给定一个大小为NxN的整数方阵A 。任务是找到通过A的下降路径的最小总和。
下降路径将从第一行的任何元素开始,并在最后一行结束。它从下一行中选择一个元素。下一行的选择必须在与前一行的列最多相差一个的列中。
例子:
Input: N = 2
mat[2][2] =
{{5, 10},
{25, 15}}
Output: 20
Selected elements are 5, 15.
Input: N = 3
mat[3][3] =
{{1, 2, 3},
{ 4, 5, 6},
{ 7, 8, 9}}
Output: 12
Selected elements are 1, 4, 7.方法:这个问题有一个最优子结构,这意味着子问题的解决方案可以用来解决这个问题的更大实例。这使得动态规划应运而生。
令dp[R][C]是从第一行[R, C]开始到 A 底行的下降路径的最小总权重。
然后, ![]() ,答案是第一行的最小值 i:e
,答案是第一行的最小值 i:e ![]() .
.
我们将创建一个辅助数组dp来缓存中间值dp[R][C] 。但是,我们将使用A来缓存这些值。我们的目标是将A的值转换为dp的值。
我们开始处理每一行,从倒数第二行开始。我们设置![]() ,优雅地处理边界条件。
,优雅地处理边界条件。
Explanation of above Approach:
Let’s look at the recursion a little more to get a handle on why it works. For an array like A = [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]], imagine you are at (1, 0) (A[1][0] = 4). You can either go to (2, 0) and get a weight of 7, or (2, 1) and get a weight of 8. Since 7 is lower, we say that the minimum total weight at (1, 0) is dp(1, 0) = 5 + 7 (7 for the original A[R][C].)
After visiting (1, 0), (1, 1), and (1, 2), A [which is storing the values of our dp], looks like [[1, 2, 3], [11, 12, 14], [7, 8, 9]]. We do this procedure again by visiting (0, 0), (0, 1), (0, 2).
We get 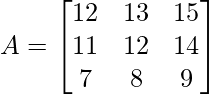 , and the final answer is min(A[0][C]) = 12 for all C in range 0 to n.
, and the final answer is min(A[0][C]) = 12 for all C in range 0 to n.
下面是上述方法的实现。
C++
// C++ Program to minimum required sum
#include
using namespace std;
const int n = 3;
// Function to return minimum path falling sum
int minFallingPathSum(int (&A)[n][n])
{
// R = Row and C = Column
// We begin from second last row and keep
// adding maximum sum.
for (int R = n - 2; R >= 0; --R) {
for (int C = 0; C < n; ++C) {
// best = min(A[R+1][C-1], A[R+1][C], A[R+1][C+1])
int best = A[R + 1][C];
if (C > 0)
best = min(best, A[R + 1][C - 1]);
if (C + 1 < n)
best = min(best, A[R + 1][C + 1]);
A[R][C] = A[R][C] + best;
}
}
int ans = INT_MAX;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
ans = min(ans, A[0][i]);
return ans;
}
// Driver program
int main()
{
int A[n][n] = { { 1, 2, 3 },
{ 4, 5, 6 },
{ 7, 8, 9 } };
// function to print required answer
cout << minFallingPathSum(A);
return 0;
} Java
// Java Program to minimum required sum
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
static int n = 3;
// Function to return minimum path falling sum
static int minFallingPathSum(int A[][])
{
// R = Row and C = Column
// We begin from second last row and keep
// adding maximum sum.
for (int R = n - 2; R >= 0; --R) {
for (int C = 0; C < n; ++C) {
// best = min(A[R+1][C-1], A[R+1][C], A[R+1][C+1])
int best = A[R + 1][C];
if (C > 0)
best = Math.min(best, A[R + 1][C - 1]);
if (C + 1 < n)
best = Math.min(best, A[R + 1][C + 1]);
A[R][C] = A[R][C] + best;
}
}
int ans = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
ans = Math.min(ans, A[0][i]);
return ans;
}
// Driver program
public static void main (String[] args) {
int A[][] = { { 1, 2, 3 },
{ 4, 5, 6 },
{ 7, 8, 9 } };
// function to print required answer
System.out.println( minFallingPathSum(A));
}
}
// This code is contributed by inder_verma..Python 3
# Python3 Program to minimum
# required sum
import sys
n = 3
# Function to return minimum
# path falling sum
def minFallingPathSum(A) :
