给定一个数组,打印数组中总和为 0 的所有子数组。
例子:
Input: arr = [6, 3, -1, -3, 4, -2, 2,
4, 6, -12, -7]
Output:
Subarray found from Index 2 to 4
Subarray found from Index 2 to 6
Subarray found from Index 5 to 6
Subarray found from Index 6 to 9
Subarray found from Index 0 to 10相关文章: 查找是否存在总和为 0 的子数组
一个简单的解决方案是一个一个地考虑所有子数组,并检查每个子数组的总和是否等于 0。该解决方案的复杂度为 O(n^2)。
更好的方法是使用哈希。
对数组中的每个元素执行以下操作
- 维护到目前为止在变量中遇到的元素的总和(比如总和)。
- 如果当前和为 0,我们找到了一个从索引 0 开始到索引当前索引结束的子数组
- 检查当前和是否存在于哈希表中。
- 如果当前总和已经存在于哈希表中,则表明该总和是一些子数组元素 arr[0]…arr[i] 的总和,现在为当前子数组 arr[0] 获得了相同的总和…arr[j] 这意味着子数组 arr[i+1]…arr[j] 的和必须为 0。
- 将当前和插入哈希表
以下是上述方法的试运行:
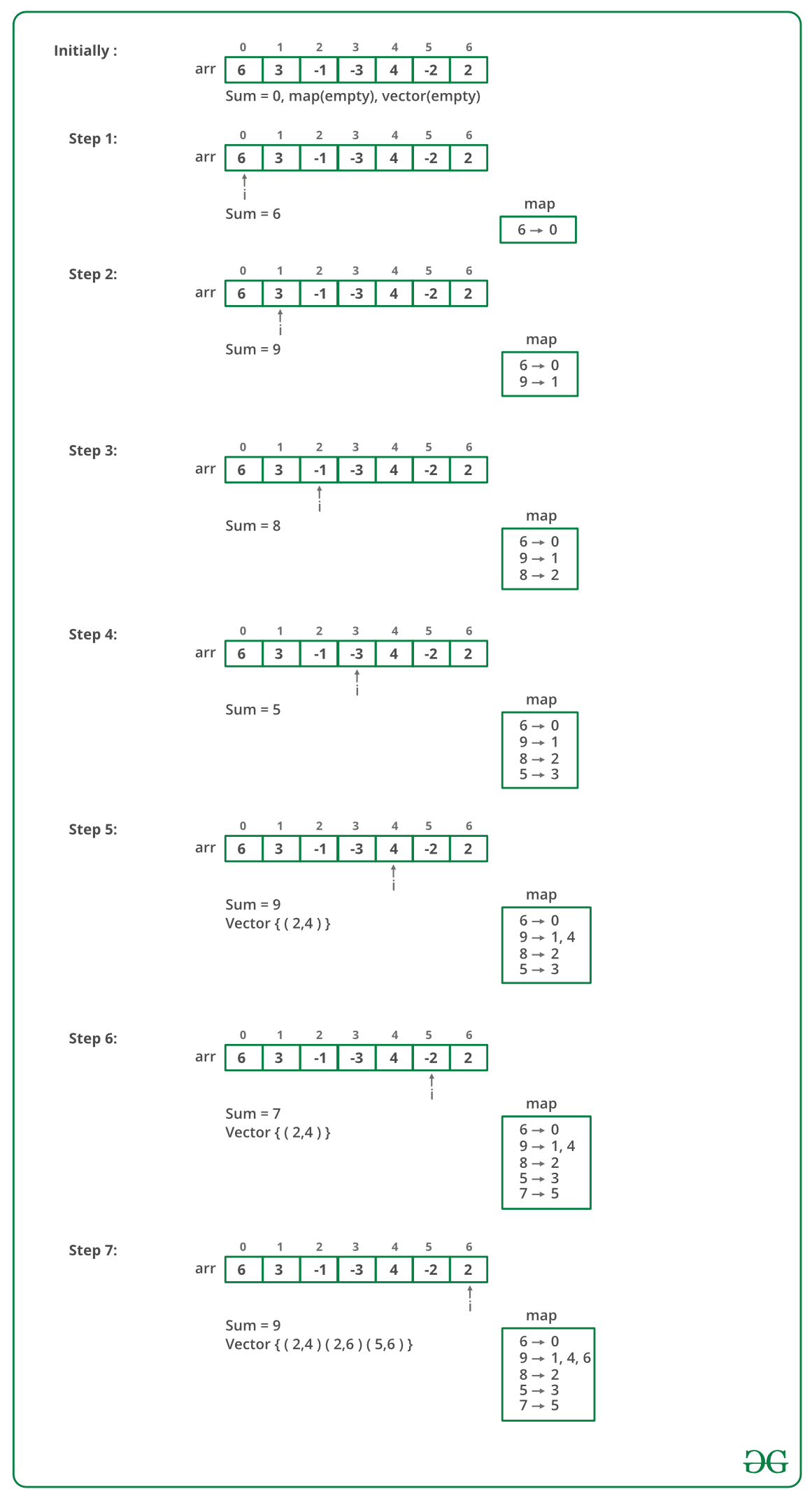
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program to print all subarrays
// in the array which has sum 0
#include
using namespace std;
// Function to print all subarrays in the array which
// has sum 0
vector< pair > findSubArrays(int arr[], int n)
{
// create an empty map
unordered_map > map;
// create an empty vector of pairs to store
// subarray starting and ending index
vector > out;
// Maintains sum of elements so far
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// add current element to sum
sum += arr[i];
// if sum is 0, we found a subarray starting
// from index 0 and ending at index i
if (sum == 0)
out.push_back(make_pair(0, i));
// If sum already exists in the map there exists
// at-least one subarray ending at index i with
// 0 sum
if (map.find(sum) != map.end())
{
// map[sum] stores starting index of all subarrays
vector vc = map[sum];
for (auto it = vc.begin(); it != vc.end(); it++)
out.push_back(make_pair(*it + 1, i));
}
// Important - no else
map[sum].push_back(i);
}
// return output vector
return out;
}
// Utility function to print all subarrays with sum 0
void print(vector> out)
{
for (auto it = out.begin(); it != out.end(); it++)
cout << "Subarray found from Index " <<
it->first << " to " << it->second << endl;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int arr[] = {6, 3, -1, -3, 4, -2, 2, 4, 6, -12, -7};
int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
vector > out = findSubArrays(arr, n);
// if we didn’t find any subarray with 0 sum,
// then subarray doesn’t exists
if (out.size() == 0)
cout << "No subarray exists";
else
print(out);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to print all subarrays
// in the array which has sum 0
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// User defined pair class
class Pair
{
int first, second;
