最终 vs 静态 vs 抽象非访问修饰符
修饰符是Java中存在的特定关键字,我们可以使用它来更改变量、方法或类的特征并限制其范围。 Java编程语言有一组丰富的修饰符。 Java中的修饰符分为两种
- 访问修饰符
- 非访问修饰符
非访问修饰符向 JVM 提供有关类、方法或变量的特征的信息。 Java中有七种类型的非访问修饰符。他们是
- 静止的
- 最终的
- 抽象的
- 同步的
- 易挥发的
- 短暂的
- 本国的
阅读有关Java中的非访问修饰符的更多信息。在本文中,我们将讨论 Final、Static 和 Abstract Non-Access Modifiers 之间的区别。
最终非访问修饰符
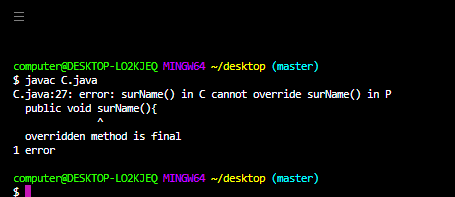
final 非访问修饰符适用于类、方法和变量。如果我们将父类方法声明为final,那么我们不能在子类中覆盖该方法,因为它的实现是final,如果一个类被声明为final,我们就不能扩展该类的功能,即我们不能创建该类的子类,即最终类不能继承。 final 类中存在的每个方法始终是 final y 默认值,但 final 类中存在的每个变量都不必是 final。 final 关键字的主要优点是我们可以实现安全性,并且可以提供独特的实现。但是 final 关键字的主要缺点是我们缺少 OOP 的关键好处,例如继承(因为 final 类)、多态性(因为 final 方法),因此如果没有特定要求,则不建议使用 final关键词。
示例 1:
Java
// Java Program to illustrate Final keyword
// Where No final keyword Is Used
// Importing required classes
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// Class 1
// Super-class
class P {
// Method 1
// To declare first name
public void firstName()
{
// Passing name and print it
System.out.println("Mayank");
}
// Method 2
// To declare last name
public void surName()
{
// Passing name and print it
System.out.println("Trivedi");
}
}
// Class 2
// Sub-class
// Extending above class
class C extends P {
// Method 1
// Trying to override the last name
public void surName()
{
// Display surname
System.out.println("Sharma");
}
// Method 2
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Display message
System.out.println("GFG");
}
}Java
// Java Program to illustrate Final keyword
// When final keyword Is Used
// Importing required classes
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// Class 1
// Super-class
class P {
// Method 1
// To declare first name
public void firstName()
{
// Passing name and print it
System.out.println("Mayank");
}
// Method 2
// To declare last name
public final void surName()
{
// Passing name and print it
System.out.println("Trivedi");
}
}
// Class 2
// Sub-class
// Extending above class
class C extends P {
// Method 1
// Trying to override the last name
public void surName()
{
// Display surname
System.out.println("Sharma");
}
// Method 2
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Display message
System.out.println("GFG");
}
}Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Static Access Modifier
// Importing required classes
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// Main class
class GFG {
// Creating a static variable and
// initializing a custom value
static int x = 10;
// Creating a instance variable and
// initializing a custom value
int y = 20;
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an object of class inside main() method
GFG t1 = new GFG();
// Accessing and re-initializing the
// static and instance variable
// using t1 reference
t1.x = 888;
t1.y = 99;
// Creating an object of class inside main() method
// again
GFG t2 = new GFG();
// Accessing the static and instance variable using
// t2 reference as we know that for each object
// there is separate copy of instance variable
// created. While same copy of static variable will
// be shared between the objects
// Displaying the value of static and instance
// variable using t2 object reference
System.out.println(
"Value of Static variable x = " + t2.x + "\n"
+ "Value of Instance variable y = " + t2.y);
}
}Java
// Java program to illustrate Abstract Access Modifier
// Importing the required packages
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// Class 1
// Helper abstract class
abstract class Vehicle {
// Declaring an abstract method getNumberOfWheel
abstract public int getNumberOfWheel();
}
// Class 2
// Helper class extending above abstract class
class Bus extends Vehicle {
// Giving the implementation
// to the parent abstract method
public int getNumberOfWheel() { return 7; }
}
// Class 3
// Helper class extending above abstract class
class Auto extends Vehicle {
// Giving the implementation
// to the parent abstract method
public int getNumberOfWheel() { return 3; }
}
// Class 4
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating Bus object
Bus b = new Bus();
// Creating Auto object
Auto a = new Auto();
// Now getting and displaying
// the number of wheels
// for Bus by calling the
// getNumberOfWheel method
System.out.println("Number of wheels in bus is"
+ " " + b.getNumberOfWheel());
// Now getting and displaying
// the number of wheels
// for Auto by calling the
// getNumberOfWheel method
