给定一个数组arr[]由N 个字符串组成,表示班级中学生的姓名,另一个数组P[][2]使得P[i][0]喜欢P[i][1] ,任务是找到要在课堂上分发的最少笔记数量,以便只有在学生直接或间接喜欢另一个学生时才能共享笔记。
例子:
Input: arr[] = {geeks, for, code, run, compile}, P[][] = {{geeks, for}, {for, code}, {code, run}, {run, compile}, {run, for}}
Output: 3
Explanation:
Below is the image to represent the relationship among the students:
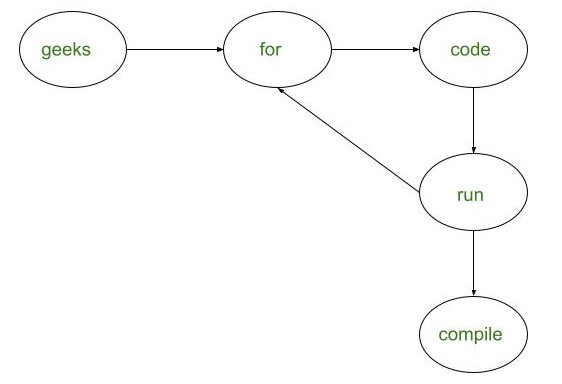
From the above image:
- Students named {“for”, “code”, “run”} require a single copy of notes, since there exists a mutual relationship between them.
- Student named {“geeks”} requires a single copy of notes.
- Student named {“compile”} also require a single copy of notes.
So, the minimum number of notes required is 3.
Input: arr[] = {geeks, for, all, run, debug, compile}, P[][] = {{geeks, for}, {for, all}, {all, geeks}, {for, run}, {run, compile}, {compile, debug}, {debug, run}}
Output: 2
方法:在给定条件下生成关系图后,可以通过在有向图中找到强连通分量的数量来解决给定问题。请按照以下步骤解决问题:
- 创建一个哈希图,比如M将学生的姓名映射到他们各自的索引值。
- 使用变量i遍历数组A并将映射M中的每个字符串A[i]映射到值i 。
- 迭代数组P中的所有对,并为每一对从 HashMap 中获取相应的值, M并在它们之间创建有向边。
- 在遍历所有对之后,形成具有N个顶点和M个边的有向图。
- 创建一个空栈S ,并执行图的 DFS 遍历:
- 创建一个递归函数,该函数采用节点的索引和访问过的数组。
- 将当前节点标记为已访问并遍历所有相邻和未标记的节点,并使用相邻节点的索引调用递归函数。
- 遍历当前节点的所有邻居后,将当前节点压入堆栈S 。
- 反转所有边的方向以获得构造图的转置。
- 迭代直到栈S不为空,执行以下步骤:
- 存储栈顶元素S 在变量V 中并将其从堆栈S 中弹出。
- 从节点V作为源执行 DFS 遍历。
- 更新连接组件的数量并将计数存储在变量 sat cnt 中。
- 完成以上步骤后,打印cnt的值作为结果。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
// Sturture of class Graph
class Graph {
// No. of vertices
int V;
// An array of adjacency lists
list* adj;
// Function that fills the stack
// with the vertices v
void fillOrder(int v, bool visited[],
stack& Stack);
// Recursive function to perform
// the DFS starting from v
void DFSUtil(int v, bool visited[]);
public:
Graph(int V);
void addEdge(int v, int w);
// Function to count the number of
// strongly connected components
void countSCCs();
// Function that returns reverse
// (or transpose) of the graph
Graph getTranspose();
};
// Constructor of the Graph
Graph::Graph(int V)
{
this->V = V;
adj = new list[V];
}
// Recursive function to perform the
// DFS starting from v
void Graph::DFSUtil(int v, bool visited[])
{
// Mark the current node as visited
visited[v] = true;
// Recurr for all the vertices
// adjacent to this vertex
list::iterator i;
for (i = adj[v].begin();
i != adj[v].end(); ++i) {
if (!visited[*i])
DFSUtil(*i, visited);
}
}
// Function to return the reverse
// (or transpose) of the graph
Graph Graph::getTranspose()
{
Graph g(V);
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) {
// Recurr for all the vertices
// adjacent to this vertex
list::iterator i;
for (i = adj[v].begin();
i != adj[v].end(); ++i) {
g.adj[*i].push_back(v);
}
}
return g;
}
// Function to add an edge
void Graph::addEdge(int v, int w)
{
// Add w to v’s list
adj[v].push_back(w);
}
// Function to fill the stack with
// the vertices during DFS traversal
void Graph::fillOrder(int v, bool visited[],
stack& Stack)
{
// Mark the current node as visited
visited[v] = true;
// Recurr for all the vertices
// adjacent to this vertex
list::iterator i;
for (i = adj[v].begin();
i != adj[v].end(); ++i) {
if (!visited[*i])
fillOrder(*i, visited, Stack);
}
// All vertices reachable from
// the node v are processed
// Update the stack
Stack.push(v);
}
// Function that counts the strongly
// connected components in the graph
void Graph::countSCCs()
{
stack Stack;
// Mark all the vertices as not
// visited (For first DFS)
bool* visited = new bool[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
visited[i] = false;
// Fill vertices in the stack
// according to their finishing
// time
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
// Vertex i is not visited
if (visited[i] == false)
fillOrder(i, visited, Stack);
}
// Create a reversed graph
Graph gr = getTranspose();
// Mark all the vertices as
// not visited (For second DFS)
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
visited[i] = false;
int cnt = 0;
// Now process all vertices in
// order defined by Stack
while (Stack.empty() == false) {
// Pop a vertex from stack
int v = Stack.top();
Stack.pop();
// Get the strongly connected
// component of the popped
// vertex
if (visited[v] == false) {
gr.DFSUtil(v, visited);
cnt++;
}
}
// Print the result
cout << cnt;
}
// Function that counts the minimum
// number of notes required with the