Pair(int a, int b)
{
first = a;
second = b;
}
}
public class GFG
{
// Function to print all subarrays in the array which
// has sum 0
static ArrayList findSubArrays(int[] arr, int n)
{
// create an empty map
HashMap> map = new HashMap<>();
// create an empty vector of pairs to store
// subarray starting and ending index
ArrayList out = new ArrayList<>();
// Maintains sum of elements so far
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// add current element to sum
sum += arr[i];
// if sum is 0, we found a subarray starting
// from index 0 and ending at index i
if (sum == 0)
out.add(new Pair(0, i));
ArrayList al = new ArrayList<>();
// If sum already exists in the map there exists
// at-least one subarray ending at index i with
// 0 sum
if (map.containsKey(sum))
{
// map[sum] stores starting index of all subarrays
al = map.get(sum);
for (int it = 0; it < al.size(); it++)
{
out.add(new Pair(al.get(it) + 1, i));
}
}
al.add(i);
map.put(sum, al);
}
return out;
}
// Utility function to print all subarrays with sum 0
static void print(ArrayList out)
{
for (int i = 0; i < out.size(); i++)
{
Pair p = out.get(i);
System.out.println("Subarray found from Index "
+ p.first + " to " + p.second);
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[])
{
int[] arr = {6, 3, -1, -3, 4, -2, 2, 4, 6, -12, -7};
int n = arr.length;
ArrayList out = findSubArrays(arr, n);
// if we did not find any subarray with 0 sum,
// then subarray does not exists
if (out.size() == 0)
System.out.println("No subarray exists");
else
print(out);
}
}
// This code is contributed by rachana soma Python3
# Python3 program to print all subarrays
# in the array which has sum 0
# Function to get all subarrays
# in the array which has sum 0
def findSubArrays(arr,n):
# create a python dict
hashMap = {}
# create a python list
# equivalent to ArrayList
out = []
# tracker for sum of elements
sum1 = 0
for i in range(n):
# increment sum by element of array
sum1 += arr[i]
# if sum is 0, we found a subarray starting
# from index 0 and ending at index i
if sum1 == 0:
out.append((0, i))
al = []
# If sum already exists in the map
# there exists at-least one subarray
# ending at index i with 0 sum
if sum1 in hashMap:
# map[sum] stores starting index
# of all subarrays
al = hashMap.get(sum1)
for it in range(len(al)):
out.append((al[it] + 1, i))
al.append(i)
hashMap[sum1] = al
return out
# Utility function to print
# all subarrays with sum 0
def printOutput(output):