System.out.println("Number of wheels in Auto is"
+ " " + a.getNumberOfWheel());
}
}输出:
GFG
示例 2:
Java
// Java Program to illustrate Final keyword
// When final keyword Is Used
// Importing required classes
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// Class 1
// Super-class
class P {
// Method 1
// To declare first name
public void firstName()
{
// Passing name and print it
System.out.println("Mayank");
}
// Method 2
// To declare last name
public final void surName()
{
// Passing name and print it
System.out.println("Trivedi");
}
}
// Class 2
// Sub-class
// Extending above class
class C extends P {
// Method 1
// Trying to override the last name
public void surName()
{
// Display surname
System.out.println("Sharma");
}
// Method 2
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Display message
System.out.println("GFG");
}
}
输出:
静态非访问修饰符
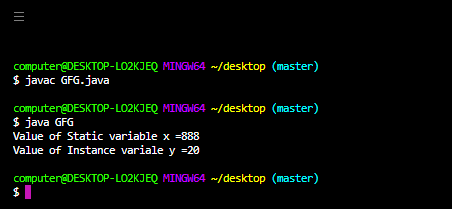
static 非访问修饰符适用于方法和变量,但不适用于类。我们可以使用 static 修饰符声明顶级类,但我们可以将内部类声明为静态(这种类型的内部类称为静态嵌套类)。在每个对象的实例变量的情况下,将创建一个单独的副本,但在静态变量的情况下,将在类级别创建一个副本并由该类的每个对象共享。
例子:
Java
// Java Program to Illustrate Static Access Modifier
// Importing required classes
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// Main class
class GFG {
// Creating a static variable and
// initializing a custom value
static int x = 10;
// Creating a instance variable and
// initializing a custom value
int y = 20;
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an object of class inside main() method
GFG t1 = new GFG();
// Accessing and re-initializing the
// static and instance variable
// using t1 reference
t1.x = 888;
t1.y = 99;
// Creating an object of class inside main() method
// again
GFG t2 = new GFG();
// Accessing the static and instance variable using
// t2 reference as we know that for each object
// there is separate copy of instance variable
// created. While same copy of static variable will
// be shared between the objects
// Displaying the value of static and instance
// variable using t2 object reference
System.out.println(
"Value of Static variable x = " + t2.x + "\n"
+ "Value of Instance variable y = " + t2.y);
}
}
输出:
抽象非访问修饰符
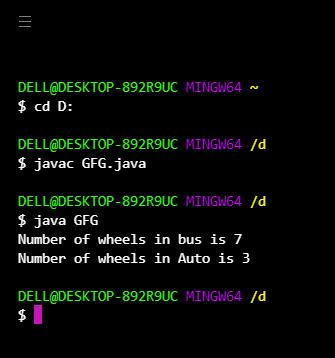
abstract 非访问修饰符仅适用于类和方法,但不适用于变量。如果我们将任何方法声明为抽象,那么该方法必须在相应类的子类中实现,因为抽象方法从不谈论实现。如果任何修饰符谈论实现,那么它与抽象修饰符形成非法组合。以类似的方式,如果对于任何Java类,如果我们不允许创建对象(因为部分实现),那么我们必须使用抽象修饰符声明这种类型的类。
例子:
Java
// Java program to illustrate Abstract Access Modifier
// Importing the required packages
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// Class 1
// Helper abstract class
abstract class Vehicle {
// Declaring an abstract method getNumberOfWheel
abstract public int getNumberOfWheel();
}
// Class 2
// Helper class extending above abstract class
class Bus extends Vehicle {
// Giving the implementation
// to the parent abstract method
public int getNumberOfWheel() { return 7; }
}
// Class 3
// Helper class extending above abstract class
class Auto extends Vehicle {
// Giving the implementation
// to the parent abstract method
public int getNumberOfWheel() { return 3; }
}
// Class 4
// Main class
public class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating Bus object
Bus b = new Bus();
// Creating Auto object
Auto a = new Auto();
// Now getting and displaying
// the number of wheels
// for Bus by calling the
// getNumberOfWheel method
System.out.println("Number of wheels in bus is"
+ " " + b.getNumberOfWheel());
// Now getting and displaying
// the number of wheels
// for Auto by calling the
// getNumberOfWheel method
System.out.println("Number of wheels in Auto is"
+ " " + a.getNumberOfWheel());
}
}
输出:
差异表
| Final Non-Access Modifier | Static Non-Access Modifier | Abstract Non-Access Modifier |
|---|---|---|
| This modifier is applicable to both outer and inner classes. | This modifier is not applicable to outer classes. | This modifier is applicable to both outer and inner classes. |
| This modifier is not applicable to interfaces | This modifier is not applicable to interfaces. | This modifier is applicable to interfaces. |
| This modifier is the only modifier that is applicable for local variables. | This modifier is not applicable for local variables. | This modifier is not applicable for local variables. |
| Final method can’t be inherited. | Static methods can only access the static members of the class and can only be called by other static methods. | Abstract method can be inherited. |