// given criteria
void solve(vector& A,
vector >& P)
{
Graph g(A.size());
// Used to map the strings to
// their respective indices
unordered_map um;
for (int i = 0; i < A.size(); i++) {
um[A[i]] = i;
}
// Iterate through all the edges
// and add them to the graph
for (int i = 0; i < P.size(); i++) {
int x = um[P[i][0]];
int y = um[P[i][1]];
g.addEdge(x, y);
}
// Function Call
g.countSCCs();
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
vector arr
= { "geeks", "for", "code",
"run", "compile" };
vector > P = { { "geeks", "for" },
{ "for", "code" },
{ "code", "run" },
{ "run", "compile" },
{ "run", "for" } };
solve(arr, P);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program for above approach
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.*;
// Sturture of class Graph
public class Graph{
// No. of vertices
int V;
// An array of adjacency lists
ArrayList> adj;
// Constructor of the Graph
Graph(int V)
{
this.V = V;
adj = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
adj.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
}
// Recursive function to perform the
// DFS starting from v
void DFSUtil(int v, boolean visited[])
{
// Mark the current node as visited
visited[v] = true;
// Recurr for all the vertices
// adjacent to this vertex
for(int i : adj.get(v))
{
if (!visited[i])
DFSUtil(i, visited);
}
}
// Function to return the reverse
// (or transpose) of the graph
Graph getTranspose()
{
Graph g = new Graph(V);
for(int v = 0; v < V; v++)
{
// Recurr for all the vertices
// adjacent to this vertex
for(int i : adj.get(v))
{
g.adj.get(i).add(v);
}
}
return g;
}
// Function to add an edge
void addEdge(int v, int w)
{
// Add w to v’s list
adj.get(v).add(w);
}
// Function to fill the stack with
// the vertices during DFS traversal
void fillOrder(int v, boolean[] visited,
Stack stack)
{
// Mark the current node as visited
visited[v] = true;
// Recurr for all the vertices
// adjacent to this vertex
for(int i : adj.get(v))
{
if (!visited[i])
fillOrder(i, visited, stack);
}
// All vertices reachable from
// the node v are processed
// Update the stack
stack.push(v);
}
// Function that counts the strongly
// connected components in the graph
void countSCCs()
{
Stack stack = new Stack<>();
// Mark all the vertices as not
// visited (For first DFS)
boolean[] visited = new boolean[V];
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++)
visited[i] = false;
// Fill vertices in the stack
// according to their finishing
// time
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++)
{
// Vertex i is not visited
if (visited[i] == false)
fillOrder(i, visited, stack);
}
// Create a reversed graph
Graph gr = getTranspose();
// Mark all the vertices as
// not visited (For second DFS)
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++)
visited[i] = false;
int cnt = 0;
// Now process all vertices in
// order defined by Stack
while (stack.empty() == false)
{
// Pop a vertex from stack
int v = stack.peek();
stack.pop();
// Get the strongly connected
// component of the popped
// vertex
if (visited[v] == false)
{
gr.DFSUtil(v, visited);
cnt++;
}
}
// Print the result
System.out.print(cnt);
}
// Function that counts the minimum
// number of notes required with the
// given criteria
static void solve(ArrayList A,
ArrayList> P)
{
Graph g = new Graph(A.size());
// Used to map the strings to
// their respective indices
HashMap um = new HashMap<>();
for(int i = 0; i < A.size(); i++)
{
um.put(A.get(i), i);
}
// Iterate through all the edges
// and add them to the graph
for(int i = 0; i < P.size(); i++)
{
int x = um.get(P.get(i).get(0));
int y = um.get(P.get(i).get(1));
g.addEdge(x, y);
}
// Function Call
g.countSCCs();
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ArrayList arr = new ArrayList<>();
arr.add("geeks");
arr.add("for");
arr.add("code");
arr.add("run");
arr.add("compile");
ArrayList > P = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
P.add(new ArrayList<>());
P.get(0).add("geeks");
P.get(0).add("for");
P.get(1).add("for");
P.get(1).add("code");
P.get(2).add("code");
P.get(2).add("run");
P.get(3).add("run");
P.get(3).add("compile");
P.get(4).add("run");
P.get(4).add("for");
solve(arr, P);
}
}
// This code is contributed by hritikrommie 3时间复杂度: O(N + M)
辅助空间: O(N)
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。