给定一个具有N 个节点、 M 条边和一个整数K的无向图G ,任务是找到可以删除的最大边数,以便在删除边后正好保留K 个连通分量。如果图形不能包含K 个连接分量,则打印-1 。
例子:
Input: N = 4, M = 3, K = 2, Edges[][] = {{1, 2}, {2, 3}, {3, 4}}
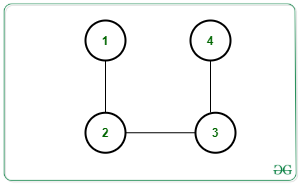
Output: 1
Explanation:
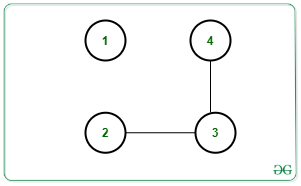
One possible way is to remove edge [1, 2]. Then there will be 2 connect components as shown below:
Input: N = 3, M = 3, K = 3, Edges[][] = {{1, 2}, {2, 3}, {3, 1}}
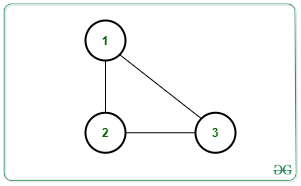
Output: 3
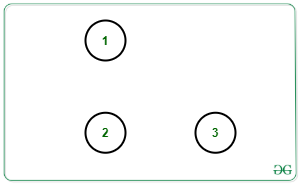
Explanation: All edges can be removed to make 3 connected components as shown below:
方法:为了解决给定的问题,计算给定图中存在的连通分量的数量。让计数为C 。观察到,如果C大于K,则没有可能的边缘移除可以生成K 个连接组件,因为连接组件的数量只会增加。否则,答案将永远存在。
为了解决这个问题,需要进行以下观察:
- 假设 C 1 , C 2 , …, C c是每个连通分量中的节点数。然后,每个组件必须具有 C 1 – 1, C 2 – 1, …, C c -1 边移除后的边。所以,
C1 – 1 + C2 – 1 + … + Cc – 1 = C1 + C2 + … + Cc – C = N – C, where N is the number of nodes.
- 上述条件将通过移除M – (N – C) 条边为我们提供C连接组件,因为需要N – C 条边来生成C组件。要获得K 个分量,必须移除(K – C) 个更多边。
- 因此,要删除的边总数由下式给出:
M – (N – C) + (K – C) = M – N + K
请按照以下步骤解决问题:
- 计算给定图中存在的连接组件的数量。让计数为C 。
- 如果C大于K ,则打印-1 。
- 否则打印M – N + K ,其中N是 f 个节点的数量, M是边的数量, K是所需的连接组件数量。
下面是上述方法的实现:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach
#include
using namespace std;
class Graph
{
public:
int V;
map> adj;
Graph(int);
void addEdge(int, int);
void DFS(int, vector &);
} * g;
// Constructor
Graph::Graph(int V)
{
// No. of vertices
this->V = V;
// Dictionary of lists
for(int i = 1; i <= V; i++)
adj[i] = vector();
}
// Function to add edge
// in the graph
void Graph::addEdge(int v, int w)
{
adj[v].push_back(w);
adj[w].push_back(v);
}
// Function to perform DFS
void Graph::DFS(int s, vector &visited)
{
// Create a stack for DFS
stack stack;
// Push the current source node
stack.push(s);
while (!stack.empty())
{
// Pop a vertex from stack
// and print it
s = stack.top();
stack.pop();
// Traverse adjacent vertices
// of the popped vertex s
for(auto node : adj[s])
{
if (!visited[node])
{
// If adjacent is unvisited,
// push it to the stack
visited[node] = true;
stack.push(node);
}
}
}
}
// Function to return the count
// edges removed
void countRemovedEdges(int N, int M, int K)
{
int C = 0;
// Initially mark all verices
// as not visited
vector visited(g->V + 1, false);
for(int node = 1; node <= N; node++)
{
// If node is unvisited
if (!visited[node])
{
// Increment Connected
// component count by 1
C = C + 1;
// Perform DFS Traversal
g->DFS(node, visited);
// Print the result
if (C <= K)
cout << M - N + K << endl;
else
cout << -1 << endl;
}
}
}
// Driver Code
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
int N = 4, M = 3, K = 2;
// Create Graph
g = new Graph(N);
// Given Edges
g->addEdge(1, 2);
g->addEdge(2, 3);
g->addEdge(3, 4);
// Function Call
countRemovedEdges(N, M, K);
}
// This code is contributed by sanjeev2552 Java
// Java program to implement
// the above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static ArrayList> graph;
// Function to perform DFS
static void DFS(int s, boolean[] visited)
{
// Create a stack for DFS
Stack stack = new Stack<>();
// Push the current source node
stack.push(s);
while (!stack.isEmpty())
{
// Pop a vertex from stack
// and print it
s = stack.peek();
stack.pop();
// Traverse adjacent vertices
// of the popped vertex s
for(Integer node : graph.get(s))
{
if (!visited[node])
{
// If adjacent is unvisited,
// push it to the stack
visited[node] = true;
stack.push(node);
}
}
}
}
// Function to return the count
// edges removed
static void countRemovedEdges(int N, int M, int K)
{
int C = 0;
// Initially mark all verices
// as not visited
boolean[] visited = new boolean[N+1];
for(int node = 1; node <= N; node++)
{
// If node is unvisited
if (!visited[node])
{
// Increment Connected
// component count by 1
C = C + 1;
// Perform DFS Traversal
DFS(node, visited);
// Print the result
if (C <= K)
System.out.println(M - N + K);
else
System.out.println(-1);
}
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main (String[] args)
{
int N = 4, M = 3, K = 2;
// Create Graph
graph = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 0; i <= N; i++)
graph.add(new ArrayList());
// Given Edges
graph.get(1).add(2);
graph.get(2).add(3);
graph.get(3).add(4);
// Function Call
countRemovedEdges(N, M, K);
}
}
// This code is contributed by offbeat. Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach
class Graph:
# Constructor
def __init__(self, V):
# No. of vertices
self.V = V
# Dictionary of lists
self.adj = {i: [] for i in range(1, V + 1)}
# Function to add edge
# in the graph
def addEdge(self, v, w):
self.adj[v].append(w)
self.adj[w].append(v)
# Function to perform DFS
def DFS(self, s, visited):
# Create a stack for DFS
stack = []
# Push the current source node
stack.append(s)
while (len(stack)):
# Pop a vertex from stack
# and print it
s = stack[-1]
stack.pop()
# Traverse adjacent vertices
# of the popped vertex s
for node in self.adj[s]:
if (not visited[node]):
# If adjacent is unvisited,
# push it to the stack
visited[node] = True
stack.append(node)
# Function to return the count
# edges removed
def countRemovedEdges(N, M, K):
C = 0
# Initially mark all verices
# as not visited
visited = [False for i in range(g.V + 1)]
for node in range(1, N + 1):
# If node is unvisited
if (not visited[node]):
# Increment Connected
# component count by 1
C = C + 1
# Perform DFS Traversal
g.DFS(node, visited)
# Print the result
if C <= K:
print(M - N + K)
else:
print(-1)
# Driver Code
N, M, K = 4, 3, 2
# Create Graph
g = Graph(N)
# Given Edges
g.addEdge(1, 2)
g.addEdge(2, 3)
g.addEdge(3, 4)
# Function Call
countRemovedEdges(N, M, K)1时间复杂度: O(N + M)
辅助空间: O(M + N)
如果您想与行业专家一起参加直播课程,请参阅Geeks Classes Live