node first, Node second)
{
// If first list is empty
if (first == null)
return second;
// If second list is empty
if (second == null)
return first;
// Pick the smaller value and adjust
// the links
if (first.data < second.data)
{
first.next = merge(first.next, second);
first.next.prev = first;
first.prev = null;
return first;
}
else
{
second.next = merge(first, second.next);
second.next.prev = second;
second.prev = null;
return second;
}
}
// function for Sorted merge of two sorted
// doubly circular linked list
static Node mergeUtil(Node head1, Node head2)
{
// if 1st list is empty
if (head1 == null)
return head2;
// if 2nd list is empty
if (head2 == null)
return head1;
// get pointer to the node which will be the
// last node of the final list
Node last_node;
if (head1.prev.data < head2.prev.data)
last_node = head2.prev;
else
last_node = head1.prev;
// store null to the 'next' link of the last nodes
// of the two lists
head1.prev.next = head2.prev.next = null;
// sorted merge of head1 and head2
Node finalHead = merge(head1, head2);
// 'prev' of 1st node pointing the last node
// 'next' of last node pointing to 1st node
finalHead.prev = last_node;
last_node.next = finalHead;
return finalHead;
}
// function to print the list
static void printList(Node head)
{
Node temp = head;
while (temp.next != head)
{
System.out.print ( temp.data+ " ");
temp = temp.next;
}
System.out.print ( temp.data + " ");
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
Node head1 = null, head2 = null;
// list 1:
head1 = insert(head1, 8);
head1 = insert(head1, 5);
head1 = insert(head1, 3);
head1 = insert(head1, 1);
// list 2:
head2 = insert(head2, 11);
head2 = insert(head2, 9);
head2 = insert(head2, 7);
head2 = insert(head2, 2);
Node newHead = mergeUtil(head1, head2);
System.out.print( "Final Sorted List: ");
printList(newHead);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Arnab KunduPython3
# Python3 implementation for Sorted merge
# of two sorted doubly circular linked list
import math
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
self.prev = None
# A utility function to insert
# a new node at the beginning
# of doubly circular linked list
def insert(head_ref, data):
# allocate space
new_node = Node(data)
# put in the data
new_node.data = data
# if list is empty
if (head_ref == None):
new_node.next = new_node
new_node.prev = new_node
else :
# pointer points to last Node
last = head_ref.prev
# setting up previous and
# next of new node
new_node.next = head_ref
new_node.prev = last
# update next and previous pointers
# of head_ref and last.
last.next = new_node
head_ref.prev = new_node
# update head_ref pointer
head_ref = new_node
return head_ref
# function for Sorted merge of two
# sorted doubly linked list
def merge(first, second):
# If first list is empty
if (first == None):
return second
# If second list is empty
if (second == None):
return first
# Pick the smaller value and
# adjust the links
if (first.data < second.data) :
first.next = merge(first.next,
second)
first.next.prev = first
first.prev = None
return first
else :
second.next = merge(first,
second.next)
second.next.prev = second
second.prev = None
return second
# function for Sorted merge of two sorted
# doubly circular linked list
def mergeUtil(head1, head2):
# if 1st list is empty
if (head1 == None):
return head2
# if 2nd list is empty
if (head2 == None):
return head1
# get pointer to the node
# which will be the last node
# of the final list last_node
if (head1.prev.data < head2.prev.data):
last_node = head2.prev
else:
last_node = head1.prev
# store None to the 'next' link of
# the last nodes of the two lists
head1.prev.next = None
head2.prev.next = None
# sorted merge of head1 and head2
finalHead = merge(head1, head2)
# 'prev' of 1st node pointing the last node
# 'next' of last node pointing to 1st node
finalHead.prev = last_node
last_node.next = finalHead
return finalHead
# function to print the list
def printList(head):
temp = head
while (temp.next != head):
print(temp.data, end = " ")
temp = temp.next
print(temp.data, end = " ")
# Driver Code
if __name__=='__main__':
head1 = None
head2 = None
# list 1:
head1 = insert(head1, 8)
head1 = insert(head1, 5)
head1 = insert(head1, 3)
head1 = insert(head1, 1)
# list 2:
head2 = insert(head2, 11)
head2 = insert(head2, 9)
head2 = insert(head2, 7)
head2 = insert(head2, 2)
newHead = mergeUtil(head1, head2)
print("Final Sorted List: ", end = "")
printList(newHead)
# This code is contributed by SrathoreC#
// C# implementation for Sorted merge of two
// sorted doubly circular linked list
using System;
class GFG
{
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node next, prev;
};
// A utility function to insert a new node at the
// beginning of doubly circular linked list
static Node insert(Node head_ref, int data)
{
// allocate space
Node new_node = new Node();
// put in the data
new_node.data = data;
// if list is empty
if (head_ref == null)
{
new_node.next = new_node;
new_node.prev = new_node;
}
else
{
// pointer points to last Node
Node last = (head_ref).prev;
// setting up previous and next of new node
new_node.next = head_ref;
new_node.prev = last;
// update next and previous pointers of head_ref
// and last.
last.next = (head_ref).prev = new_node;
}
// update head_ref pointer
head_ref = new_node;
return head_ref;
}
// function for Sorted merge of two
// sorted doubly linked list
static Node merge(Node first, Node second)
{
// If first list is empty
if (first == null)
return second;
// If second list is empty
if (second == null)
return first;
// Pick the smaller value and adjust
// the links
if (first.data < second.data)
{
first.next = merge(first.next, second);
first.next.prev = first;
first.prev = null;
return first;
}
else
{
second.next = merge(first, second.next);
second.next.prev = second;
second.prev = null;
return second;
}
}
// function for Sorted merge of two sorted
// doubly circular linked list
static Node mergeUtil(Node head1, Node head2)
{
// if 1st list is empty
if (head1 == null)
return head2;
// if 2nd list is empty
if (head2 == null)
return head1;
// get pointer to the node which will be the
// last node of the final list
Node last_node;
if (head1.prev.data < head2.prev.data)
last_node = head2.prev;
else
last_node = head1.prev;
// store null to the 'next' link of the last nodes
// of the two lists
head1.prev.next = head2.prev.next = null;
// sorted merge of head1 and head2
Node finalHead = merge(head1, head2);
// 'prev' of 1st node pointing the last node
// 'next' of last node pointing to 1st node
finalHead.prev = last_node;
last_node.next = finalHead;
return finalHead;
}
// function to print the list
static void printList(Node head)
{
Node temp = head;
while (temp.next != head)
{
Console.Write(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
}
Console.Write(temp.data + " ");
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
Node head1 = null, head2 = null;
// list 1:
head1 = insert(head1, 8);
head1 = insert(head1, 5);
head1 = insert(head1, 3);
head1 = insert(head1, 1);
// list 2:
head2 = insert(head2, 11);
head2 = insert(head2, 9);
head2 = insert(head2, 7);
head2 = insert(head2, 2);
Node newHead = mergeUtil(head1, head2);
Console.Write( "Final Sorted List: ");
printList(newHead);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Princi SinghJavascript
输出:
Final Sorted List: 1 2 3 5 7 8 9 11时间复杂度: O(n1 + n2)。
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。