for i in output:
print ("Subarray found from Index " +
str(i[0]) + " to " + str(i[1]))
# Driver Code
if __name__ == '__main__':
arr = [6, 3, -1, -3, 4, -2,
2, 4, 6, -12, -7]
n = len(arr)
out = findSubArrays(arr, n)
# if we did not find any subarray with 0 sum,
# then subarray does not exists
if (len(out) == 0):
print ("No subarray exists")
else:
printOutput (out)
# This code is contributed by Vikas ChitturiC#
// C# program to print all subarrays
// in the array which has sum 0
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
// User defined pair class
class Pair
{
public int first, second;
public Pair(int a, int b)
{
first = a;
second = b;
}
}
class GFG
{
// Function to print all subarrays
// in the array which has sum 0
static List findSubArrays(int[] arr, int n)
{
// create an empty map
Dictionary> map =
new Dictionary>();
// create an empty vector of pairs to store
// subarray starting and ending index
List outt = new List();
// Maintains sum of elements so far
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// add current element to sum
sum += arr[i];
// if sum is 0, we found a subarray starting
// from index 0 and ending at index i
if (sum == 0)
outt.Add(new Pair(0, i));
List al = new List();
// If sum already exists in the map there exists
// at-least one subarray ending at index i with
// 0 sum
if (map.ContainsKey(sum))
{
// map[sum] stores starting index
// of all subarrays
al = map[sum];
for (int it = 0; it < al.Count; it++)
{
outt.Add(new Pair(al[it] + 1, i));
}
}
al.Add(i);
if(map.ContainsKey(sum))
map[sum] = al;
else
map.Add(sum, al);
}
return outt;
}
// Utility function to print all subarrays with sum 0
static void print(List outt)
{
for (int i = 0; i < outt.Count; i++)
{
Pair p = outt[i];
Console.WriteLine("Subarray found from Index " +
p.first + " to " + p.second);
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String []args)
{
int[] arr = {6, 3, -1, -3, 4, -2,
2, 4, 6, -12, -7};
int n = arr.Length;
List outt = findSubArrays(arr, n);
// if we did not find any subarray with 0 sum,
// then subarray does not exists
if (outt.Count == 0)
Console.WriteLine("No subarray exists");
else
print(outt);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji 输出:
Subarray found from Index 2 to 4
Subarray found from Index 2 to 6
Subarray found from Index 5 to 6
Subarray found from Index 6 to 9
Subarray found from Index 0 to 10时间复杂度: O(N^2)
辅助空间: O(N)
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。