与数组不同,链表元素不存储在连续的位置;元素使用指针链接。在这篇文章中,讨论了在链表中插入新节点的方法。一个节点可以通过三种方式插入到链表的前面、给定节点之后或链表的末尾。正如我们已经讨论过的,双向链表 (DLL) 确实包含一个额外的指针,通常称为前一个指针,以及存在于单向链表中的下一个指针和数据。
类似地,为T riply大号着墨大号IST(TLL)包含一个额外的指针,通常被称为顶部指针,与下一个指针,以往的,和数据是否有在双向链表在一起。这里称为顶部的额外指针可用于各种目的。例如,在同一级别存储相等的值。请参阅下图以更好地理解。在本文中,我们将按排序顺序在链表中插入节点。我们将在同一级别存储相等的元素,这意味着它们将被顶部指针访问。
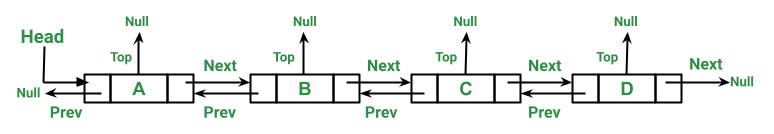

插图: DLL 节点的表示
// Class for Triply Linked List
public class TLL {
// Triply Linked list Node
class Node {
int data;
Node prev;
Node next;
Node top;
}
// Head and Tail pointer
Node head = null, tail = null;
// To keep track of the number
// of nodes
int node_count = 0;
}程序:
1.插入新节点
由于我们按排序顺序存储节点,这就是为什么我们必须在链表中找到给定节点的正确位置。
- 如果列表中没有节点( List 为空),则只需将头部和尾部指向该节点即可。
- 如果给定节点小于头节点,则只需在开头插入节点。
- 如果给定节点不小于头节点,则遍历链表,找到第一个大于给定节点的节点。
- 如果这样的节点不存在,这意味着给定的节点大于所有节点。所以将它插入到 List 的末尾。
- 如果确实存在这样的节点,则在找到的节点之前插入给定的节点。
- 如果给定节点等于某个已经存在的节点,则将给定节点插入到列表的顶部。
2(A):从Head开始遍历List,从head开始,继续到下一个节点。如果当前节点的顶部不为空,则先打印顶部节点,然后继续遍历列表的其余部分。
2(B):从尾部遍历列表或反向遍历,从尾部开始,一直到上一个节点。如果当前节点的顶部不为空,则先打印顶部节点,然后继续遍历列表的其余部分。
例子:
Java
// Java Program to Implement Triply Linked List
// Importing all utility classes
import java.util.*;
// Main Class
public class GFG {
// First let us create a Node class
class Node {
// Data refers to the value in node
int data;
// Being triply linked list,
// three pointers needs to be defined
Node prev;
Node next;
Node top;
// Parameterized constructor of Node class
// to initialize the node whenever created
Node(int data)
{
// this keyword refers to current object itself
this.data = data;
// Intializing all 3 pointers to null
prev = null;
next = null;
top = null;
}
}
// Defining two new pointers for iterate over to perform
// operations over the triply linked list Head and Tail
// pointer
Node head = null, tail = null;
// Declaring and initializing variable to
// keep track of the number of nodes
int node_count = 0;
// Method 1
// To insert a new node
public void insert(int new_data)
{
// Create new node with the given data
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
// curr_node to traverse the List
Node curr_node = null;
// If List is empty then
// make head and tail
// equal to this node
if (node_count == 0) {
// Case 1: Of LinkedList is empty
// If there is no such node existing
tail = new_node;
head = new_node;
curr_node = head;
// So next will be assigned a null
curr_node.next = null;
curr_node.prev = null;
curr_node.top = null;
// Increment the node count
node_count++;
}
// Case 2: If LinkedList is not empty
// Case 2(A): If given node is less then the head
else {
// Make curr_node point to head
curr_node = head;
// If given node is less then the head
// insert at the beginning
if (new_node.data < curr_node.data) {
// Linking two nodes through addresses
new_node.next = curr_node;
curr_node.prev = new_node;
new_node.prev = null;
head = new_node;
curr_node = head;
// Adjusting the tail
do {
curr_node = curr_node.next;
} while (curr_node.next != null);
tail = curr_node;
}
// CAse 2(B): If given node is not less then the
// head
else {
// last_node to keep track of
// the last visited node
Node last_node = curr_node;
// Goal is to traverse the List and
// find first node greater than new_node
while (curr_node != null
&& new_node.data > curr_node.data) {
last_node = curr_node;
curr_node = curr_node.next;