# R = Row and C = Column
# We begin from second last row and keep
# adding maximum sum.
for R in range(n - 2, -1, -1) :
for C in range(n) :
# best = min(A[R+1][C-1], A[R+1][C],
# A[R+1][C+1])
best = A[R + 1][C]
if C > 0 :
best = min(best, A[R + 1][C - 1])
if C + 1 < n :
best = min(best, A[R + 1][C + 1])
A[R][C] = A[R][C] + best
ans = sys.maxsize
for i in range(n) :
ans = min(ans, A[0][i])
return ans
# Driver code
if __name__ == "__main__" :
A = [ [ 1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6],
[ 7, 8, 9] ]
# function to print required answer
print(minFallingPathSum(A))
# This code is contributed by
# ANKITRAI1C#
// C# Program to minimum required sum
using System;
class GFG {
static int n = 3;
// Function to return minimum path falling sum
static int minFallingPathSum(int[,] A)
{
// R = Row and C = Column
// We begin from second last row and keep
// adding maximum sum.
for (int R = n - 2; R >= 0; --R) {
for (int C = 0; C < n; ++C) {
// best = min(A[R+1,C-1], A[R+1,C], A[R+1,C+1])
int best = A[R + 1,C];
if (C > 0)
best = Math.Min(best, A[R + 1,C - 1]);
if (C + 1 < n)
best = Math.Min(best, A[R + 1,C + 1]);
A[R,C] = A[R,C] + best;
}
}
int ans = int.MaxValue;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
ans = Math.Min(ans, A[0,i]);
return ans;
}
// Driver program
public static void Main () {
int[,] A = { { 1, 2, 3 },
{ 4, 5, 6 },
{ 7, 8, 9 } };
// function to print required answer
Console.WriteLine( minFallingPathSum(A));
}
}
// This code is contributed by Subhadeep..Javascript
Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach
def fallingpathsum(grid, row, col, Row, Col, dp):
# Base condition
if row == Row-1 and col == Col-1:
return grid[row][col]
# Base condition
if row > Row-1 or col > Col-1:
return 0
# Respective directions
rightdown = fallingpathsum(grid, row+1, col, Row, Col, dp)
rdd = fallingpathsum(grid, row+1, col+1, Row, Col, dp)
ldd = fallingpathsum(grid, row+1, col-1, Row, Col, dp)
# Checking for duplicates
if dp[row][col] == -1:
dp[row][col] = grid[row][col] + min(rightdown, ldd, rdd)
return dp[row][col]
grid = [[1,2,3], [4,5,6],[7,8,9]]
Row = len(grid)
Col = len(grid[0])
dp = [[-1 for i in range(Row)]for _ in range(Col)]
print(fallingpathsum(grid, 0, 0, Row, Col, dp))
# CODE CONTRIBUTED BY RAMPRASAD KONDOJU12时间复杂度: O(N 2 )
自上而下的方法:
- 计算一个函数并跟踪递归解决方案。
- 考虑所有基本条件。
- 开始向问题中提到的所有可能的方向移动。
- 当到达网格的末端角时,只需考虑最小下落路径总和。
- 返回最小下降路径总和。
下面是上述方法的实现:
蟒蛇3
# Python3 program for the above approach
def fallingpathsum(grid, row, col, Row, Col, dp):
# Base condition
if row == Row-1 and col == Col-1:
return grid[row][col]
# Base condition
if row > Row-1 or col > Col-1:
return 0
# Respective directions
rightdown = fallingpathsum(grid, row+1, col, Row, Col, dp)
rdd = fallingpathsum(grid, row+1, col+1, Row, Col, dp)
ldd = fallingpathsum(grid, row+1, col-1, Row, Col, dp)
# Checking for duplicates
if dp[row][col] == -1:
dp[row][col] = grid[row][col] + min(rightdown, ldd, rdd)
return dp[row][col]
grid = [[1,2,3], [4,5,6],[7,8,9]]
Row = len(grid)
Col = len(grid[0])
dp = [[-1 for i in range(Row)]for _ in range(Col)]
print(fallingpathsum(grid, 0, 0, Row, Col, dp))
# CODE CONTRIBUTED BY RAMPRASAD KONDOJU
20时间复杂度: O(N)
如果您希望与专家一起参加现场课程,请参阅DSA 现场工作专业课程和学生竞争性编程现场课程。