给定一个BST,将其转换为更大的总和树,其中每个节点包含大于该节点的所有节点的总和。
强烈建议您最小化浏览器,然后自己尝试。
方法1(天真):
此方法不需要树成为BST。以下是步骤。
1.逐个节点遍历(顺序,预排序等)
2.对于每个节点,找到所有大于当前节点的节点,然后将这些值相加。存储所有这些款项。
3.通过按照与步骤1中相同的顺序遍历,将每个节点值替换为其相应的总和。
这需要O(n ^ 2)时间复杂度。
方法2(仅使用一个遍历)
通过利用树是BST的事实,我们可以找到O(n)解决方案。想法是以相反的顺序遍历BST。 BST的反向有序遍历使我们的密钥按降序排列。在访问一个节点之前,我们访问该节点的所有更大的节点。在遍历时,我们会跟踪键的总和,即所有键的总和大于当前节点的键。
C++
// C++ program to transform a BST to sum tree
#include
using namespace std;
// A BST node
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *left, *right;
};
// A utility function to create a new Binary Tree Node
struct Node *newNode(int item)
{
struct Node *temp = new Node;
temp->data = item;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
// Recursive function to transform a BST to sum tree.
// This function traverses the tree in reverse inorder so
// that we have visited all greater key nodes of the currently
// visited node
void transformTreeUtil(struct Node *root, int *sum)
{
// Base case
if (root == NULL) return;
// Recur for right subtree
transformTreeUtil(root->right, sum);
// Update sum
*sum = *sum + root->data;
// Store old sum in current node
root->data = *sum - root->data;
// Recur for left subtree
transformTreeUtil(root->left, sum);
}
// A wrapper over transformTreeUtil()
void transformTree(struct Node *root)
{
int sum = 0; // Initialize sum
transformTreeUtil(root, &sum);
}
// A utility function to print indorder traversal of a
// binary tree
void printInorder(struct Node *root)
{
if (root == NULL) return;
printInorder(root->left);
cout << root->data << " ";
printInorder(root->right);
}
// Driver Program to test above functions
int main()
{
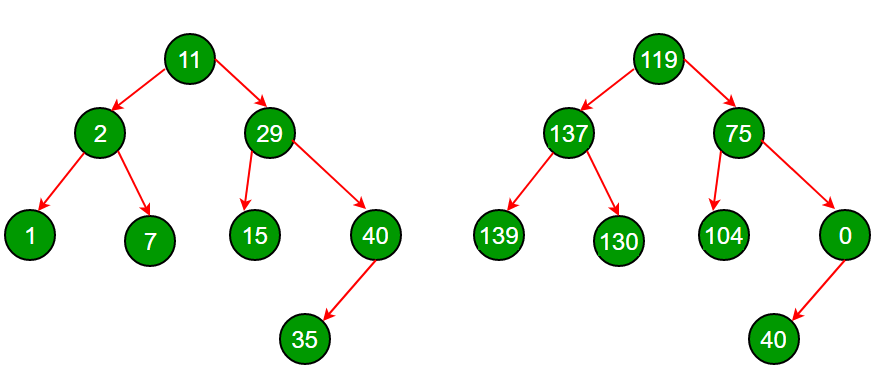
struct Node *root = newNode(11);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(29);
root->left->left = newNode(1);
root->left->right = newNode(7);
root->right->left = newNode(15);
root->right->right = newNode(40);
root->right->right->left = newNode(35);
cout << "Inorder Traversal of given tree\n";
printInorder(root);
transformTree(root);
cout << "\n\nInorder Traversal of transformed tree\n";
printInorder(root);
return 0;
} Java
// Java program to transform a BST to sum tree
import java.io.*;
class Node
{
int data;
Node left, right;
// A utility function to create a new Binary Tree Node
Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
class GFG
{
static int sum = 0;
static Node Root;
// Recursive function to transform a BST to sum tree.
// This function traverses the tree in reverse inorder so
// that we have visited all greater key nodes of the currently
// visited node
static void transformTreeUtil(Node root)
{
// Base case
if (root == null)
return;
// Recur for right subtree
transformTreeUtil(root.right);
// Update sum
sum = sum + root.data;
// Store old sum in current node
root.data = sum - root.data;
// Recur for left subtree
transformTreeUtil(root.left);
}
// A wrapper over transformTreeUtil()
static void transformTree(Node root)
{
transformTreeUtil(root);
}
// A utility function to print indorder traversal of a
// binary tree
static void printInorder(Node root)
{
if (root == null)
return;
printInorder(root.left);
System.out.print(root.data + " ");
printInorder(root.right);
}
// Driver Program to test above functions
public static void main (String[] args) {
GFG.Root = new Node(11);
GFG.Root.left = new Node(2);
GFG.Root.right = new Node(29);
GFG.Root.left.left = new Node(1);
GFG.Root.left.right = new Node(7);
GFG.Root.right.left = new Node(15);
GFG.Root.right.right = new Node(40);
GFG.Root.right.right.left = new Node(35);
System.out.println("Inorder Traversal of given tree");
printInorder(Root);
transformTree(Root);
System.out.println("\n\nInorder Traversal of transformed tree");
printInorder(Root);
}
}
// This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155Python3
# Python3 program to transform a BST to sum tree
class Node:
def __init__(self, x):
self.data = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
# Recursive function to transform a BST to sum tree.
# This function traverses the tree in reverse inorder so
# that we have visited all greater key nodes of the currently
# visited node
def transformTreeUtil(root):
# Base case
if (root == None):
return
# Recur for right subtree
transformTreeUtil(root.right)
# Update sum
global sum
sum = sum + root.data
# Store old sum in current node
root.data = sum - root.data
# Recur for left subtree
transformTreeUtil(root.left)
# A wrapper over transformTreeUtil()
def transformTree(root):
# sum = 0 #Initialize sum
transformTreeUtil(root)
# A utility function to prindorder traversal of a
# binary tree
def printInorder(root):
if (root == None):
return
printInorder(root.left)
print(root.data, end = " ")
printInorder(root.right)
# Driver Program to test above functions
if __name__ == '__main__':
sum=0
root = Node(11)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(29)
root.left.left = Node(1)
root.left.right = Node(7)
root.right.left = Node(15)
root.right.right = Node(40)
root.right.right.left = Node(35)
print("Inorder Traversal of given tree")
printInorder(root)
transformTree(root)
print("\nInorder Traversal of transformed tree")
printInorder(root)
# This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29Javascript
输出:
Inorder Traversal of given tree
1 2 7 11 15 29 35 40
Inorder Traversal of transformed tree
139 137 130 119 104 75 40 0该方法的时间复杂度为O(n),因为它可以对树进行简单遍历。
https://youtu.be/hx8IADDBqb0?list=PLqM7alHXFySHCXD7r1J0ky9Zg_GBB1dbk