// If curr_node is null that
// means we have reached the
// end of the list so insert the
// node at the end and update the tail
if (curr_node == null) {
last_node.next = new_node;
new_node.prev = last_node;
new_node.next = null;
tail = new_node;
// Haulting the execution of the
// program using break keyword
break;
}
else if (new_node.data
<= curr_node.data) {
// If curr_node is greater than
// the new_node then insert the
// new_node before curr_nod and
// update the tail
if (new_node.data
< curr_node.data) {
last_node.next = new_node;
new_node.prev = last_node;
new_node.next = curr_node;
curr_node.prev = new_node;
if (curr_node.next != null) {
do {
curr_node
= curr_node.next;
}
while (curr_node.next
!= null);
}
tail = curr_node;
break;
}
// If curr_node is equal to the
// new_node then insert the
// new_node to the top of the
// curr_nod and update the tail
else if (curr_node.data
== new_node.data) {
last_node = curr_node;
while (last_node.top != null) {
last_node = last_node.top;
}
last_node.top = new_node;
new_node.top = null;
break;
}
}
}
}
}
}
// Method 2
// Traversing list from head
public void traverse_head()
{
Node node = head;
Node curr = null;
while (node != null) {
System.out.print(node.data + "\t");
curr = node;
// If curr has top node
// then traverse them first
while (curr.top != null) {
curr = curr.top;
// Print top node first followed by rest of
// list
System.out.print("top->" + curr.data
+ "\t");
}
// Update the node to next node
node = node.next;
}
// New line
System.out.println();
}
// Method 3
// Traversing list from tail
public void traverse_tail()
{
Node node = tail;
Node curr = null;
while (node != null) {
System.out.print(node.data + "\t");
curr = node;
// If curr has top node
// then traverse them first
while (curr.top != null) {
curr = curr.top;
// Print top node first followed by rest of
// list
System.out.print("top->" + curr.data
+ "\t");
}
// Update the node to prev node
node = node.prev;
}
// New line
System.out.println();
}
// Method 4
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Creating an object of main class in the main()
// method
// by starting with the empty list
GFG tll = new GFG();
// Inserting custom input integer numbers
// using insert() method
// Number Set = {7,9,1,5,7}
// Insert the first number i.e 7,
// so linked list become
// 7 -> NULL
tll.insert(7);
// Insert the second number i.e 9,
// so linked list becomes
// 7 -> 9 -> NULL
tll.insert(9);
// Insert the third number i.e 1,
// so linked list becomes
// 1 -> 7 -> 9 -> NULL
tll.insert(1);
// Insert the fourth number i.e 5,
// so linked list becomes
// 1 -> 5 -> 7 -> 9 -> NULL
tll.insert(5);
// Insert the fifth number i.e 7,
// so linked list becomes
// 1 -> 5 -> 7 (top->7) -> 9 -> NULL
tll.insert(7);
// Display message only
System.out.println(
"\nTraversing Linked List head: ");
// Calling the traverse_head() method () / Method 2
tll.traverse_head();
// Display message only
System.out.println(
"\nTraversing Linked List tail: ");
// Calling the traverse_tail() method / Method 3
tll.traverse_tail();
}
}输出
Traversing Linked List head:
1 5 7 top->7 9
Traversing Linked List tail:
9 7 top->7 5 1 The representation of workflow the linked list after running the above program is pictorially depicted and is as follows:

如果您想与行业专家一起参加直播课程,请参阅Geeks Classes Live